Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Application-3
From 2011.igem.org
|
|
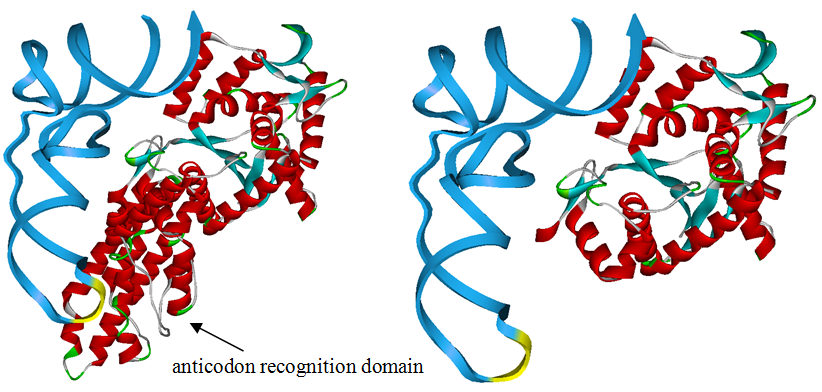
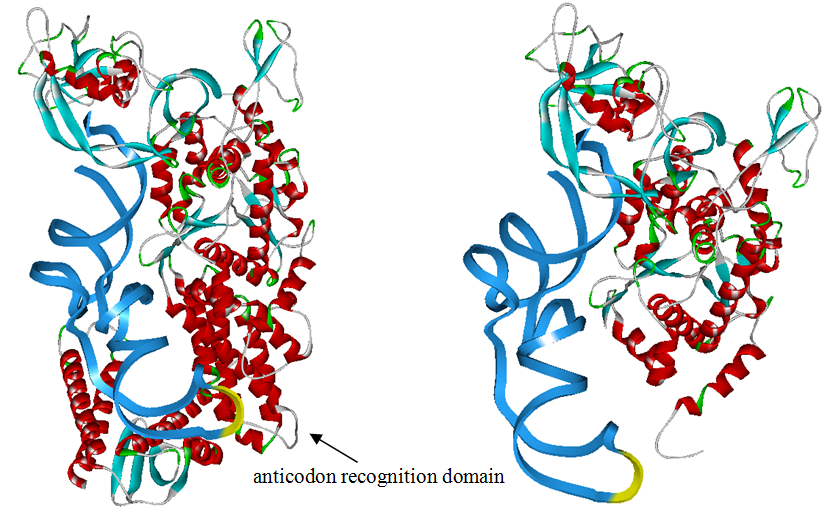
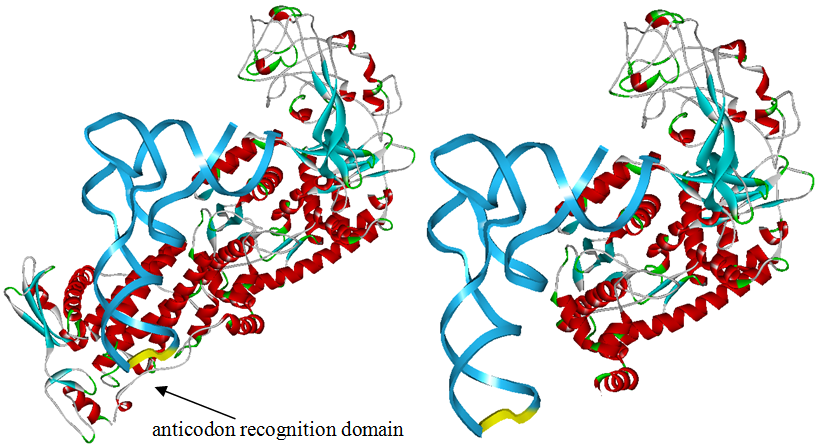
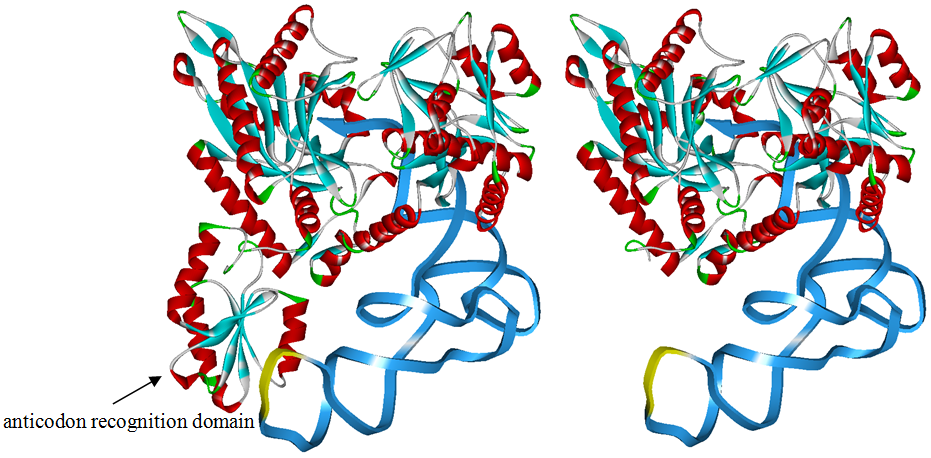
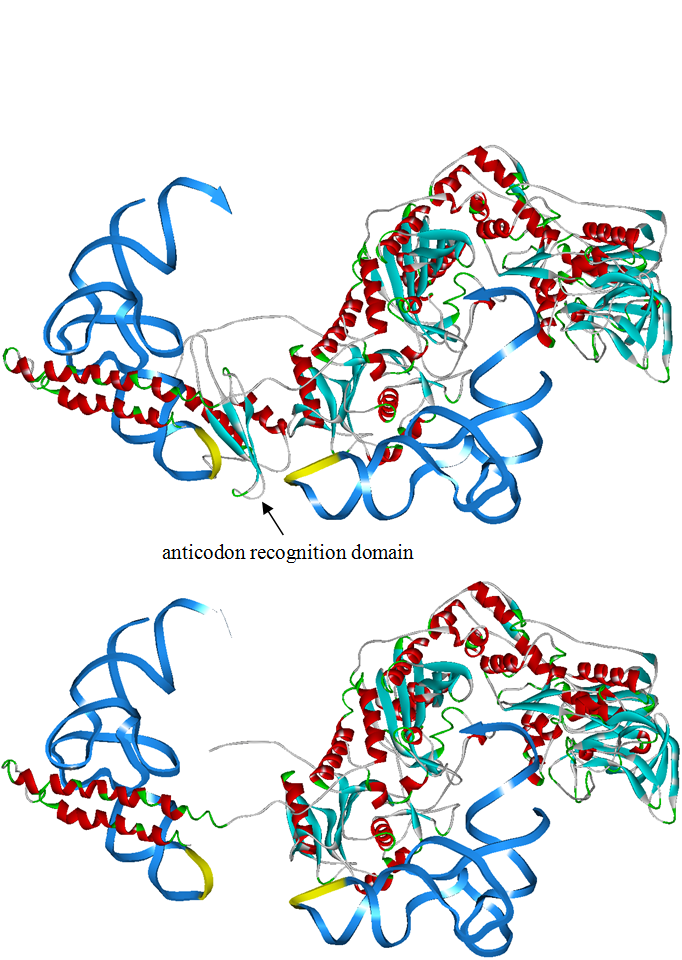
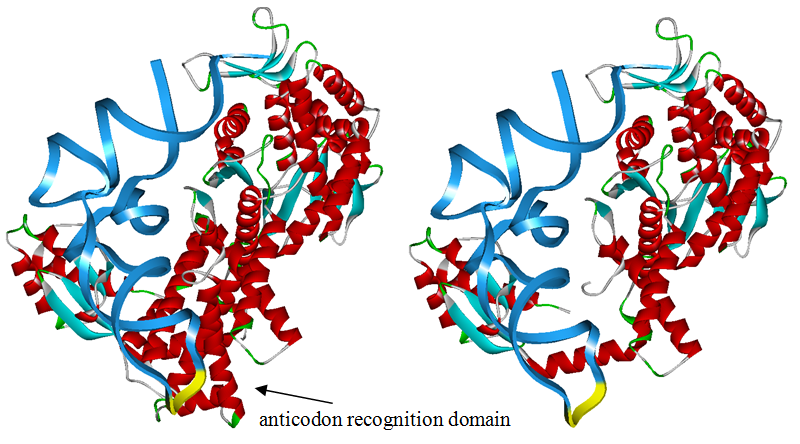
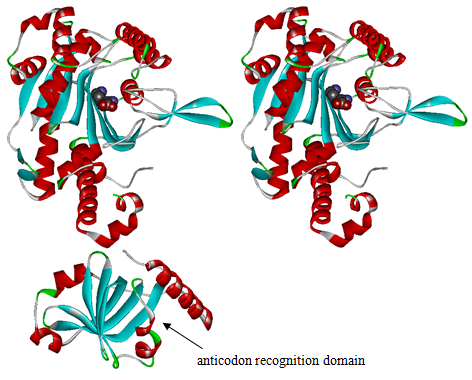
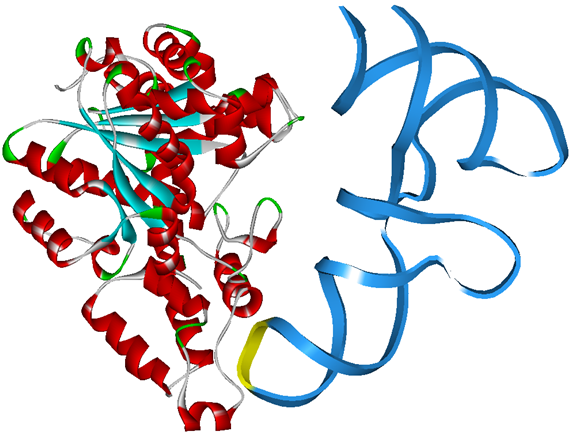
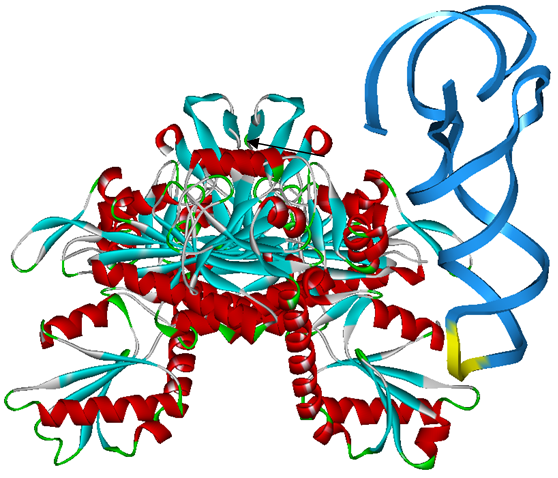
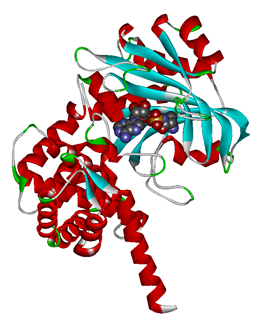
Modified aaRS LibraryIn Rare Codon Switch and Stop Codon Switch, we have modified tRNAAsp and aspartyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (AspRS). tRNAAsp is modified so that it can recognize rare codon AGG. Aspartyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (AspRS) is modified so that it loses the specificity for original tRNAAsp. To expand our Modified aaRS Library, we intend to modify the tRNA and aaRS of amino acids other than Asp. For tRNA, the anticodon can be mutated to base-pair rare codons other than AGG. For aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS), the function of the anticodon recognition should be lowered or eliminated. The 20 aaRS can be classified into two types, one with their anticodon recognition domains at the protein’s terminus, the other with their anticodon recognition domains inside the protein. For the first type, removing the anticodon recognition domains may not influence the overall structure and the aminoacylation function of the enzyme. For the second type, removing the domain may lead to incorrect folding of the protein. Type OneWe have designed the truncated version of the 14 Type One proteins based on their structures. See the designs below. Type TwoAfter we have analyzed the structure of the proteins below, we believe directed evolution is needed to obtain the modified enzyme.
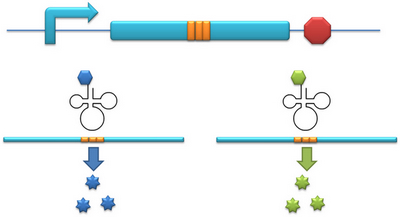
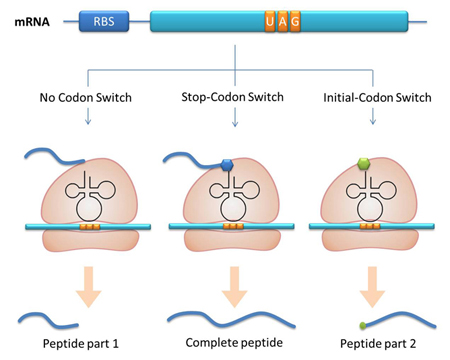
Methods For Protein Function ResearchThe aaRS library can not only to be used to expand our regulating system but also can be used as tools for protein function analysis. I. One Codon, Different Amino AcidsThe modified aaRS can be used as a tool to incorporate point mutation into protein. In our project for instance, we have modified tRNAAsp’s anticodon to base pair with AGG, which is originally the codon for Arg. Then we have modified the AspRS. This modified AspRS can charge Asp to tRNAAsp-AGG. For the protein, codon AGG is originally decoded as Arg yet now it is translated into Asp, thus incorporating point mutation. This method is fit for any other codon and any other tRNAs. II. One mRNA, Different ProteinsInitial-Codon Switch can be used as a tool to study the important domains of a protein. With Initial-Codon Switch, we can start translation at any given site, selectively expressing part of an ORF by introducing a new start codon, a new tRNAfmet, a new aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and a new 16S rRNA. We replace the first codon of the selected part of the peptide with a rare codon. Here, the rare codon is used as the start codon (Reporter). Concurrently, an altered tRNAmet with anticodon base pairing the rare codon and its corresponding aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase are introduced into the cell (Initial-Codon Switch). In order to guarantee the recognition of ribosome to mRNA, the base pairing between RBS of mRNA and MBS of 16SrRNA should be assured. The 5 nucleotides which are 7 nucleotides upstream of start (rare) codon is selected as the RBS sequence. The gene of an MBS base-pairing the selected RBS sequence is introduced into the 16s rRNA gene, replacing the original MBS. Thus the cell has a new type of ribosome which can recognize the selected RBS. This procedure mimics the original base pairing between RBS and MBS by changing the conserved RBS according to the sequence of the gene. With the design above, we can achieve the selective expression of part of an ORF. |
 "
"