Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Application-3
From 2011.igem.org
(→Application:) |
(→Application:) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|width="690px" style="padding:0 15px 15px 20px; vertical-align:top;"| | |width="690px" style="padding:0 15px 15px 20px; vertical-align:top;"| | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==Modified aaRS Library== | ==Modified aaRS Library== | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 28 October 2011
|
|
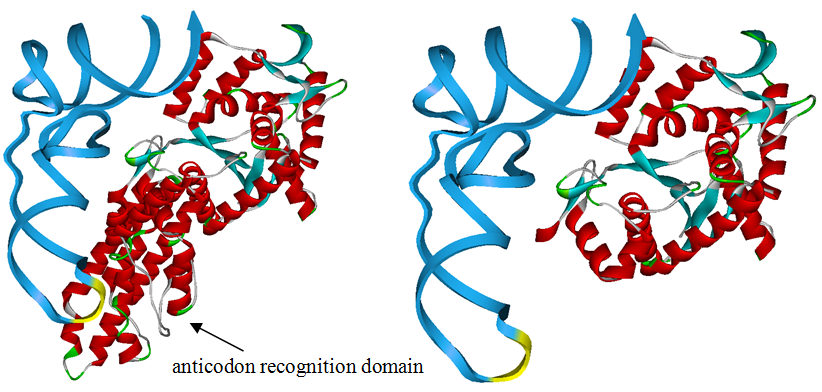
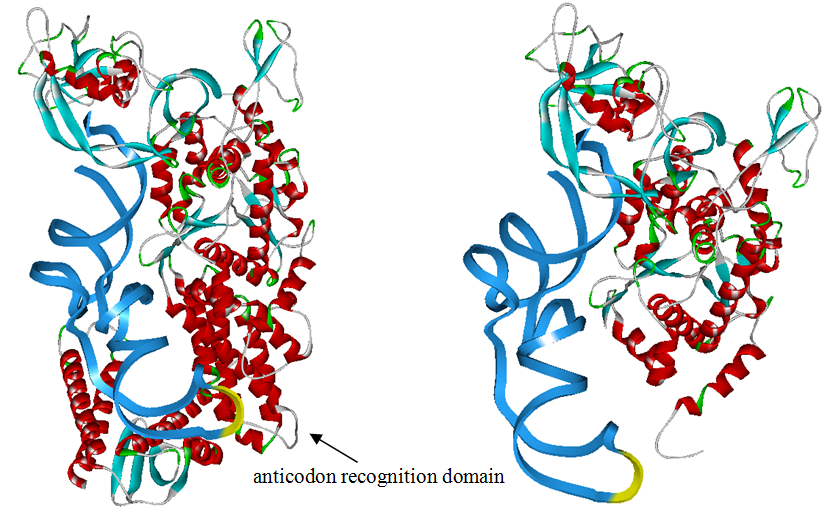
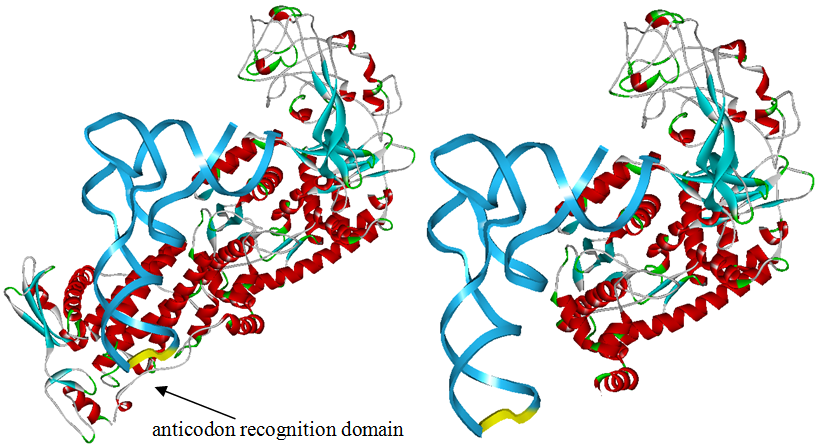
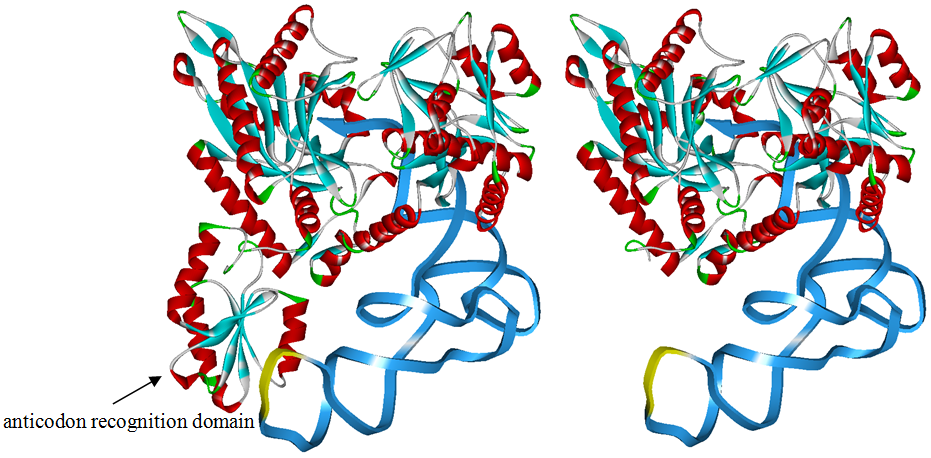
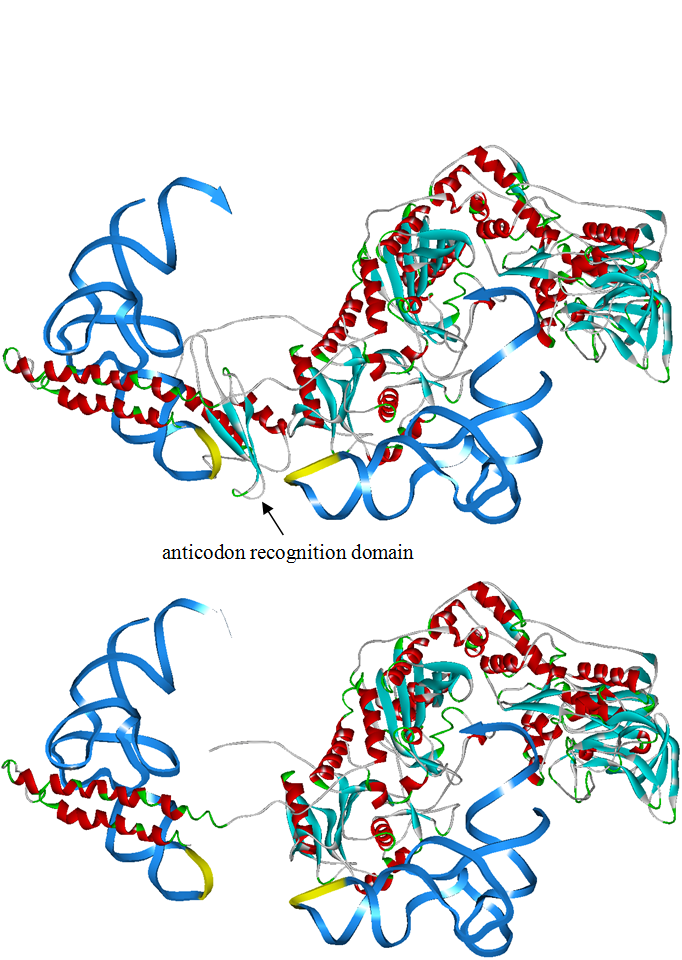
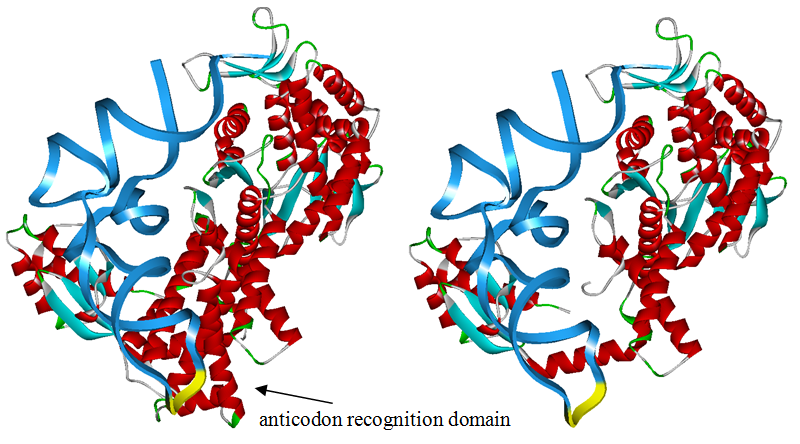
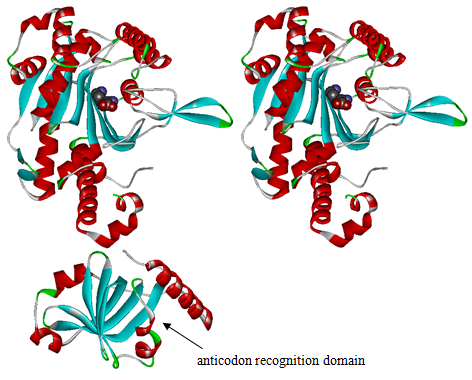
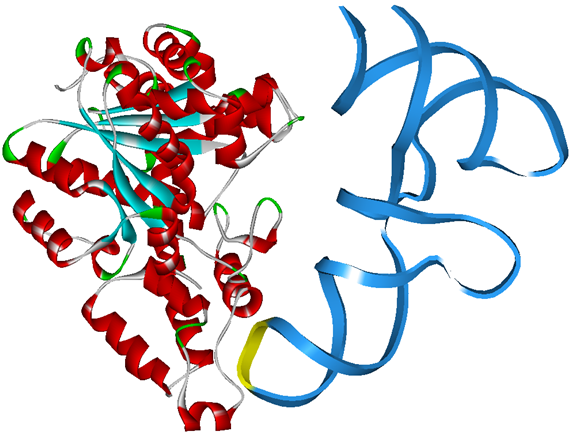
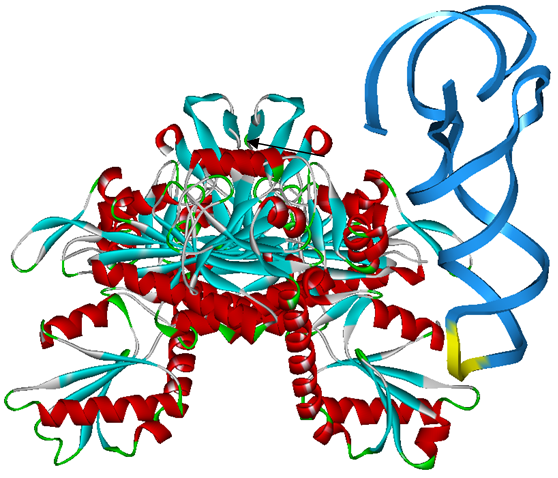
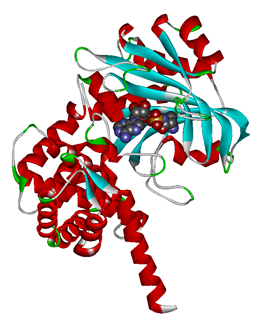
Modified aaRS LibraryIn Rare Codon Switch and Stop Codon Switch, we have modified tRNAAsp and aspartyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (AspRS). tRNAAsp is modified so that it can recognize rare codon AGG. Aspartyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (AspRS) is modified so that it loses the specificity for original tRNAAsp. To expand our Modified aaRS Library, we intend to modify the tRNA and aaRS of amino acids other than Asp. For tRNA, the anticodon can be mutated to base-pair rare codons other than AGG. For aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS), the function of the anticodon recognition should be lowered or eliminated. The 20 aaRS can be classified into two types, one with their anticodon recognition domains at the protein’s terminus, the other with their anticodon recognition domains inside the protein. For the first type, removing the anticodon recognition domains may not influence the overall structure and the aminoacylation function of the enzyme. For the second type, removing the domain may lead to incorrect folding of the protein. Type OneWe have designed the truncated version of the 14 Type One proteins based on their structures. See the designs below. Type TwoAfter we have analyzed the structure of the proteins below, we believe directed evolution is needed to obtain the modified enzyme. |
 "
"