|
|
Rare-Codon Switch
aaRS Modulator + Reporter for Qualitative Analysis
Results
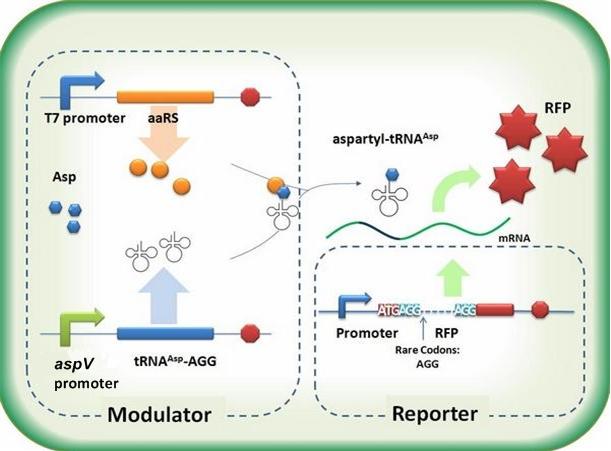
To deprive AspRS of its anticodon specificity, we analyzed the structure of AspRS and expressed a truncated AspRS without anticodon recognition domain. Our design is shown below. This modified enzyme keeps its ability of aminoacylation while loses its activity of recognizing anticodon of tRNA.
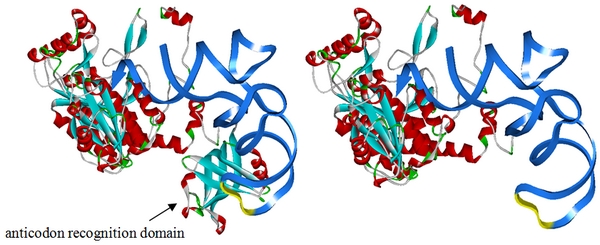 Fig 1. The design for modification is based on the crystal structure of E.coli AspRS coupled with tRNA (PDB ID: 1C0A). This figure shows E.coli aspartyl-tRNA synthetase with and without anticodon recognition domain. After this domain is depleted, the enzyme cannot bind tRNAAsp anticodon. Yet the ability of aminoacylation is maintained. We have used PT7-RFP-6AGG ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K567017 BBa_K567017]) as our Reporter. We have constructed tRNAAsp-AGG and PT7-TDRS (AspRS without anticodon recognition domain, ) ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K567012 BBa_K567012] and [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K567011 BBa_K567011])as the Modulator. tRNAAsp-AGG, which can recognize rare codon AGG, is under constitutive promoter. Our device works as follows: Without Modulator, RFP with 6 consecutive AGG insertions can hardly be expressed. When Modulator works, tRNAAsp-AGG can be charged with Asp by TDRS. tRNAAsp-AGG recognizes rare codon AGG on the Reporter RFP-6AGG. The ribosome gets through this part of the mRNA more easily. RFP is expressed. Red fluorescence is observed. Our experiment results are shown below.
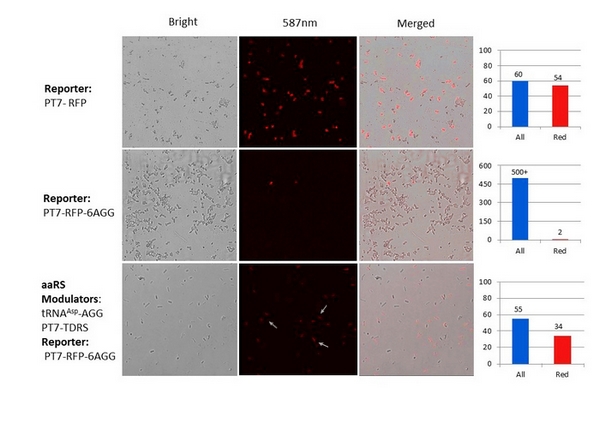 Fig 2. With our Modulator ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K567012 BBa_K567012] and [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K567011 BBa_K567011]), Reporter RFP-6AGG is expressed, demonstrating that our system works well.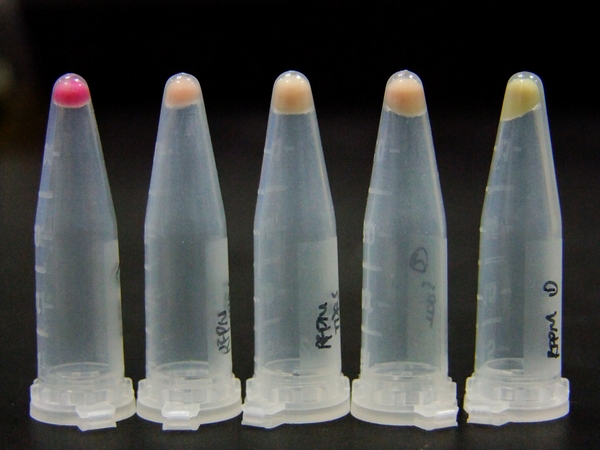  Fig 3. aaRS Modulator + Reporter for Qualitative Analysis. aaRS Modulator + RFP-6AGG(the middle three) emit red fluorescence. Wild type RFP (the first one from the left) exhibits bright red fluorescenceis. Control (first one from the right) exhibits no red fluoresence.
Conclusions
We have successfully constructed the aaRS Modulator and Reporter for qualitative analysis and tested their functions. aaRS Modulator includes modified AspRS without anticodon recognition domain and tRNAAsp-AGG. Experiment results show that with the help of aaRS Modulator, ribosome gets through the consecutive rare codons on the mRNA more easily. This device can be used to control protein biosynthesis.
The device can also be expanded. tRNA anticodons can be mutated to base-pair rare codons other than AGG. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS) other than AspRS can also be modified. We have done modeling of 14 aminoacyl tRNA synthetase deprived of anticodon specificity and have actually obtained 2 modified aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, TDRS and metGM/N.
|
 "
"



