Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Application
From 2011.igem.org
|
|
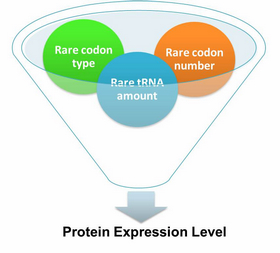
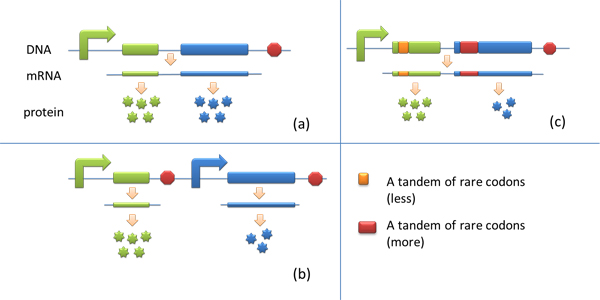
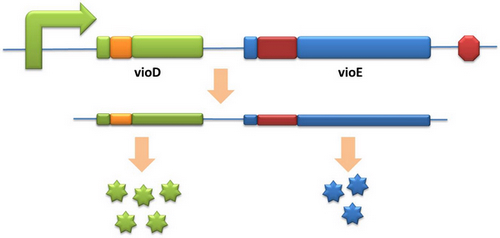
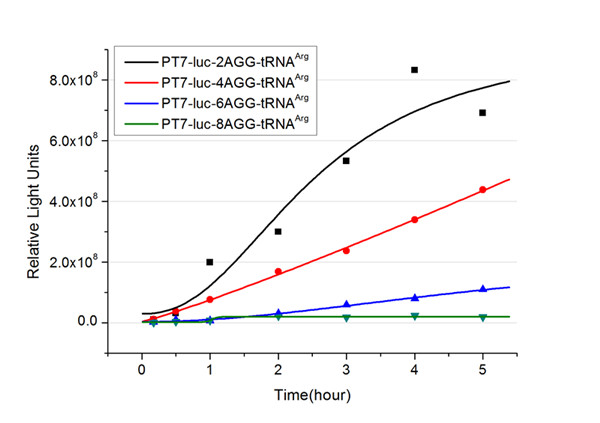
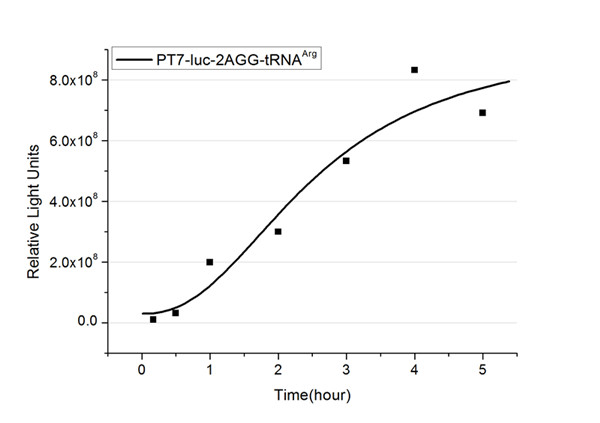
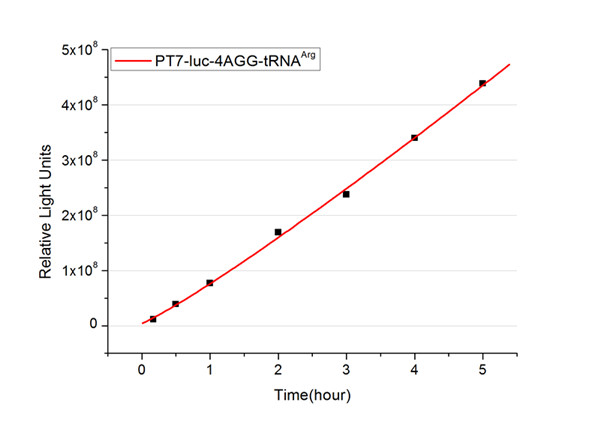
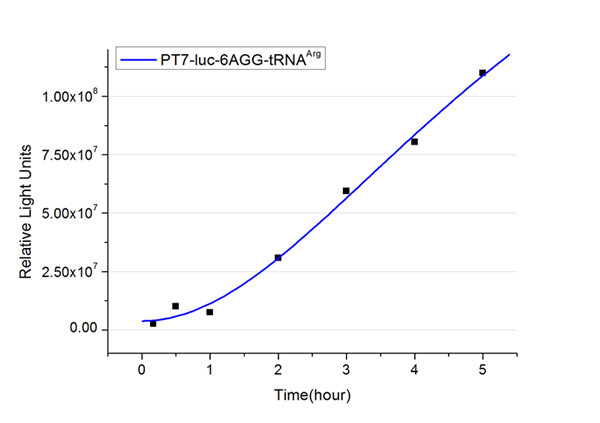
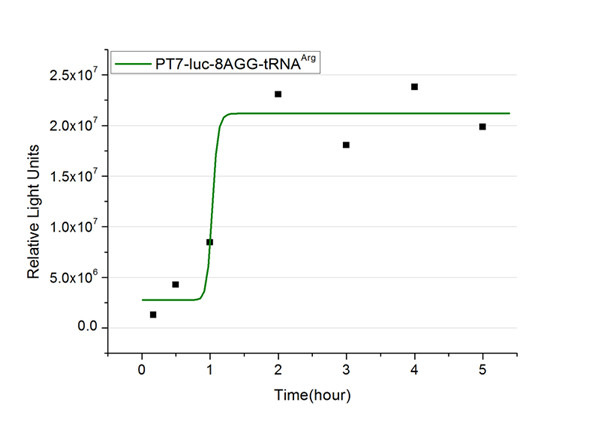
Expansion of Regulating Tools for Synthetic BiologyI. Multi-Level RegulationOur device has expanded the regulating tools for synthetic biology. We control protein biosynthesis through rare codon types, rare codon numbers and rare tRNA amount. Different combinations of these three elements can bring different outcomes in protein expression levels. rare codon types: AGA, AGG, CGA, CUA… rare codon numbers: 1, 2,3, 4,5, 6,7, 8,9, 10… rare tRNA amount: controlled by different strengths of promoters or riboswitch. II. Direct and Precise RegulationAs a translational regulatory tool, our device achieves more precise tuning of protein expression when compared with transcriptional tools. The controlling elements we use in this device are codons and tRNAs, the major participants of translation process. Thus manipulating these elements exert direct effects on protein biosynthesis. Here we offer two potential models for how this device can be used in pathway construction. Model 1Many genes are involved in complex metabolic pathways. The expression level of each gene may be different and affecting the production of final product. If a series of genes are under the control of a single promoter, these genes are likely to express on almost the same level. (a) Yet to achieve maximum production, each protein amount should be individually regulated. Traditionally we use different promoters to control different genes. (b) However with our device, genes can be put under one single promoter yet producing different amount of protein. (c) Our model can be used in building certain metabolic pathways, such as the violacein synthetic pathway. The relative amount of VioE and VioD will influence violacein production. Based on our model, the two genes can be placed under a single promoter yet different productions of the two enzymes can be achieved when we add different number of AGG codons to different sites on the tag with different copy numbers of AGG tandems. Different expression levels of the two genes can be achieved which may be used to increase final production. Model 2FeedbackIn biosynthetic pathways, feedback can affect protein production greatly. Our device can act as a feedback regulating tool to regulate the biosynthesis of target protein.Target protein and rare tRNA are under the control of the same promoter. Rare tRNA amount can regulate target protein biosynthesis through the rare codons inserted into the gene. We have simplified the process of constructing positive feedback in the metabolic pathways. We simply add AGG codons before the target gene and insert a 74bp tRNAArg gene in the same operon. We inserted the tDNAArg and luciferase gene into T7 operon so that both genes can be transcribed. tRNAArg can be correctly processed and become matured. Luciferase mRNA will be further translated into protein. The induced tRNAArg can facilitate the translation of luciferase-nAGG, achieving positive feedback. The rest of the working curves are shown here: Note:Click to see large figures. According to these working curves we proposed that the positive feedback can make the working curves linear instead of titration curves. LinkageAnother factor that influences protein biosynthesis may be the relative amount of two proteins. Our device can serve as a linker to regulate the relative amount of Protein A and Protein B. Rare codons are put into Gene A and Gene B. When rare tRNA is produced, it can influence the amount of both Protein A and Protein B, along with rare codon types and numbers.
|
 "
"