Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project
From 2011.igem.org
(→Abstract) |
(→Abstract) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
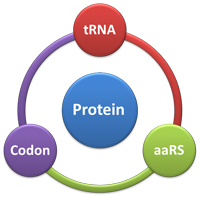
SJTU-BioX-Shanghai iGEM team is designing a set of Codon-Switches that regulate target protein biosynthesis (translation). | SJTU-BioX-Shanghai iGEM team is designing a set of Codon-Switches that regulate target protein biosynthesis (translation). | ||
| - | In our [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject1|'''Rare-Codon Switch''']], the translation of the protein can be finely turned up/down with the control of | + | |
| + | In our [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject1|'''Rare-Codon Switch''']], the translation of the protein can be finely turned up/down with the control of [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject1-1|rare tRNA amount]], [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject1-2|aaRS that charges the rare tRNA]] and [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject1-3|rare codons]]. | ||
Besides, our device can be made into switches that can be turned on/off without background noise in two ways. One is to use stop codon as the controlling element, the [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject2|'''Stop-Codon Switch''']]. The other is to use any codon but the original start codon to initiate translation, the [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject3|'''Initial-Codon Switch''']]. | Besides, our device can be made into switches that can be turned on/off without background noise in two ways. One is to use stop codon as the controlling element, the [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject2|'''Stop-Codon Switch''']]. The other is to use any codon but the original start codon to initiate translation, the [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Subproject3|'''Initial-Codon Switch''']]. | ||
| - | Our design has expanded the regulating tools for synthetic biology | + | Our design has expanded the regulating tools for synthetic biology and introduced brand-new methods for protein function analysis. See more about project applications, click [[Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/Application|'''here''']]. |
===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
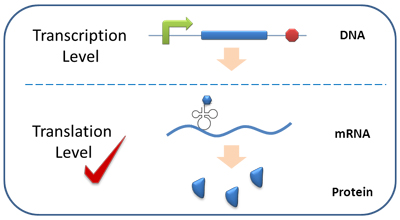
Gene expression regulation focuses mainly on two levels, transcription level and translation level. The former is currently the mainstream. However, for transcription regulating tools such as lac operator and ara operator, protein biosynthesis cannot be finely tuned. Besides, background noise is nearly inevitable because of promoter leek. | Gene expression regulation focuses mainly on two levels, transcription level and translation level. The former is currently the mainstream. However, for transcription regulating tools such as lac operator and ara operator, protein biosynthesis cannot be finely tuned. Besides, background noise is nearly inevitable because of promoter leek. | ||
| - | [[image:11SJTU_Project_01.jpg|frame|''Fig | + | [[image:11SJTU_Project_01.jpg|frame|''Fig.2'' Gene Expression Regulation Levels]] |
Translational regulation exists widely in natural biological systems in various forms, including miRNA or siRNA directed gene silencing, mRNA degradation as well as riboswitch. Compared with transcriptional regulation, translational regulation is more direct and precise. Background noise can be eliminated under certain circumstances. | Translational regulation exists widely in natural biological systems in various forms, including miRNA or siRNA directed gene silencing, mRNA degradation as well as riboswitch. Compared with transcriptional regulation, translational regulation is more direct and precise. Background noise can be eliminated under certain circumstances. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:00, 29 October 2011
|
|
Project: Condon Switch Controlling Protein BiosynthesisAbstractSJTU-BioX-Shanghai iGEM team is designing a set of Codon-Switches that regulate target protein biosynthesis (translation). In our Rare-Codon Switch, the translation of the protein can be finely turned up/down with the control of rare tRNA amount, aaRS that charges the rare tRNA and rare codons. Besides, our device can be made into switches that can be turned on/off without background noise in two ways. One is to use stop codon as the controlling element, the Stop-Codon Switch. The other is to use any codon but the original start codon to initiate translation, the Initial-Codon Switch. Our design has expanded the regulating tools for synthetic biology and introduced brand-new methods for protein function analysis. See more about project applications, click here. BackgroundGene expression regulation focuses mainly on two levels, transcription level and translation level. The former is currently the mainstream. However, for transcription regulating tools such as lac operator and ara operator, protein biosynthesis cannot be finely tuned. Besides, background noise is nearly inevitable because of promoter leek. Translational regulation exists widely in natural biological systems in various forms, including miRNA or siRNA directed gene silencing, mRNA degradation as well as riboswitch. Compared with transcriptional regulation, translational regulation is more direct and precise. Background noise can be eliminated under certain circumstances. tRNA, a key element in translation, can act as a regulating tool. The abundance of tRNA is different in organisms. In natural biological systems, rare codons and the abundance of rare tRNA can regulate protein biosynthesis level. Based on this, we want to mimic and expand this phenomenon into devices that can regulate protein biosynthesis level with rare codons and rare tRNAs. IntroductionOur project is divided into three sub-projects:Rare-Codon Switch, Stop-Codon Switch and Initial-Codon Switch. Usage: a device that turns up/down protein translation controlling elements: rare codon, rare codon recognizer tRNAs and engineered corresponding aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (aaRS) Usage: a device that turns on/off protein translation controlling elements: stop codon, stop codon recognizer tRNAs and engineered corresponding aaRS Usage: a device that turns on/off protein translation controlling elements: modified tRNAMetand engineered methyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (MetRS) |
 "
"