Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal
From 2011.igem.org

On this page we summarize the (successful) results and achievements of our teamwork.
Week 1: 2nd - 8th may
- cloning of <partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> behind weak (<partinfo>J23103</partinfo>) and medium strong (<partinfo>J23110</partinfo>) constitutive promoter (each part and both parts polycistronic)
- cloning of fusionprotein between <partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>, also assembly behind weak and medium strong constitutive promoter
- testing and establishing of HPLC method for BPA detection
- expression of the successfully assembled BPA degrading BioBricks in E. coli TOP10
- successful PCR on the S-layer genes of Brevibacterium flavum and Corynebacterium crenatum
- successful cloning of the S-layer gene of B. flavum without TAT-sequence
Organizational:
- meeting with Bielefeld Marketing to discuss our participation at the science festival GENIALE in Bielefeld
Week 2: 9th - 15th may
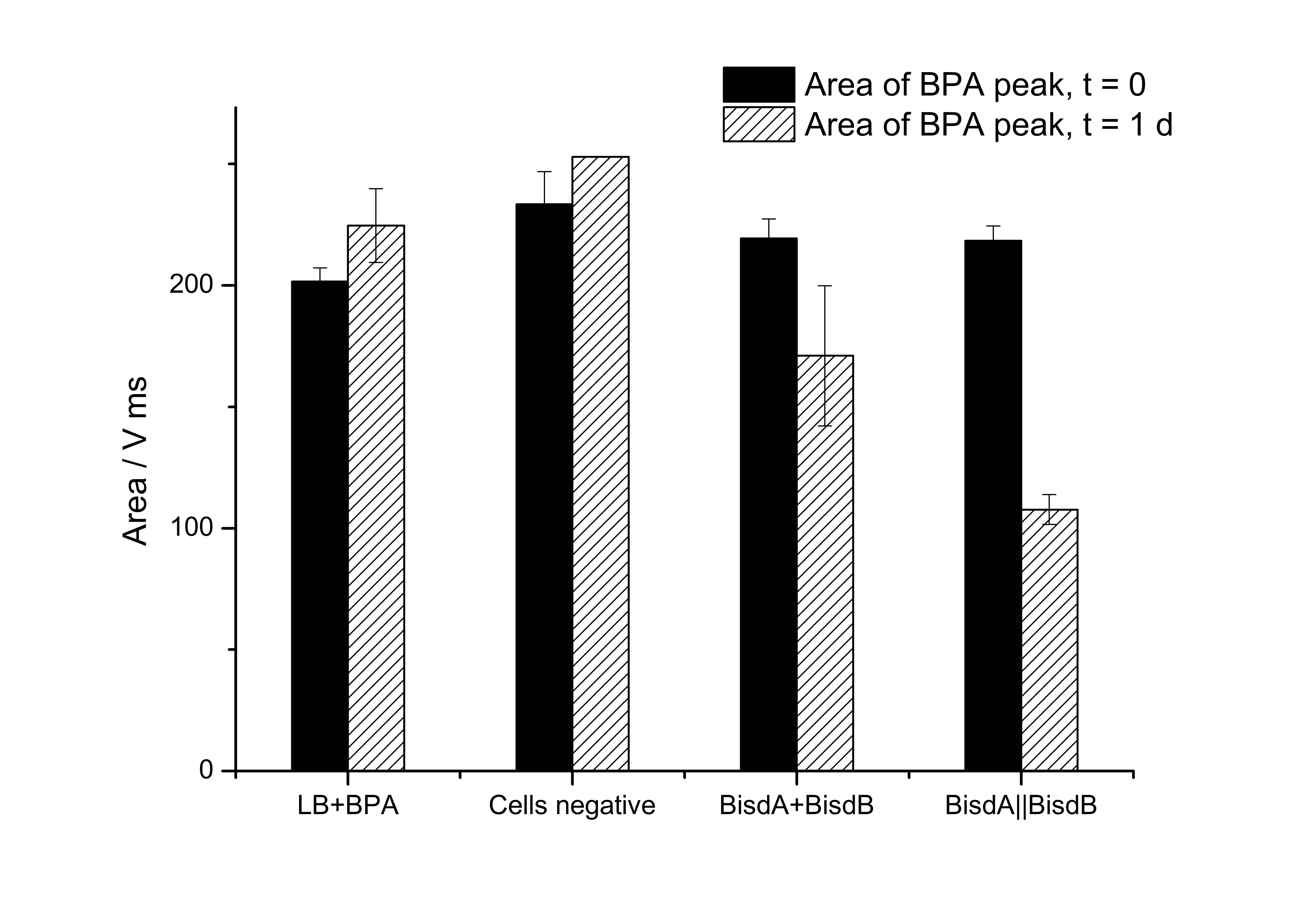
Figure 1: HPLC results of the first experiment on BPA degradation in E. coli TOP10. Cultivations were carried out in LB medium with 100 mg L-1 BPA at 30 °C. Samples were taken at the beginning of the cultivation and after one day. The HPLC results are shown above (area of the BPA peak). BisdA + BisdB is the polycistronic gene and BisdABisdB is the fusion protein.
Bisphenol A:
- assembly of <partinfo>K157011</partinfo> behind existing BPA degrading parts (for purification and testing of <partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> in a cell free system)
- HPLC results: fusionprotein between <partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> can degrade BPA and seems to work better than the polycistronic version (compare fig. 1)
S-layer:
- expression of the S-layer gene without TAT-sequence of B. flavum in E. coli KRX and BL21-Gold(DE3) after sequencing gave correct results
- successful PCR on the S-layer gene of Corynebacterium halotolerans
Organizational:
- moving to our own room in the CeBiTec
Week 3: 16th - 22nd may
Bisphenol A:
- successful PCR on the NADP oxidoreductase gene from E. coli TOP10
S-layer:
- successful cloning of the complete S-layer gene cspB of B. flavum, C. crenatum and C. halotolerans
- successful cloning of the S-layer genes of B. flavum and C. halotolerans without TAT-sequence, without lipid anchor and without both (only self-assembly domain)
Organizational:
Week 4: 23rd - 29th may
Bisphenol A:
- establishing a new method for analysis of BPA concentrations (extraction + LC-ESI-QTOF-MS)
S-layer:
Organizational:
- arrange a BBQ for our workgroup in the CeBiTec to get to know our coworkers
- substantiating our contribution to the GENIALE
Week 5: 30th may - 5th june
Bisphenol A:
- beginning of first characterization experiments for BPA degrading BioBricks (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>)
S-layer:
Organizational:
- meeting with Prof. Alfred Pühler to plan our contribution to the CeBiTec symposium in july
Week 6: 6th - 12th june
Organizational:
- presentation of the iGEM competition at the 2nd BIO.NRW (PhD) Student Convention
Week 7: 13th - 19th june
S-Layer:
- successful fusion of modified cspB genes of B. flavum and C. halotolerans with a monomeric RFP (BBa_E1010) using Gibson assembly.
- B. flavum:
- C. halotolerans:
Bisphenol A:
- cloning of NADP oxidoreductase in pJET1.2 finally successful -> waiting for sequencing results to remove illegal restriction sites
Week 8: 20th - 26th june
S-layer:
- successful cloning of K525232 using Gibson assembly.
- K525232: fusion of modified cspB of C. halotolerans without lipid anchor and TAT-sequence (K525203) with BBa_E1010.
Organizational:
- finishing our first press release
- all devices (thermocycler etc.) and materials (competent cells, polymerase, kits) from our sponsors arrived
Week 9: 27th june - 3rd july
S-Layer:
Week 10: 4th july - 10th july
Bisphenol A:
- experiments on the influence of temperature, promotor intensity and the characteristics of the fusion protein <partinfo>K123000</partinfo> || <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> on BPA degradation
Organizational:
- presenting our posters from the teams of 2010 and 2011 at the congress Biotechnologie2020+ in Berlin hosted by the "Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung" (Federal Ministry of Education and Research).
Week 11: 11th july - 17th july
Bisphenol A / S-Layer:
- our BioBrick order (some fluorescences proteins and cleavage sites) from iGEM HQ arrived
Organizational:
- presenting the iGEM competition and our team project at the secondary school Ravensberger Gynmasium in Herford (Photos)
Week 12: 18th july - 24th july
Organizational:
- presenting our projects from 2010 and 2011 at the CeBiTec Symposium 2011 in Bielefeld
- meeting and having fun with the iGEM teams from Delft/NL, Edinburgh/UK, Odense/DK. Freiburg/DE and Ljubljana/SL at the Symposium (Photos)
Bisphenol A / S-Layer:
- removing illegal restiction sites to get valid BioBricks
- cloning the NAD+ dependent ligase from E. coli into BioBrick backbones
Week 13: 25th july - 31th july
S-Layer:
- fusing the synthesized S-Layers to a bunch of fluorescent proteins
Bisphenol A:
- testing new BPA extraction protocols for LC-MS including an internal standard (bisphenol F)
Week 14: 1st august - 7th august
Bisphenol A:
- BPA analysis with extraction and LC-MS finally works and is very accurate
- Better results for BPA degradation in E. coli -> our fusion protein (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo> to <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>) can completely degrade BPA
- Measuring characterization results for different BPA degrading BioBricks
Molecular Beacons:
- Successful characterization of two differently labeled Molecular Beacons as a preparation for the NAD+ bioassay including autonomously produced NAD+ dependent DNA ligase from E. coli
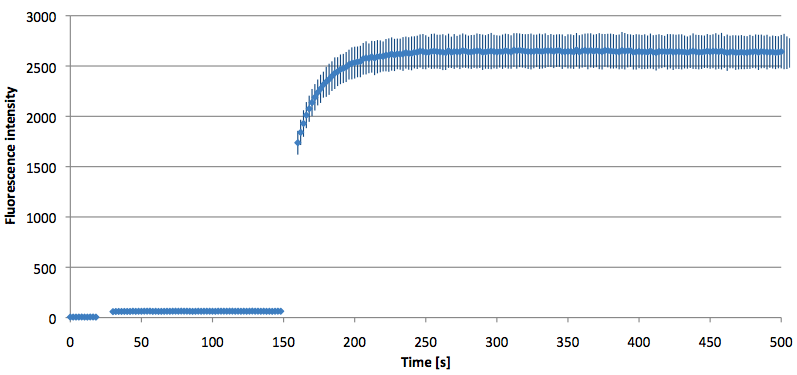
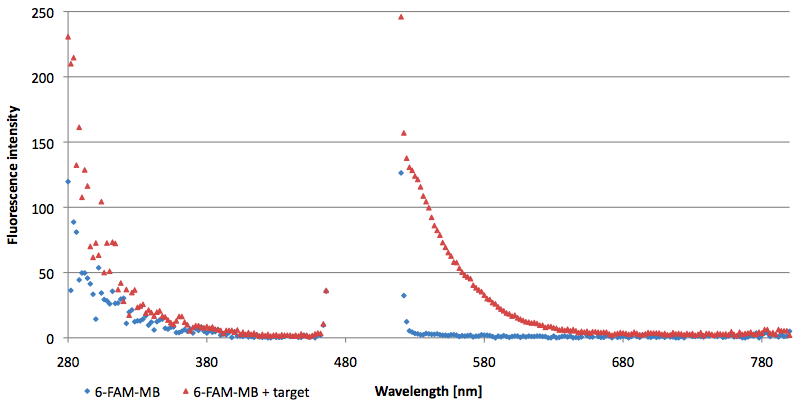
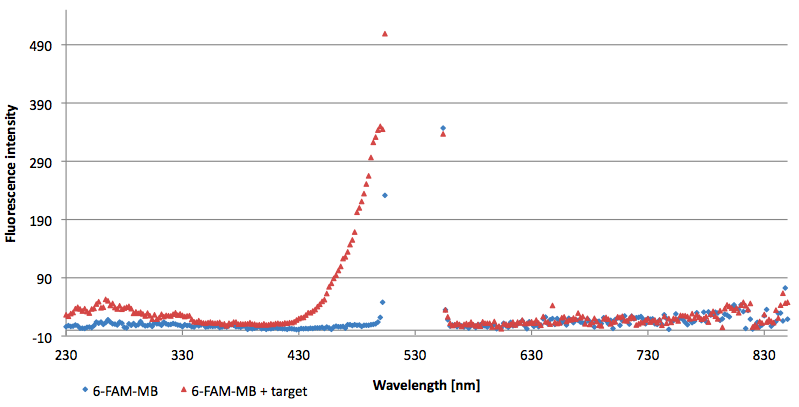
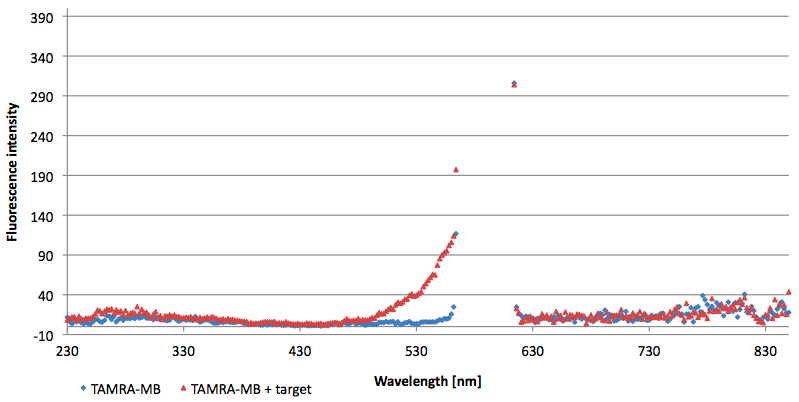
Figure 10: Signal-to-background ratio (S/B) determination of 6-FAM labeled Molecular Beacon in its closed or open state at an extinction wavelength 495 nm and emission wavelength 530 nm. Molecular Beacons and the target were added one after another (see gaps) each after equilibrium was reached. Calculated S/B: 45,52 (n=3).
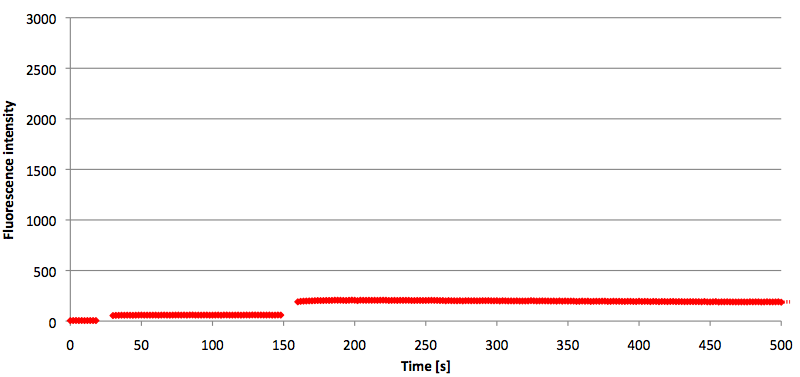
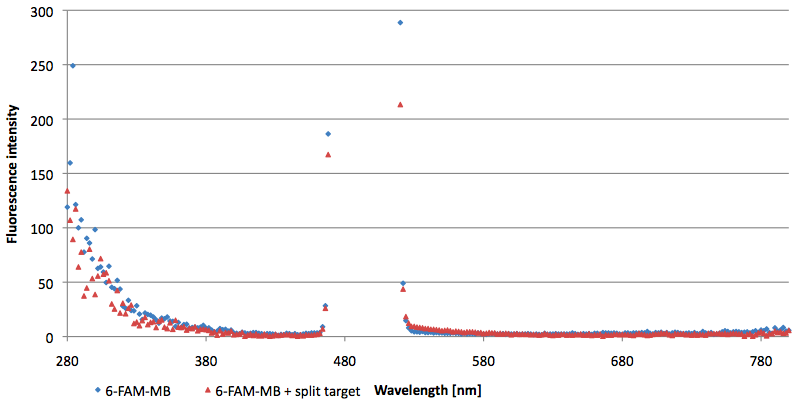
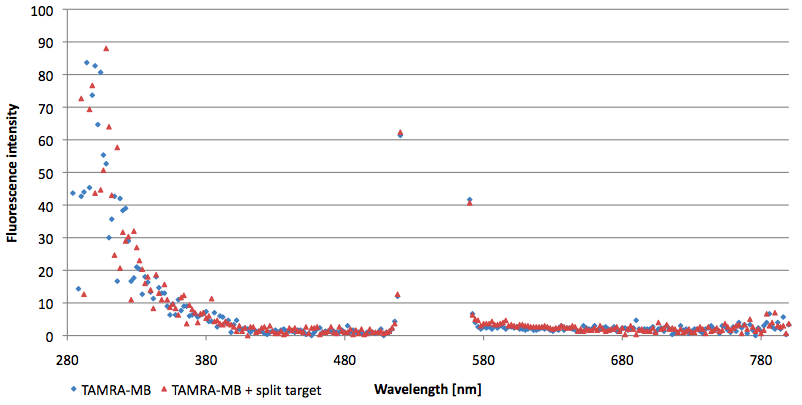
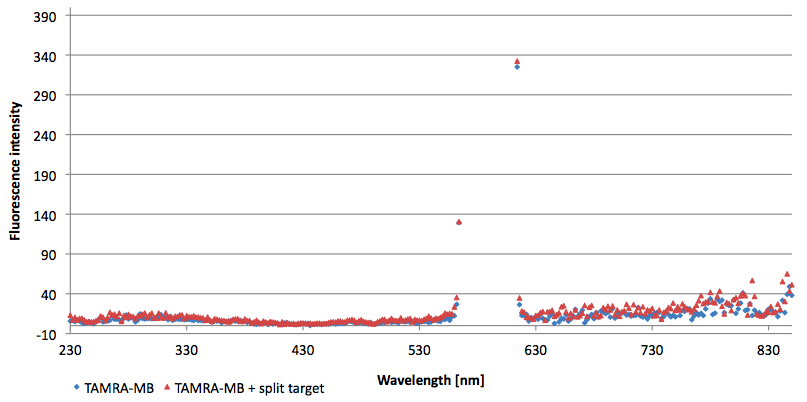
Figure 11: Signal-to-background ratio (S/B) determination of 6-FAM labeled Molecular Beacon in its closed state at an extinction wavelength 495 nm and emission wavelength 530 nm. Molecular Beacons and the split target were added one after another (see gaps) each after equilibrium was reached. Calculated S/B: 3,36 (n=3).
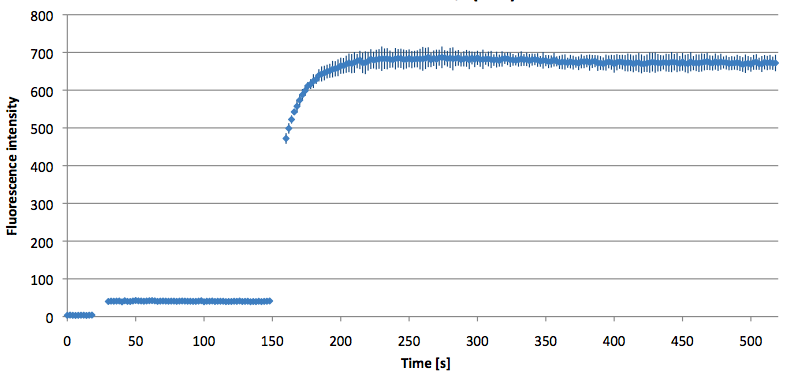
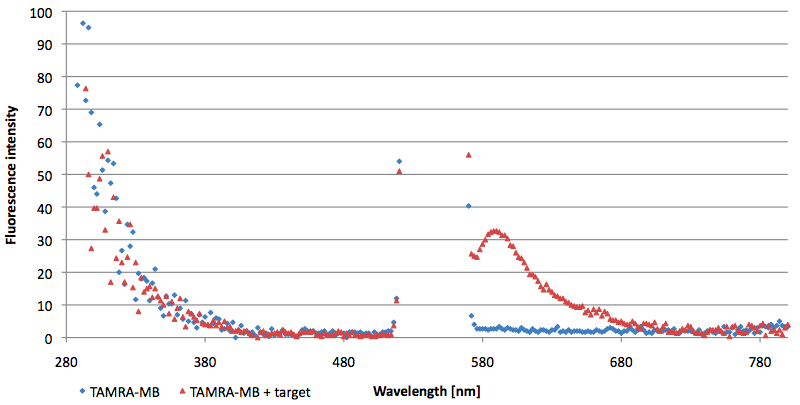
Figure 12: Signal-to-background ratio (S/B) determination of TAMRA labeled Molecular Beacon in its closed or open state at an extinction wavelength 552 nm and emission wavelength 590 nm. Molecular Beacons and the target were added one after another (see gaps) each after equilibrium was reached. Calculated S/B: 18,21 (n=3).
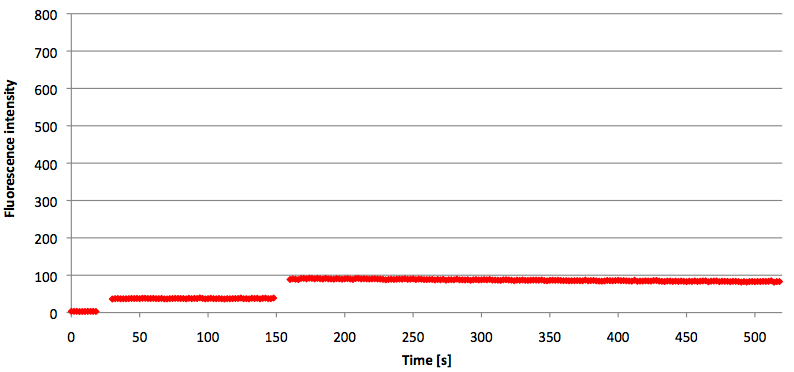
Figure 13: Signal-to-background ratio (S/B) determination of TAMRA labeled Molecular Beacon in its closed state at an extinction wavelength 552 nm and emission wavelength 590 nm. Molecular Beacons and the split target were added one after another (see gaps) each after equilibrium was reached. Calculated S/B: 2,31 (n=3).
File:Bielefeld-Germany-2011
Figure 14: Thermal profile of 6-FAM labeled Molecular Beacon alone and with either target or split target added (n=5).
Week 15: 8th august - 14th august
Bisphenol A:
- BPA analysis with extraction and HPLC with UV detector leads to very similar results as the analysis with LC-MS (except for low BPA concentrations -> LOD / LOQ of LC-MS is lower than that of "normal" HPLC, compare figure 15)
- measuring of more samples from cultivations with BPA degrading BioBricks for further characterization
- we discovered some interesting results in our MS data - soon more
- testing methods to purify his-tagged BisdA and BisdB for cell free BPA degradation and further characterization of these proteins
- testing the influence of BPA on the growth of E. coli
- developing a modell for BPA degradation by E. coli (compare fig. 16)
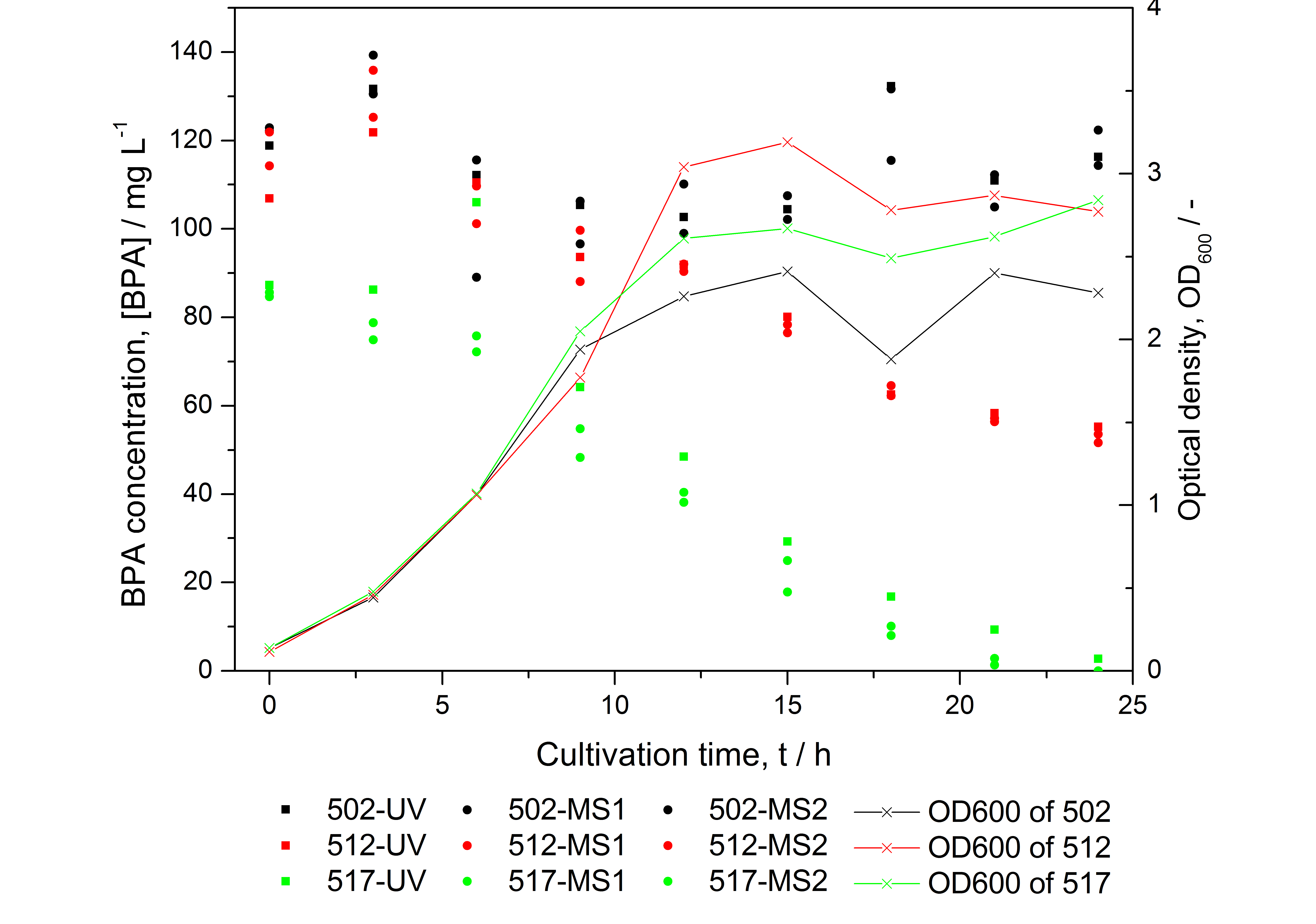
Figure 15: HPLC results and optical density of experiments on BPA degradation of E. coli KRX. Cultivations were carried out in LB medium with ~ 100 mg L-1 BPA at 30 °C. Samples were taken every three hours over one day. BPA concentration was measured by HPLC with either UV detector or ESI-qTOF-MS. 502: negative control (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo>), 512: polycistronic <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123000</partinfo>, 517: fusionprotein between <partinfo>K123001</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123000</partinfo>, every part behind medium strong constitutive promoter.
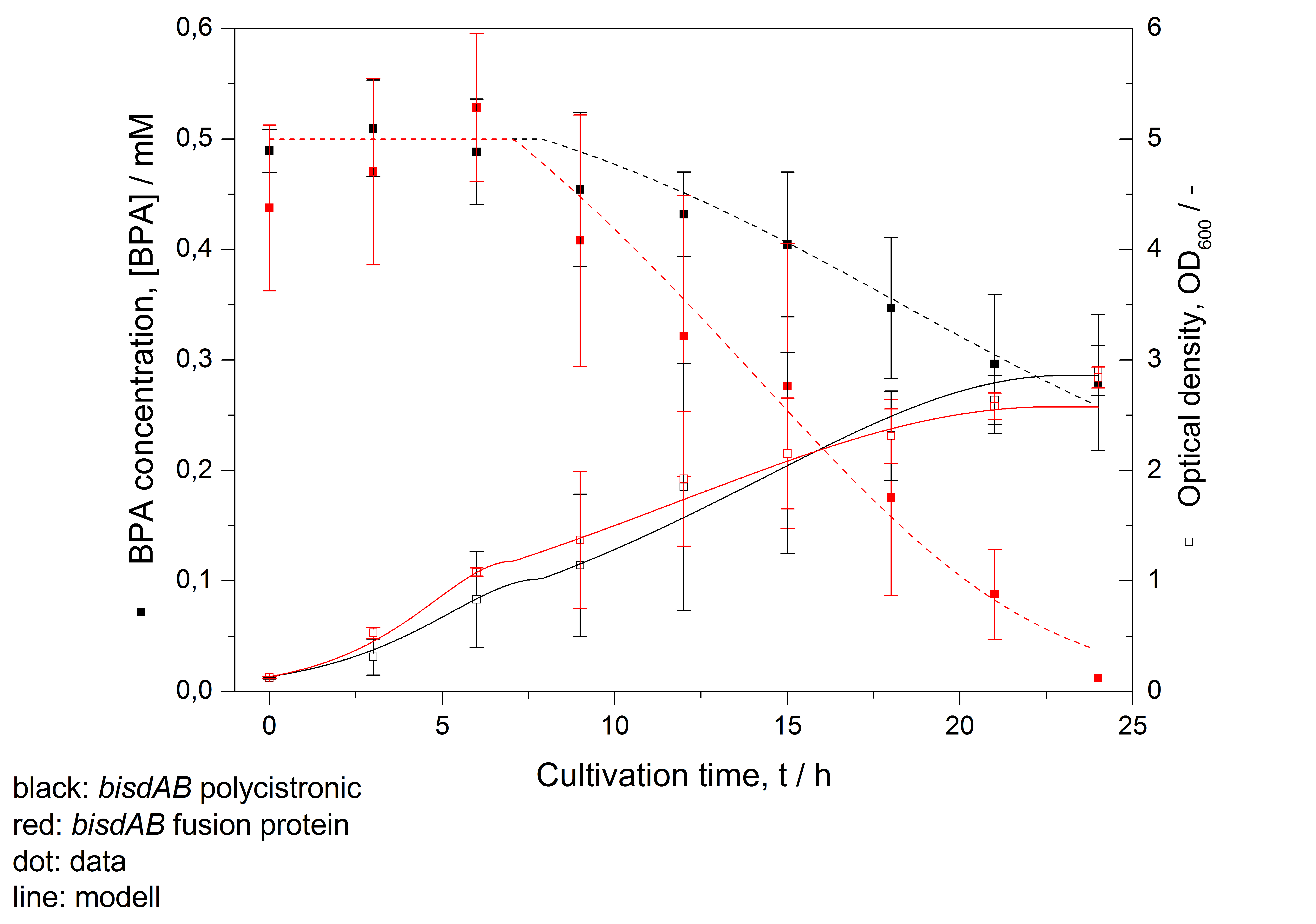
Figure 16: Modelling of BPA degradation (filled squares) by and OD600 (open squares) of E. coli KRX carrying genes for BisdA and BisdB (polycistronic bisdAB (black) and fusion protein between BisdA and BisdB (red)) behind the medium strong promoter <partinfo>J23110</partinfo>. Cultivations were carried out at 30 °C in LB + Amp + BPA medium for 24 h with automatic sampling every three hours in 300 mL shaking flasks without baffles with silicon plugs. Three biological replicates were analysed.
S-layer:
- MALDI-TOF analysis of SDS-PAGEs to characterize the function of the TAT-sequence and the lipid anchor of PS2 (encoded by cspB gene) in E. coli
Week 16: 15th august - 21st august
S-layer:
- finally found our S-layer proteins in E. coli -> now we can plan purification strategy
- fusion of FPs to sgsE successful
Bisphenol A:
- all metabolites of natural BPA degradation pathway found during degradation of BPA in E. coli by LC-MS -> now MS/MS to check structure of these metabolites to be sure
- testing whether E. coli can grow on BPA as the only carbon source (on M9 plates)
Week 17: 22nd august - 28th august
S-layer:
- cultivation and purification of sgsE fusion proteins
Bisphenol A:
- purification of his-tagged BisdA and BisdB
- first characterization results entered into partsregistry
- cloning of fusion protein FNR:BisdA:BisdB successful
 "
"