Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Data Page
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→We have also characterized the following parts) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
# [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525512 Main Page] - '''Polycistronic expression of BisdA and BisdB''': This is the version of BPA degrading BioBricks found in the partsregistry - comparison to our fusion protein <partinfo>K525515</partinfo>. | # [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525512 Main Page] - '''Polycistronic expression of BisdA and BisdB''': This is the version of BPA degrading BioBricks found in the partsregistry - comparison to our fusion protein <partinfo>K525515</partinfo>. | ||
# [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525517 Main Page] - '''Fusion Protein of BisdA and BisdB (expressed)''': This fusion protein improves the bisphenol A degradation in ''E. coli'' compared to the so far in the partsregistry existing BPA degrading BioBricks. | # [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525517 Main Page] - '''Fusion Protein of BisdA and BisdB (expressed)''': This fusion protein improves the bisphenol A degradation in ''E. coli'' compared to the so far in the partsregistry existing BPA degrading BioBricks. | ||
| - | # [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525234 Main Page] - '''Fusion protein of S-layer CspB and mRFP''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation as well as purification methods for CspB S-layers. | + | # [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K525234 Main Page] - '''Fusion protein of S-layer CspB and mRFP''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation as well as purification methods for CspB S-layers from from ''Corynebacterium halotolerans''. |
| + | # [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K525121 Main Page] - '''S-layer protein CspB with TAT-sequence and lipid anchor''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. | ||
| + | # [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K525123 Main Page] - '''S-layer protein CspB with lipid anchor''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. | ||
| + | # [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K525222 Main Page] - '''S-layer protein CspB''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. | ||
| + | # [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K525223 Main Page] - '''S-layer protein CspB with lipid anchor''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. | ||
| + | # [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K525224 Main Page] - '''S-layer protein CspB with TAT-sequence''': This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. | ||
Revision as of 23:59, 21 September 2011


This page gives a basic overview about our cell-free bisphenol A biosensor system and the BioBricks we have used. A more detailed description of the biosensor system can be found in our project description as well as in the bisphenol A, S-layer and NAD+ detection background subsections.
Contents |
How our system works
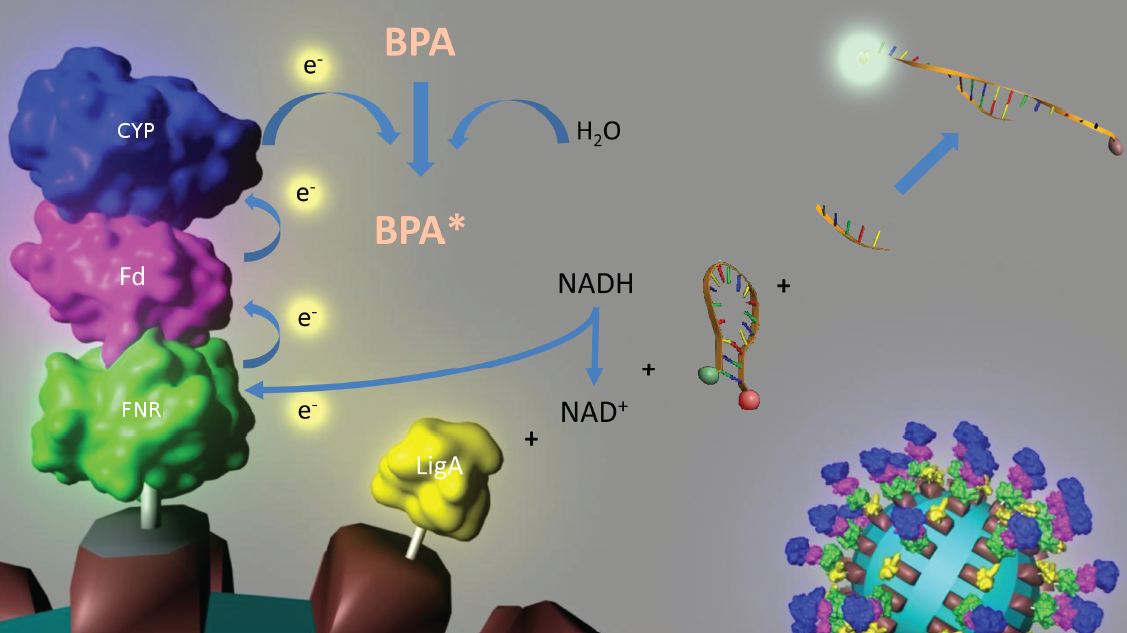
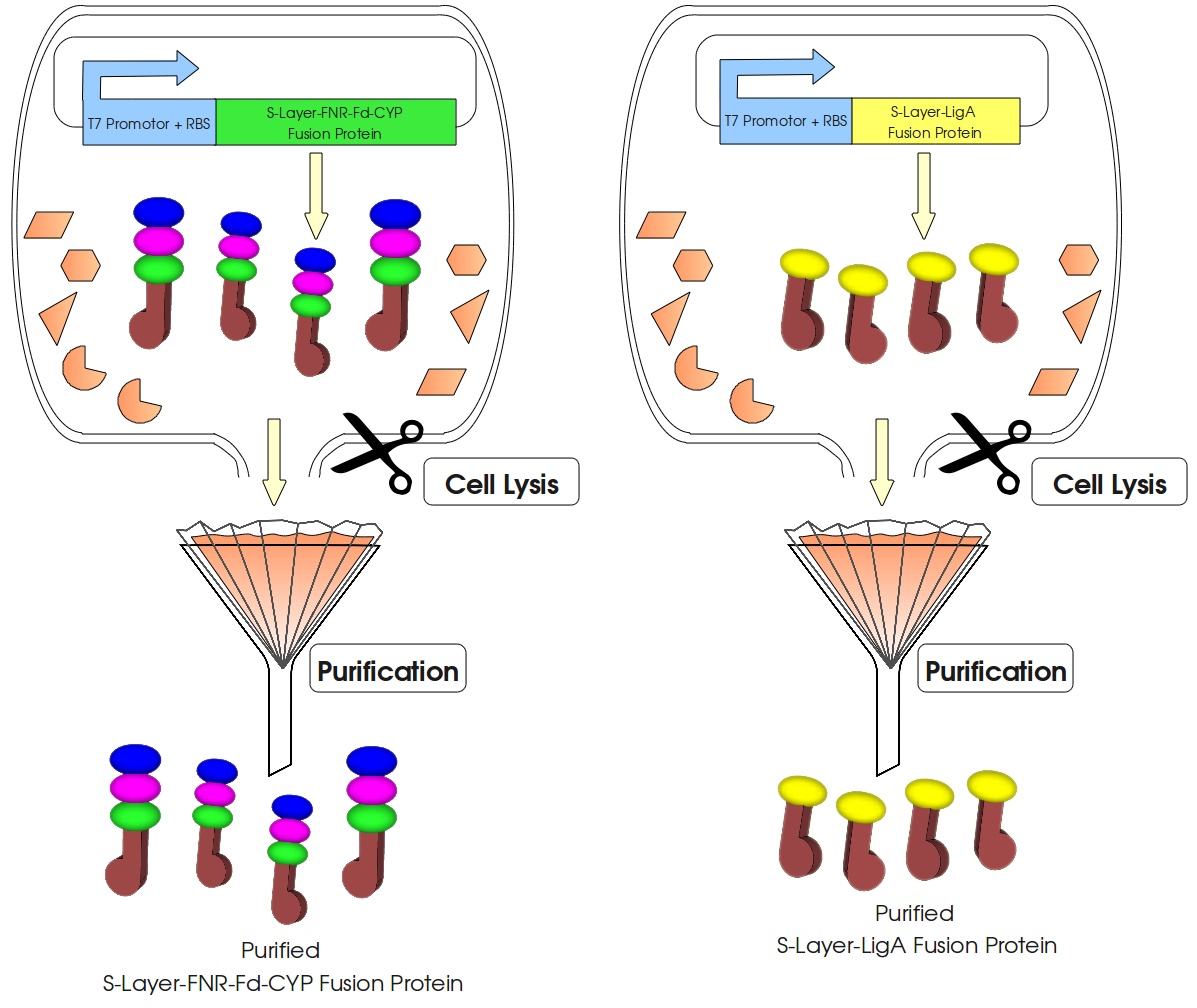
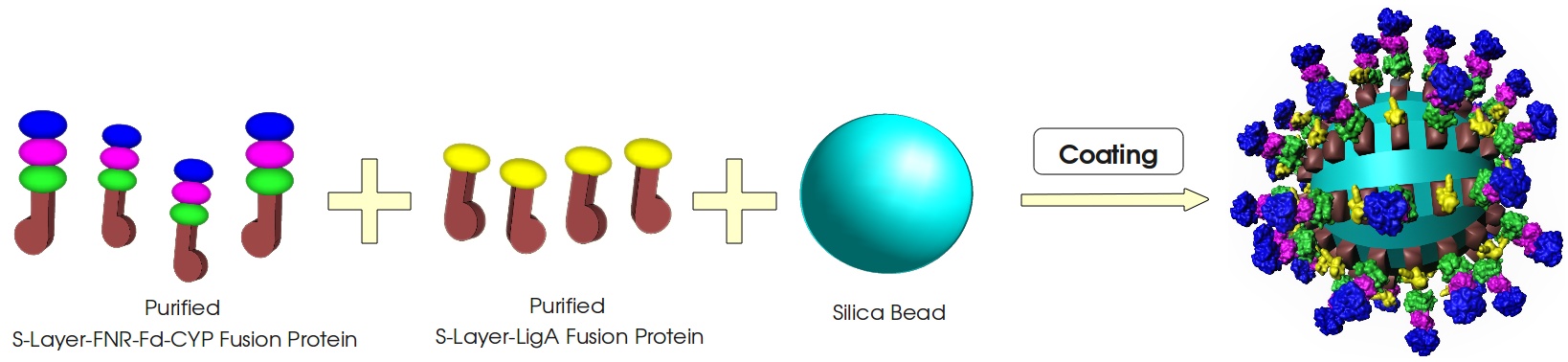
Figure 3: Visualization of our cell-free bisphenol A biosensor system with all essential components. Bisphenol A (BPA) is reduced by the electrons from NADH transferred by the ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase (FNR, <partinfo>BBa_K525499</partinfo>), ferredoxin (Fd, <partinfo>BBa_K123000</partinfo>) and cytochrome P450 (CYP, <partinfo>BBa_K123001</partinfo>) which are fused to a S-layer protein. The molecular beacon (hairpin structure) binds two short DNA oligos. The NAD+-dependent ligase (LigA), which is also fused to S-layer proteins, ligates the two oligos so that the hairpin structure opens up and the fluorophore is able to emit light after extinction.
Data for our favorite new parts
- Main Page - Fusion protein of S-layer SgsE and mCitrine: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize purification methods and to demonstrate the S-layers ability to self-assemble on surfaces.
- Main Page - Fusion protein of BisdA and BisdB: This fusion protein improves the bisphenol A degradation in E. coli compared to the so far in the partsregistry existing BPA degrading BioBricks.
- Main Page - NAD+-dependent DNA ligase from E. coli (LigA) : This enzyme enables determination of NAD+ even in very low concentrations by introducing it to a molecular beacon based bioassay.
Data for pre-existing parts
- Experience - BisdA degrades Bisphenol A when used with BisdB, BBa_K123000 (University of Alberta, iGEM 2008): Complete degradation of 120 mg L-1 Bisphenol A with polycistronic bisdAB gene in 30 - 33 h. Even faster (21 - 24 h) when using a fusion protein of BisdA and BisdB.
- Experience - BisdB degrades Bisphenol A when used with BisdA, BBa_K123001 (University of Alberta, iGEM 2008): Complete degradation of 120 mg L-1 Bisphenol A with polycistronic bisdAB gene in 30 - 33 h. Even faster (21 - 24 h) when using a fusion protein of BisdA and BisdB.
We have also characterized the following parts
- Main Page - Fusion protein of S-layer SbpA and mCitrine: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize purification methods and to demonstrate the S-layers ability to self-assemble on surfaces.
- Main Page - Polycistronic expression of BisdA and BisdB: This is the version of BPA degrading BioBricks found in the partsregistry - comparison to our fusion protein <partinfo>K525515</partinfo>.
- Main Page - Fusion Protein of BisdA and BisdB (expressed): This fusion protein improves the bisphenol A degradation in E. coli compared to the so far in the partsregistry existing BPA degrading BioBricks.
- Main Page - Fusion protein of S-layer CspB and mRFP: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation as well as purification methods for CspB S-layers from from Corynebacterium halotolerans.
- Main Page - S-layer protein CspB with TAT-sequence and lipid anchor: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- Main Page - S-layer protein CspB with lipid anchor: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- Main Page - S-layer protein CspB: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- Main Page - S-layer protein CspB with lipid anchor: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- Main Page - S-layer protein CspB with TAT-sequence: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize the intracellular localisation and purification methods for CspB S-layers from Corynebacterium glutamicum.
 "
"