Team:Cambridge/Experiments/Initial Exercise Group Alpha
From 2011.igem.org
(→Method) |
Felix Zhou (Talk | contribs) (→Technical Data) |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
===Technical Data=== | ===Technical Data=== | ||
| - | We used Finnzymes melting temperature calculator to work out the melting temperature of the primer part (not the tail) of our Gibson Assembly oligos (this was the 3' 20bp of each oligo) these values in ºC are shown below | + | We used the Finnzymes melting temperature calculator to work out the melting temperature of the primer part (not the tail) of our Gibson Assembly oligos (this was the 3' 20bp of each oligo) these values in ºC are shown below |
JMF1 - 56.91 | JMF1 - 56.91 | ||
Revision as of 23:21, 13 July 2011
Fusion of SrfA promoter with GFP
Contents |
Aim
Our week 1 experimental challenge was to generate a temporal and or spatial pattern of GFP expression in Bacillus subtilis, using Gibson Assembly to join a sequence of interest to a GFP coding plasmid. We chose to visualise sporulation via a fusion of SrfA promoter with GFP.
Role of SrfA
- SrfA codes for surfactin production, a protein that is produced by B. subtilis prior to sporulation.
- SrfA is regulated by ComA, a protein which itself responds to an intercellular population-density-signalling molecule, CSF, in a concentration dependent manner.
- ComA has low activity at low CSF concentration(low population density), highly active as CSF levels increase, and less active at high CSF concentrations.
Construct Design
We wish to:
- keep the original promotor for SrfA and comA boxes
- remove GFP promotor sequence
- maintain ComGA stabiliser sequence
- do not include restriction sites
Predicted results
- Bacillus colonies exhibit a range of colony patterns and superimposed on the colony shape we expect a temporal pattern of green fluorescence marking sporulation activity.
- intially zero or low GFP detection, higher GFP activity on activation of SrfA prior to sporulation.
- Flourescence will mark spatially sporulation sites.
Method
- 20bp primers with 20bp tails were designed to perform PCR to amplify our chosen DNA sequences and Gibson Assembly to fuse the SrfA promoter with a plasmid containing GFP.
- 100 μM stock solutions of the primers were made and subsequently diluted four-fold to make 25μM 'working solutions'
- Particular care was taken in preparing the inital stock as these affect all future dilutions and were 'contingency' solutions in case of mistake.
- Genomic DNA of B. subtilis were provided and the vector plasmid containing GFP in two fragments
- The two primers to combine the two fragments of the plasmid were provided.
PCR
Our three PCR reactions consisted of:
- 1.
- 1μl primer JMF2
- 1μl primer JMF3
- 1μl B. subtilis genomic DNA
- 2.
- 1μl primer JMF1
- 1μl primer A Forward (provided)
- 1μl vector DNA
- 3
- 1μl primer JMF4
- 1μl primer B reverse (provided)
- 1μl vector DNA
to each tube we also added:
- 9.5μl of water
- 12.5μl Master mix (SyBR Green and Rox, Hotstart Taq polymerase, dNTPs and dyes)
for a total volume 25μl
The complete tubes were run in a real-time PCR machine for 30 cycles with a 2 minute extension time and a primer annealing temperature of 50ºc.
Experiment 2 used the same primers and templates as above, but we made a new master mix including phusion a much more processive polymerase. The total volume of master mix was 22ul, which was comprised of:
5ul buffer 0.5ul dNTP 0.25ul phusion polymerase 16.25ul H2O
Gibson Assembly
In order to combine the fragments of the GFP containing fragment and our chosen sequence of interest (SrfA promoter) we performed Gibson Assembly. The protocols page describes the theory behind this technique and also the reagents we used. The experiment performed is summarised below:
The amplified fragments from the PCR reaction above were added into a PCR tube with a Gibson assembly master mix
| Quantity (1μl) | Reagent |
|---|---|
| 1μl | Amplified SrfA fragment |
| 1μl | Amplified Vector fragment 1 |
| 1μl | Amplified Vector fragment 2 |
| 9μl | Master Mix |
The thermocycler was set at 50 degrees C for 1 hour.
Following Gibson Assembly we transformed E.coli with the DNA we had combined. This step utilises E.coli to amplify our plasmid and the culture can provide more DNA for future experiments. See the protocols page for how to do Transformation of E.coli. This page also describes how to plate E.coli. The protocols page of
Technical Data
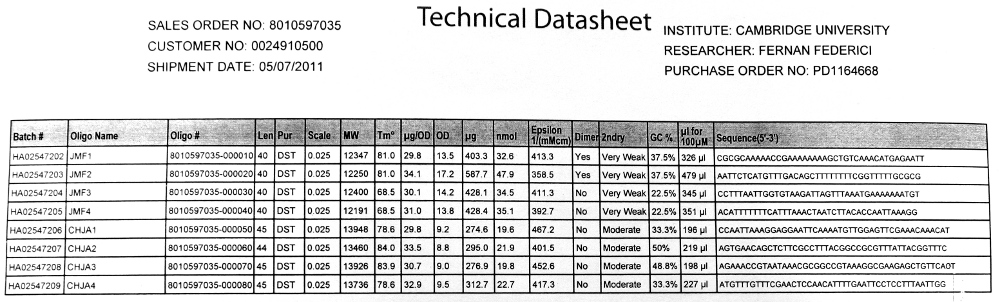
We used the Finnzymes melting temperature calculator to work out the melting temperature of the primer part (not the tail) of our Gibson Assembly oligos (this was the 3' 20bp of each oligo) these values in ºC are shown below
JMF1 - 56.91 JMF2 - 68.8 JMF3 - 50.48 JMF4 - 53.09
Results
- Reaction 1 and 3 were amplified in the PCR however reaction 2 was not
- It is suspected this was a result of a compromise run of the PCR where:
- Annealing temperature set at an arbitrary 50ºc to produce annealling for every group
- Primer extension time was arbitrarily set at 3 mins
- Results from all groups indicated the PCR failed for the longest fwdA fragment which we ascribe to the use of the Taq and not phusion polymerase
- It is intended to carry out the PCR again using Phusion polymerase.
References
Sporulation occurs late in the life cycle of B. subtilis when the colony reaches a high population density and we hope that GFP could be visualised following overnight growth. This paper[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1178101/?page=2] details some sporulation inducing culture conditions.
 "
"