Team:British Columbia/Accomplishments
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<b></b> | <b></b> | ||
| - | <font size="2"><h3> | + | <font size="2"><h3>In vitro assay production of monoterpene in bacteria</h3></font> |
<b></b><font size="1"><h3>Geranyl Pyrophosphate (GPP) Assay</h3></font> | <b></b><font size="1"><h3>Geranyl Pyrophosphate (GPP) Assay</h3></font> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<b></b> | <b></b> | ||
| - | <font size="2"><h3> | + | <font size="2"><h3>Diterpene production in yeast</h3></font> |
<b></b> | <b></b> | ||
| - | <font size="2"><h3> | + | <font size="2"><h3>Mountain Pine Beetle & Yeast Co-culture</h3></font> |
To prove the effectiveness of our theoretical model of release of Saccharomyces cerevisiae into the wild, we investigated whether wild-type yeast will survive during the transporation process (via the mountain pine beetles) from plate of origin (plate with yeast products; simulating our trapbox) to the next media plate. Beetles were incubated with yeast and were challenged with diferent amount of times away from the next media plates (in empty plates for 0, 10, 24, and 36 hours of time; simulating the transfer period when beetles leave the trapbox and fly off to the next tree). Results were analyzed qualitatively for the presence of GFP after growth on selective media plates from each time challenge. Based on these results, we can conclude that pine beetles do can carry wild-type yeast and transfer them onto the next media plate. It appears that our yeast product can survive on the beetles for 36 hours away from media plate. However, it cannot be determined whether the amount of yeast products on the beetles declines with time. | To prove the effectiveness of our theoretical model of release of Saccharomyces cerevisiae into the wild, we investigated whether wild-type yeast will survive during the transporation process (via the mountain pine beetles) from plate of origin (plate with yeast products; simulating our trapbox) to the next media plate. Beetles were incubated with yeast and were challenged with diferent amount of times away from the next media plates (in empty plates for 0, 10, 24, and 36 hours of time; simulating the transfer period when beetles leave the trapbox and fly off to the next tree). Results were analyzed qualitatively for the presence of GFP after growth on selective media plates from each time challenge. Based on these results, we can conclude that pine beetles do can carry wild-type yeast and transfer them onto the next media plate. It appears that our yeast product can survive on the beetles for 36 hours away from media plate. However, it cannot be determined whether the amount of yeast products on the beetles declines with time. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<html><iframe width="425" height="349" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/-fXdy8plAR8?hl=en&fs=1" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></html> | <html><iframe width="425" height="349" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/-fXdy8plAR8?hl=en&fs=1" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></html> | ||
<b></b> | <b></b> | ||
| - | <font size="2"><h3> | + | <font size="2"><h3>Blue Stain Fungi & Yeast Co-culture Co-culture</h3></font> |
<font size="4"><h3>Modeling Achievements</h3></font> | <font size="4"><h3>Modeling Achievements</h3></font> | ||
Revision as of 04:06, 28 October 2011

Wet Laboratory Achievements
In vitro assay production of monoterpene in bacteria
Geranyl Pyrophosphate (GPP) Assay
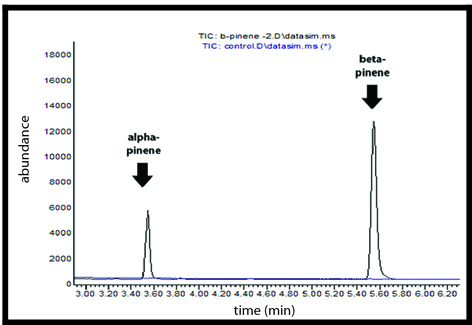
Alpha-pinene and Beta-pinene synthases were purified using His SpinTrap Ni-affinity columns and were assayed in vitro with GPP. Using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GCMS), we confirmed the synthesis of alpha and beta pinene monoterpenes from our enzyme assays.
GC-MS Chromatogram
Diterpene production in yeast
Mountain Pine Beetle & Yeast Co-culture
To prove the effectiveness of our theoretical model of release of Saccharomyces cerevisiae into the wild, we investigated whether wild-type yeast will survive during the transporation process (via the mountain pine beetles) from plate of origin (plate with yeast products; simulating our trapbox) to the next media plate. Beetles were incubated with yeast and were challenged with diferent amount of times away from the next media plates (in empty plates for 0, 10, 24, and 36 hours of time; simulating the transfer period when beetles leave the trapbox and fly off to the next tree). Results were analyzed qualitatively for the presence of GFP after growth on selective media plates from each time challenge. Based on these results, we can conclude that pine beetles do can carry wild-type yeast and transfer them onto the next media plate. It appears that our yeast product can survive on the beetles for 36 hours away from media plate. However, it cannot be determined whether the amount of yeast products on the beetles declines with time.
Blue Stain Fungi & Yeast Co-culture Co-culture
Modeling Achievements
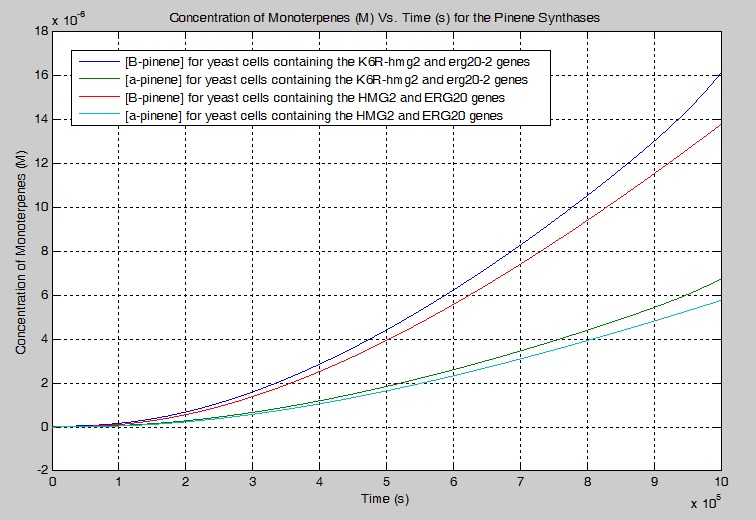
Monoterpene Production Model
We modeled a simplified and modified version of the mevalonate pathway that describes our engineered yeast cells. We created a series of differential equations to model each chemical reaction that were based on first-order Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Enzyme constants were estimated/found using literature values and the simulations were conducted using MATLAB.
Our simulation showed that 17.10% more beta-pinene is produced and 17.00 % more alpha-pinene is produced when K6R-hmg2 and erg20-2 are used instead of HMG2 and ERG20 alone in a yeast cell. For manufacturing purposes, sensitivity analysis was performed and it was determined that the pathway could be improved to increase the production of monoterpenes by increasing the concentration of the enzymes K6R-HMG2 and IDI1 for DMA-PP. In particular, the tripling the [K6R-HMG2] increases the [GPP] by 8.7000 times. The tripling the [K6R-HMG2] and [IDI1] for the production of DMA-PP increases the [B-pinene] by 7.3166 times and 1.3052 times respectively.
We simulated the expansion of the MPB population from year 2011 to 2020 using the estimates obtained from the clustering analysis. For cost estimation and prediction of emergence of subpopulations, refer to our Model Methodology above.
 "
"