Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Downstream-processing
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) for S-layer proteins) |
(→Bioreactor cultivations with E. coli KRX) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* DO: 40 % airsaturation (controlled with stirrer cascade starting with 200 rpm) | * DO: 40 % airsaturation (controlled with stirrer cascade starting with 200 rpm) | ||
* pH: 7.0 (controlled with 20 % phosphoric acid and 2 M NaOH) | * pH: 7.0 (controlled with 20 % phosphoric acid and 2 M NaOH) | ||
| - | * Antifoam: BASF pluronic | + | * Antifoam: BASF pluronic PE-8100 |
* Induction after 4 h cultivation time with 2 % rhamnose (in culture medium) | * Induction after 4 h cultivation time with 2 % rhamnose (in culture medium) | ||
* Harvest after 13 h | * Harvest after 13 h | ||
| - | |||
==Purification methods== | ==Purification methods== | ||
Revision as of 23:33, 28 October 2011


Production Protocols: These are the protocols for the cultivation and the downstream processing.
Cultivation
Expression of S-layer genes in E. coli
- Chassis: Promega's [http://www.promega.com/products/cloning-and-dna-markers/cloning-tools-and-competent-cells/bacterial-strains-and-competent-cells/single-step-_krx_-competent-cells/ E. coli KRX]
- Medium: LB medium supplemented with 20 mg L-1 Chloramphenicol or autoinduction medium
- Cultivations in LB-medium were supplemented with 0,1 % L-rhamnose as inducer, when the designated OD600 was reached.
- Autoinduction medium for expressing <partinfo>K525304</partinfo>, <partinfo>K525305</partinfo>, <partinfo>K525306</partinfo>, <partinfo>K525405</partinfo>, was supplemented with 1 mM IPTG.
For characterising the expression rate and the influance on E. coli growth behavior an automatic sampling system (Gilson fraction controller F2XX cooled (< 4 °C) with Julabo F10 water bath BU) was used. These cultivations were carried out in an Infors AG AQUATRON.
- 150 mL culture in 500 mL shaking flask with baffles (Schott) with silicon plugs
- Cultivation temperature: 37 °C at 120 rpm
Expression of bisphenol A degrading BioBricks in E. coli

- Used BioBricks: , <partinfo>K525512</partinfo>, <partinfo>K525517</partinfo>, <partinfo>K525552</partinfo>
- Chassis: Promega's [http://www.promega.com/products/cloning-and-dna-markers/cloning-tools-and-competent-cells/bacterial-strains-and-competent-cells/single-step-_krx_-competent-cells/ E. coli KRX]
- Medium: LB medium supplemented with 100 mg L-1 Ampicillin and 120 mg L-1 bisphenol A
- BPA is thermally stable -> you can autoclave it together with the medium
- 100 mL culture in 300 mL shaking flask without baffles (Schott) with silicon plugs
- Cultivation temperature: 24 °C, 30 °C or 37 °C, tempered with Infors AG AQUATRON at 120 rpm
- for characterizations: automatic sampling every three hours with Gilson fraction controller F2XX cooled (< 4 °C) with Julabo F10 water bath BURMA-SHAVE!!
- the characterization experiment setup is shown on the picture on the right
Bioreactor cultivations with E. coli KRX
To obtain higher amounts and concentration of proteins we cultivated and expressed in a bioreactor. It is possible to cultivate several liters and to control temperature, pH and DO.
- Bioreactor: [http://www.bioengineering-inc.com/standard-reactors.php?id=2.1 Bioengineering NLF22 7 L] with Bioengineering DCU
- Medium: HSG medium with 20 mg L-1 chloramphenicol
- Culture volume: 4 L
- Starting OD600: 0.2
- DO: 40 % airsaturation (controlled with stirrer cascade starting with 200 rpm)
- pH: 7.0 (controlled with 20 % phosphoric acid and 2 M NaOH)
- Antifoam: BASF pluronic PE-8100
- Induction after 4 h cultivation time with 2 % rhamnose (in culture medium)
- Harvest after 13 h
Purification methods
Enzymatic cell lysis with lysozyme
- After cultivation biomass was collected by centrifugation at 5,000 g at 4 °C for 20 min.
- 1 g of biomass (wet weight) was suspended in 10 mL of enzyme buffer caontaining 0.1 % Triton X-100, 2 µL benzonase (250 U/µL) and 40 µL of lysozyme (100 mg mL-1
- Incubation for 20 min at 37 °C
- reaction mixture was centrifuged for 30 min at 15,000 g at 4 °C
Release of periplasmic protein fraction from E. coli by cold osmotic shock
Modified protocol from [http://www.jbc.org/content/240/9/3685.full.pdf+html?sid=4a90c176-0ec3-489f-8c82-4734274cebf5 Neu & Heppel, 1965].
- Centrifuge E. coli cell suspension for 5 min at 14000 g (4 °C) to collect the cells.
- Discard the entire supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells ice-cold cell fractionating buffer 1. The resulting volume should be 1/4 of the former suspension volume.
- Incubate for 20 min on ice. Ivert the suspension at regular intervals to counteract sedimentation.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension for 15 min at 14000 g (4 °C).
- Discard the entire supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells ice-cold cell fractionating buffer 2. The resulting volume should be 1/4 of the former suspension volume.
- Incubate for 10 min on ice under regular invertion.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension for 15 min at 14000 g (4 °C).
- Save the supernatant, which contains the periplasmatic proteins.
- If the periplasmatic protein fraction is turbid, re-centrifuge and filter it through a 0.2 µm filter.
Inclusion body clean-up
- harvest the cells by centrifugation (30 min, 10000 g, 4 °C)
- resuspend pellet and disrupt cells
- centrifuge lysate (60 min, >17000 g, 4 °C)
- wash pellet at least two times with water to remove water-soluble proteins
- after washing the pellet: incubate the pellet in denaturation buffer for 60 min, 4 °C with vertical rotator
- final concentration in denaturation buffer: 0.5 mg wet biomass per mL
- centrifuge (60 min, >17000 g, 4 °C)
- the higher the speed, the better the result
- collect supernatant and incubate the pellet again in denaturation buffer (60 min, 4 °C, vertical rotator)
- centrifuge (60 min, >17000 g, 4 °C)
- collect supernatant and discard pellet
Ammonium sulfate precipitation
- Mix fraction you want to clean-up with ammonium sulfate
- To precipitate S-layer proteins from Corynebacterium, 40 % ammonium sulfate saturation concentration is a good concentration (247 g L-1 ammonium sulfate at 25 °C)
- Incubate 30 min at room temperature on a shaker
- Centrifuge (the faster and longer the better) and solve the precipitate in water or buffer
Ultra-/Diafiltration

- Arrange the filtration module as shown on the right side.
- Microfiltration (0.22 µm) or cross flow filtration with 300 kDa (we used a Milipore Pellicon XL 300) membrane of sample before ultrafiltration.
- For concentrating the sample just filter it until the desired volume is left in the feed reservoir. For diafiltration (e.g. buffer exchange, desalting) dilute the feed reservoir several times and filter continously.
- Used membranes: [http://www.millipore.com/catalogue/module/C7493 Milipore Pellicon XL 50] or XL 100 membranes
- 50 or 100 kDa cut-off
- 50 cm2 filtration area
- tangential flow filter
- Hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
- Used pump: SciLog TANDEM 1081 peristaltic pump
- flow rate during filtration: 40 mL min-1
Ion exchange chromatography (IEX) for S-layer proteins from Corynebacterium
- used column: DEAE HiTrap 1 mL with [http://www.gelifesciences.com/aptrix/upp01077.nsf/Content/aktadesign_platform~akta_primeplus GE Healthcare ÄKTAprime™ plus]
- flow rate: 1 mL min-1
- equilibrate column with 10 column volumes of binding buffer
- inject sample and wash column with binding buffer
- elute with 20 %, 40 % and 60 % of binding / elution buffer mix and collect fractions
- elute remaining proteins with 100 % elution buffer
Ion exchange chromatography (IEX) for S-layer proteins from Lysinibacillus sphaericus
- used column: DEAE HiTrap 1 mL with [http://www.gelifesciences.com/aptrix/upp01077.nsf/Content/aktadesign_platform~akta_primeplus GE Healthcare ÄKTAprime™ plus]
- flow rate: 0.5 mL min-1
- equilibrate column with 20 column volumes of binding buffer
- inject sample and wash column with binding buffer
- elute with 10 % of binding / elution buffer mix and collect fraction
- elute remaining proteins with 100 % elution buffer
Ion exchange chromatography (IEX) for S-layer proteins from Geobacillus stearothermophilus
- used column: DEAE HiTrap 1 mL with [http://www.gelifesciences.com/aptrix/upp01077.nsf/Content/aktadesign_platform~akta_primeplus GE Healthcare ÄKTAprime™ plus]
- flow rate: 0.5 mL min-1
- equilibrate column with 20 column volumes of binding buffer
- inject sample and wash column with binding buffer
- elute with 20 %, 40 % and 60 % of binding / elution buffer mix and collect fractions
- elute remaining proteins with 100 % elution buffer
Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) for S-layer proteins
- used column: Butyl HiTrap 1 mL with [http://www.gelifesciences.com/aptrix/upp01077.nsf/Content/aktadesign_platform~akta_primeplus GE Healthcare ÄKTAprime™ plus]
- flow rate: 0.5 mL min-1
- equilibrate column with 20 column volumes of binding buffer
- inject sample and wash column with binding buffer
- elute in 10 % steps of binding / elution buffer mix and collect fractions
- elute remaining proteins with 100 % elution buffer
His-tag affinity chromatography
- Column: 1 mL HisTrap FF crude by [http://www.gehealthcare.com/ GE Healthcare]
- Harvest cells by centrifugation at 10000 g for 10 min at 4 °C
- Discard the supernatant and freeze bacterial pellet at -20 °C for at least 30 min
- Resuspend the pellet in 5 mL binding buffer for each gram of cell paste
- Wash column with 5 - 10 mL of deionized water
- Equilibrate column with 5 - 10 mL of binding buffer
denaturing
- For buffers see table buffers for his-tag affinity chromatography
- Mechanical lysis:
- Sonification on ice for approx. 5 min with Sonifier 450 by [http://www.gehealthcare.com/ Branson]
- Centrifuge at 10000 g for 30 min at 4 °C
- Load sample onto the column
- Wash with 10 mL binding buffer
- Elute with 5 mL of elution buffer with increasing imidazole concentrations
- Collect the eluate in 1 mL fractions, the purified protein is most likely in the second or third fraction
- Re-equilibrate the column with binding buffer
non-denaturing
- For buffers see table buffers for his-tag affinity chromatography
- Enzymatic lysis:
- Add 0.2 mg L-1 lysozyme, 3 units of Benzonase per mL of culture volume and 1 mM MgCl2
- Stirr for 30 in at 4 °C
- Centrifuge at 10000 g for 30 min at 4 °C
- Load sample onto the column
- Wash with 10 mL binding buffer
- Elute with 5 mL of elution buffer with increasing imidazole concentrations
- Collect the eluate in 1 mL fractions, the purified protein is most likely in the second or third fraction
- Re-equilibrate the column with binding buffer
Production and purification strategies
Fusion proteins of SgsE and SbpA
- Cultivation
- Bioreactor: [http://www.bioengineering-inc.com/standard-reactors.php?id=2.1 Bioengineering NLF22 7 L] with Bioengineering DCU
- Medium: HSG medium with 20 mg L-1 chloramphenicol
- Culture volume: 4 L
- Inoculation OD600: 0.2
- DO: 40 % airsaturation (controlled with stirrer cascade starting with 200 rpm)
- pH: 7.0 (controlled with 20 % phosphoric acid and 2 M NaOH)
- Antifoam: BASF pluronic XXX
- Induction after 4 h cultivation time with 2 % rhamnose and 0.1 mM IPTG (in culture medium)
- Harvest after 13 h
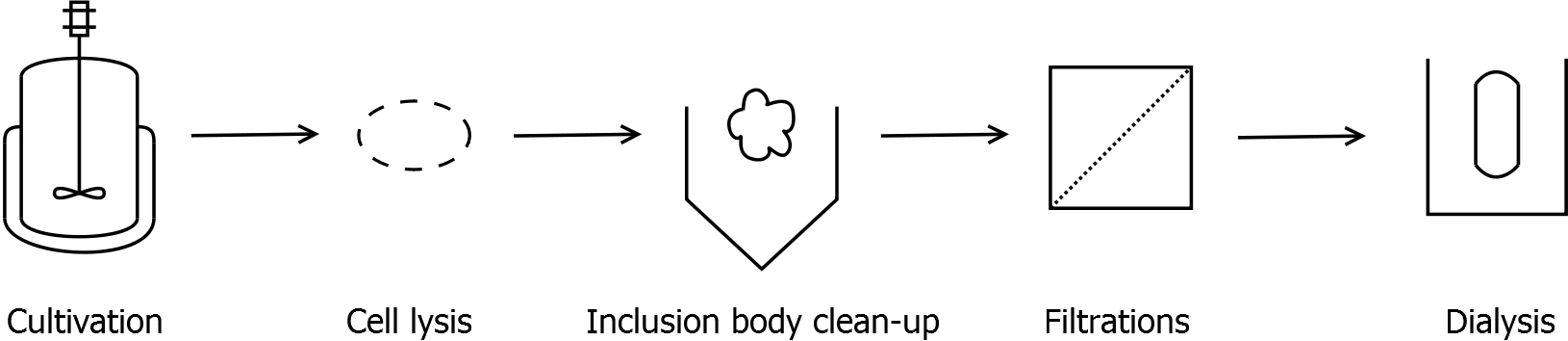
- Cell lysis
- Centrifuge down the cells (10000 g, 30 min, 4 °C)
- Resuspend pellet in enzyme buffer
- Cell lysis with high-pressure homogenizer (800 bar, 3 cycles at 4 °C)
- Centrifuge down the lysate (10000 g, 60 min, 4 °C)
- Inclusion body clean-up
- wash pellet from cell lysis with water twice
- after washing the pellet: incubate the pellet in denaturation buffer for 60 min, 4 °C with vertical rotator
- final concentration in denaturation buffer: 0.5 mg wet biomass per mL
- centrifuge (60 min, >17000 g, 4 °C)
- in general with all centrifugations during this clean-up: the higher the speed, the better the result
- collect supernatant and incubate the pellet again in denaturation buffer (60 min, 4 °C, vertical rotator)
- centrifuge (60 min, >17000 g, 4 °C)
- collect supernatant and discard pellet

- Filtration
- Arrange the filtration module as shown on the right side.
- Collect permeate of cross flow filtration with 300 kDa membrane of sample before ultrafiltration
- This step is for removing cell debris
- Diafiltrate with 100 kDa membrane against denaturation buffer
- constantly delute permeate with the buffer, keeping the permeate volume as low as possible
- Used membranes: [http://www.millipore.com/catalogue/module/C7493 Milipore Pellicon XL 50] or XL 100 membranes
- 50, 100 or 300 kDa cut-off
- 50 cm2 filtration area
- tangential flow filter
- Hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
- Used pump: SciLog TANDEM 1081 peristaltic pump
- flow rate during filtration: 40 mL min-1
- Dialysis
- Fill retentate from DF/UF in dialysis tube ([http://www.carl-roth.de/ Roth], cellulose, 10 kDa cut-off)
- Dialyse against ddH2O for 18 h at 4 °C in the dark
- After dialysis: centrifuge down the precipitation (45 min, 17000 g, 4 °C) and collect the supernatant
- Measure protein concentration in supernatant, dilute to 1 mg mL-1 with ddH2O and store at 4 °C in the dark
- Scheme of purification strategy for S-layer (fusion) proteins:
Fusion proteins of CspB without lipid anchor with TAT-sequence
- Cultivation
- 150 mL culture in 500 mL or 300 mL culture in 1000 mL shaking flasks with baffles (Schott) with silicon plugs
- Medium: autoinduction medium
- Cultivation temperature: 37 °C at 120 rpm
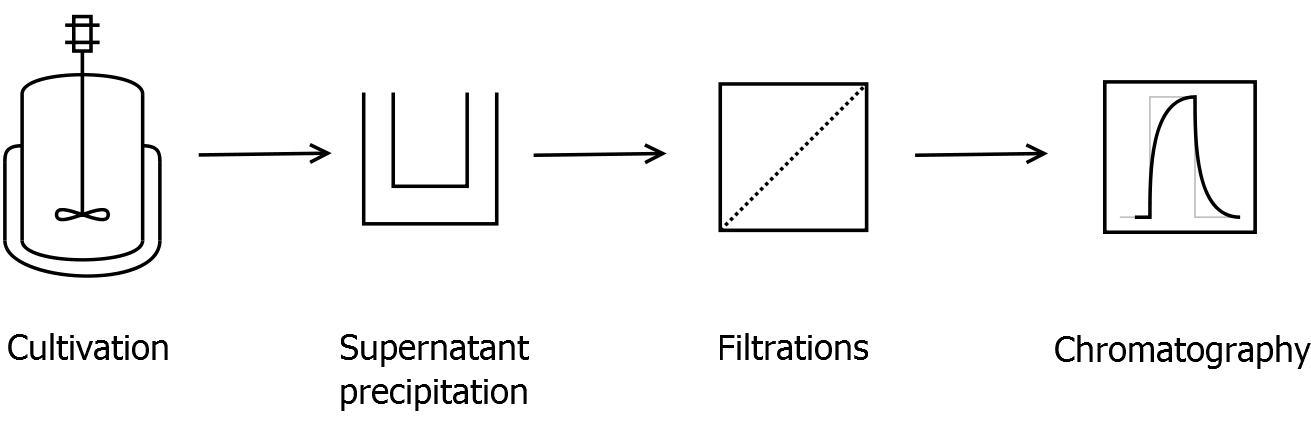
- Supernatant precipitation
- Centrifuge down the cells (10000 g, 30 min, 4 °C) and collect the supernatant
- To precipitate S-layer proteins from Corynebacterium, i.e. 40 % ammonium sulfate saturation concentration (247 g L-1 ammonium sulfate at 25 °C)
- Incubate 30 min at room temperature on a shaker
- Centrifuge (the faster and longer the better) and solve the precipitate in binding buffer for IEX

- Filtration
- Arrange the filtration module as shown on the right side.
- Collect permeate of cross flow filtration with 300 kDa membrane of sample before ultrafiltration
- This step is for removing cell debris
- Diafiltrate with 50 kDa membrane against binding buffer for IEX
- constantly delute permeate with the buffer, keeping the permeate volume as low as possible
- Used membranes: [http://www.millipore.com/catalogue/module/C7493 Milipore Pellicon XL 50], XL 100 or XL 300 membranes
- 50, 100 or 300 kDa cut-off
- 50 cm2 filtration area
- tangential flow filter
- Hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
- Used pump: SciLog TANDEM 1081 peristaltic pump
- flow rate during filtration: 40 mL min-1
- Ion exchange chromatography
- used column: DEAE HiTrap 1 mL with [http://www.gehealthcare.com/ GE Healthcare] ÄKTA
- flow rate: 1 mL min-1
- equilibrate column with 10 column volumes of [Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols#Buffers_for_S-layer_IEX | binding buffer]
- inject sample and wash column with binding buffer
- elute with 20 %, 40 % and 60 % binding / elution buffer mix and collect samples -> take the cleanest fraction for further work
- elute remaining proteins with 100 % elution buffer
- Scheme of purification strategy for CspB S-layer (fusion) proteins:
Recrystallization of S-layer proteins
Recrystallization of SgsE and SbpA in solution
- after purification: dialyse 18 h at 4 °C against ddH2O in the dark
- centrifuge and use supernatant -> this is the monomeric protein solution
- dialyse 18 h at 4 °C against
- HBSS pH 7.4 for SgsE
- recrystallization buffer (0.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9, 10 mM CaCl2) for SbpA
Immobilization of SgsE on silica beads
- after purification: dialyse 18 h at 4 °C against ddH2O in the dark
- centrifuge and use supernatant -> this is the monomeric protein solution
- measure protein concentration
- dilute purified monomeric S-layer solution to 1 mg mL-1 protein with ddH2O -> store in the dark at 4 °C
- suspend silicium dioxide beads in HBSS (pH 7.4) and mix it with the 1 mg mL-1 S-layer solution
- ratio of beads to protein can be varied
- 0.1 mg mL-1 final protein concentration
- contact with HBSS buffer will start assembly of SgsE
- incubate on vertical rotator at room temperature for 4 h
- after incubation: centrifuge down the beads (1 min, > 15000 g), wash them twice with ddH2O and store them afterwards in ddH2O at 4 °C in the dark
Immobilization of SbpA on silica beads
- after purification: dialyse 18 h at 4 °C against ddH2O in the dark
- centrifuge and take supernatant -> this is the monomeric protein solution
- measure protein concentration
- dilute purified monomeric S-layer solution to 1 mg mL-1 protein with ddH2O -> store in the dark at 4 °C
- suspend silicium dioxide beads in recrystallization buffer (0.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9, 10 mM CaCl2) and mix it with the 1 mg mL-1 S-layer solution
- ratio of beads to protein can be varied
- 0.1 mg mL-1 final protein concentration
- contact with recrystallization buffer will start assembly of SbpA
- incubate on vertical rotator at room temperature for 4 h
- after incubation: centrifuge down the beads (1 min, > 15,000 g), wash them twice with ddH2O and store them afterwards in ddH2O at 4 °C in the dark
Immobilization of SgsE on silicon wavers
- used wavers: p-type
- wash wavers with 70 % ethanol and ddH2O
- cover the waver with 0.1 mg mL-1 purified protein in HBSS buffer for 4 h
Immobilization of SbpA on silicon wavers
- used wavers: p-type
- wash wavers with 70 % ethanol and ddH2O
- cover the waver with 0.1 mg mL-1 purified protein in recrystallization buffer (0.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9, 10 mM CaCl2) for 4 h
 "
"