Team:Cambridge/Experiments/Thin Films
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Felix Zhou (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Team:Cambridge/CAM_2011_TEMPLATE_HEAD}} | {{Template:Team:Cambridge/CAM_2011_TEMPLATE_HEAD}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | See youtube videos of our thin films [http://www.youtube.com/user/cambridgeigem2011 here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
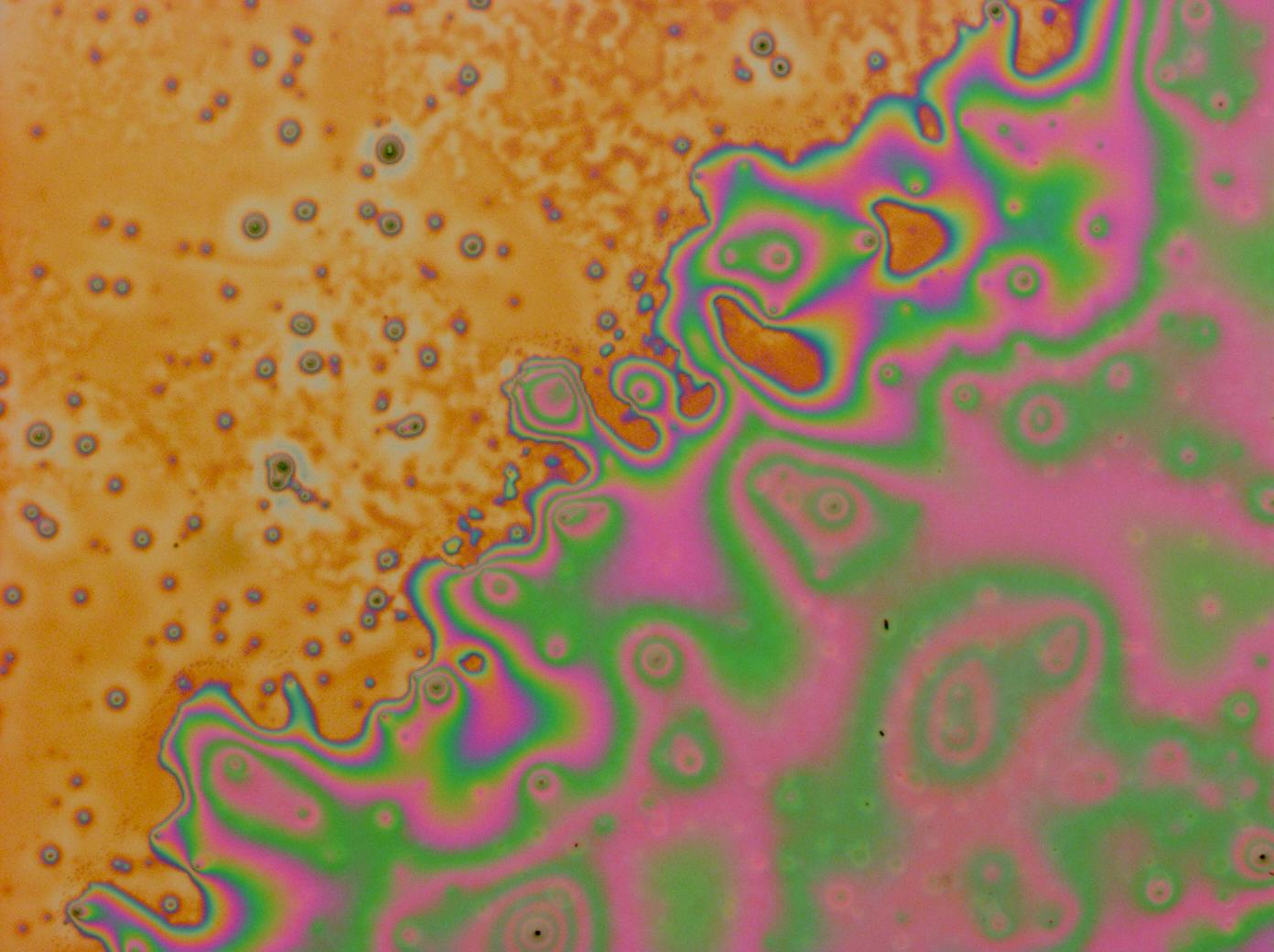
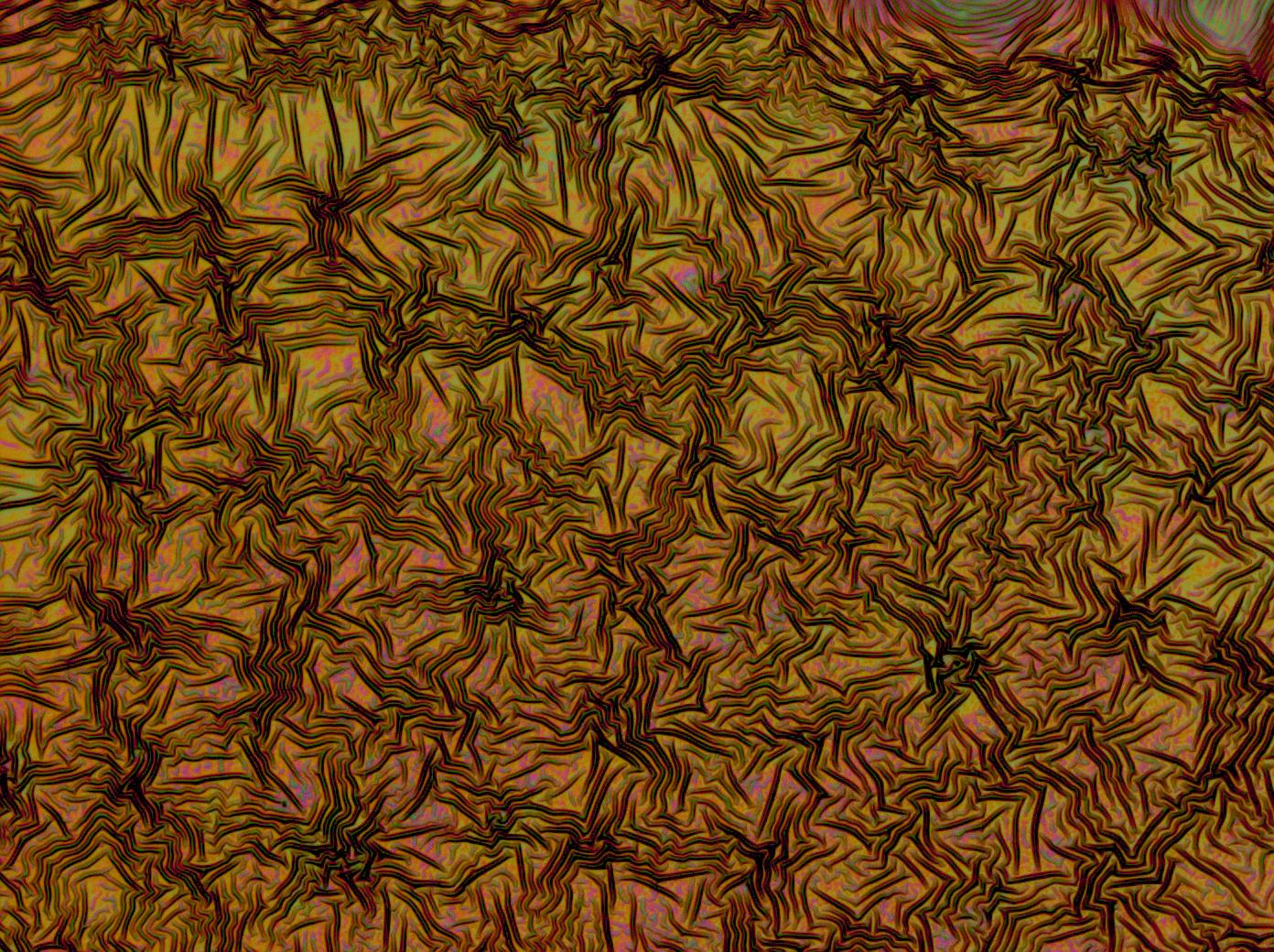
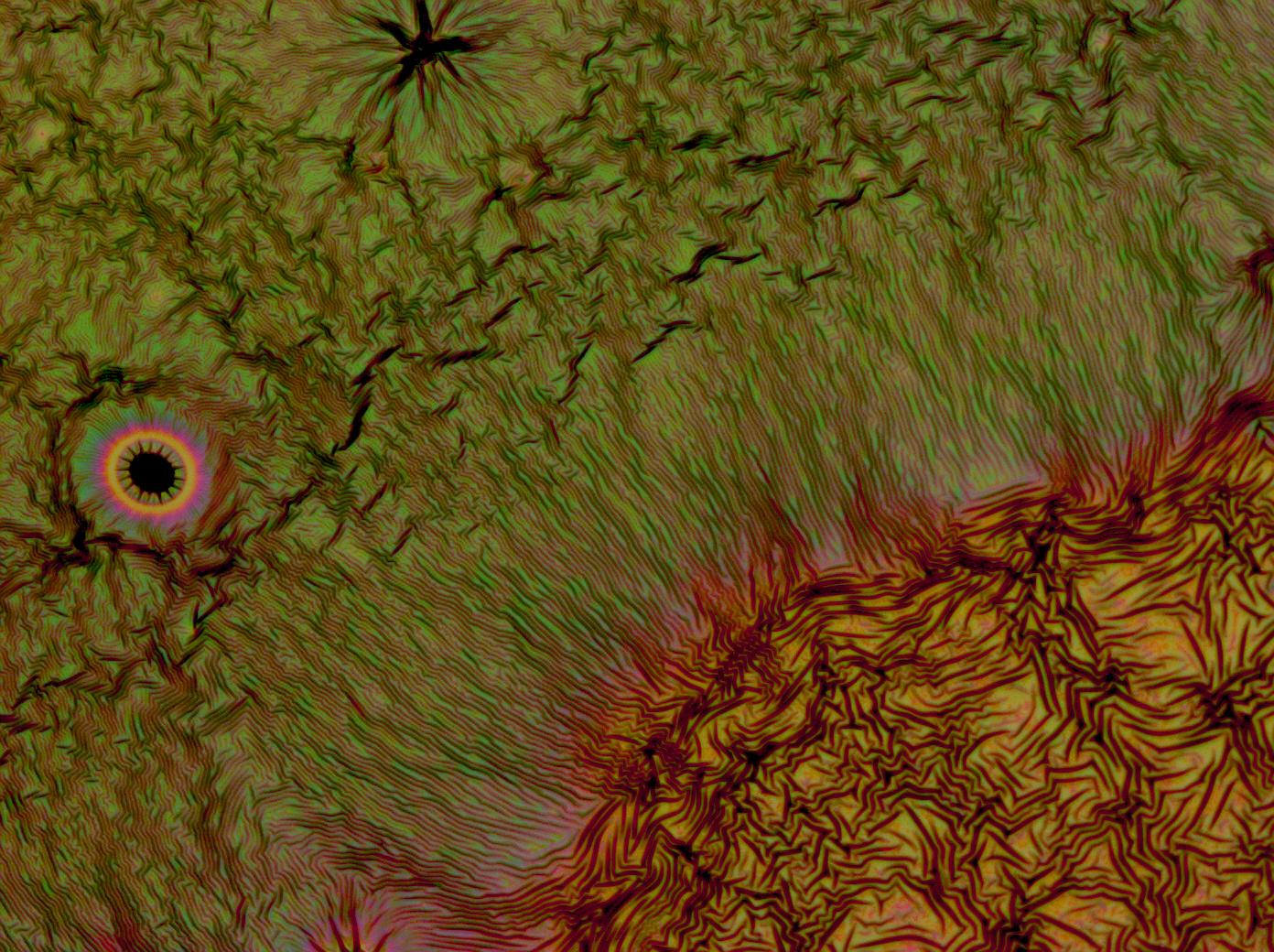
| + | <gallery caption='A sample of the microscope images taken of multi-layered thin films.' widths=140px> | ||
| + | File:Cam Multilayer drop 1.jpg | ||
| + | File:Cam Crazy multilayer single AP 2k spin2nd.jpg | ||
| + | File:Cam crazy multilayer2.jpg | ||
| + | File:Cam_crazy_multilayer3.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
We conducted a number of experiments with the thin films, outlined below. | We conducted a number of experiments with the thin films, outlined below. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 39: | ||
* Problems with stability of reflectin due to impurities hinder progress but produce 'protein art' | * Problems with stability of reflectin due to impurities hinder progress but produce 'protein art' | ||
| - | ====[[Team:Cambridge/Experiments/Reflectin_Thin_Films_VI | Attempts to increase film stability lead to first multilayer]]==== | + | ====[[Team:Cambridge/Experiments/Reflectin_Thin_Films_VI | Attempts to increase film stability lead to first stable multilayer]]==== |
* Dilution and centrifuging of samples and using only the very top layer seem to provide better stability for urea containing reflectin | * Dilution and centrifuging of samples and using only the very top layer seem to provide better stability for urea containing reflectin | ||
* Dialysed protein seemed to be more stable however suffers from dewetting | * Dialysed protein seemed to be more stable however suffers from dewetting | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====[[Team:Cambridge/Experiments/Reflectin_Thin_Films_VII | Spectral Measurements of Thin Films]]==== | ||
| + | * Spectral measurements of single, double and triple refectin-PDMS layers and PDMS control with video footage | ||
| + | * Film swelling and colour changes induced by breathing due to reflectin layers illustrating the tunability of reflectin | ||
{{Template:Team:Cambridge/CAM_2011_TEMPLATE_FOOT}} | {{Template:Team:Cambridge/CAM_2011_TEMPLATE_FOOT}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:49, 22 September 2011
Loading...
See youtube videos of our thin films [http://www.youtube.com/user/cambridgeigem2011 here].
We conducted a number of experiments with the thin films, outlined below.
Contents |
Reflectin Thin Films I
- Description of the basic method
- Colourful thin films created with reflectin & HFIP
- Thin film colour not uniform
- HFIP thin film control did not show structural colour
Reflectin Thin Films II
- Method refined in an attempt to reduce impurities
- Bovine Serum Album (BVA) control to test whether generic proteinacious thin films produce colour
- Did not show structural colour
- Reflectin thin films appear to crystalize on drying
Reflectin Thin Films III
- Control indicates that Urea may be to blame for thin film crystalization
- More controls show that neither GFP nor BSA exhibit structural colour when spun into thin films
Colour Intense Films - First Breakthrough
- Less is more - using the same concentration, spinning a small volume leads to better wetting and more colour intense films
- Introducing the 'Piranha solution' for surface cleaning
Uniform Films and Multilayers
- Quality over quantity - purer reflectin and greater control over spin lead to colour uniformity
- Attempts to create multilayers with alternating PDMS and reflectin.
- Problems with stability of reflectin due to impurities hinder progress but produce 'protein art'
Attempts to increase film stability lead to first stable multilayer
- Dilution and centrifuging of samples and using only the very top layer seem to provide better stability for urea containing reflectin
- Dialysed protein seemed to be more stable however suffers from dewetting
Spectral Measurements of Thin Films
- Spectral measurements of single, double and triple refectin-PDMS layers and PDMS control with video footage
- Film swelling and colour changes induced by breathing due to reflectin layers illustrating the tunability of reflectin
 "
"