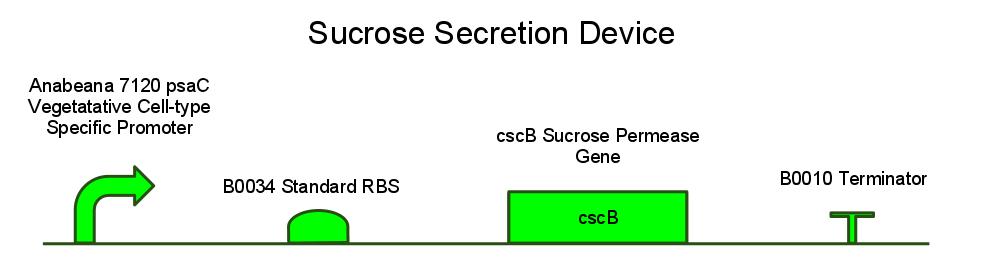
Team:Brown-Stanford/PowerCell/Methods
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Methods and Materials) |
(→Methods and Materials) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== '''Methods and Materials''' == | == '''Methods and Materials''' == | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | '''Cyanobacterial cultures''': we used wild type strains of Anabaena PCC7120, Synechocystis PCC6803, Nostoc punctiforme ATCC 29133, and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942, all courtesy of James Golden. These were raised at 30˚C with shaking at 121rpm and ~40µEinsteins of light in liquid BG11 media. | |
[[File:Brown-Stanford SucroseSecretionDevice.jpg|center|700px]] | [[File:Brown-Stanford SucroseSecretionDevice.jpg|center|700px]] | ||
{{:Team:Brown-Stanford/Templates/Foot}} | {{:Team:Brown-Stanford/Templates/Foot}} | ||
| + | Rippka, R., J. Deruelles, J. B Waterbury, M. Herdman, and R. Y Stanier. 1979. “Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria.” Journal of General Microbiology 111 (1): 1. | ||
Revision as of 23:29, 17 August 2011
Methods and Materials
Cyanobacterial cultures: we used wild type strains of Anabaena PCC7120, Synechocystis PCC6803, Nostoc punctiforme ATCC 29133, and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942, all courtesy of James Golden. These were raised at 30˚C with shaking at 121rpm and ~40µEinsteins of light in liquid BG11 media.
Rippka, R., J. Deruelles, J. B Waterbury, M. Herdman, and R. Y Stanier. 1979. “Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria.” Journal of General Microbiology 111 (1): 1.
 "
"