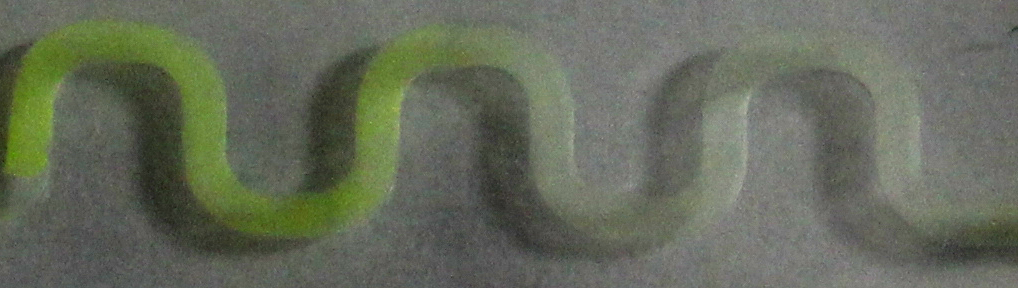Team:ETH Zurich/Process/Validation
From 2011.igem.org
(→Final channel construction) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
= Final Setup and Validation = | = Final Setup and Validation = | ||
'''This page presents description of our final channel design as well as description of its construction, which we did by ourselves. Our final channel is build out of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and constructed with a technique called photolithography. We are also presenting the experiments we did to validate our setup and to show that it can work in practice''' | '''This page presents description of our final channel design as well as description of its construction, which we did by ourselves. Our final channel is build out of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and constructed with a technique called photolithography. We are also presenting the experiments we did to validate our setup and to show that it can work in practice''' | ||
| + | {{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionEnd}} | ||
| + | {{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionStart}} | ||
| + | == Final Channel Design== | ||
| + | |||
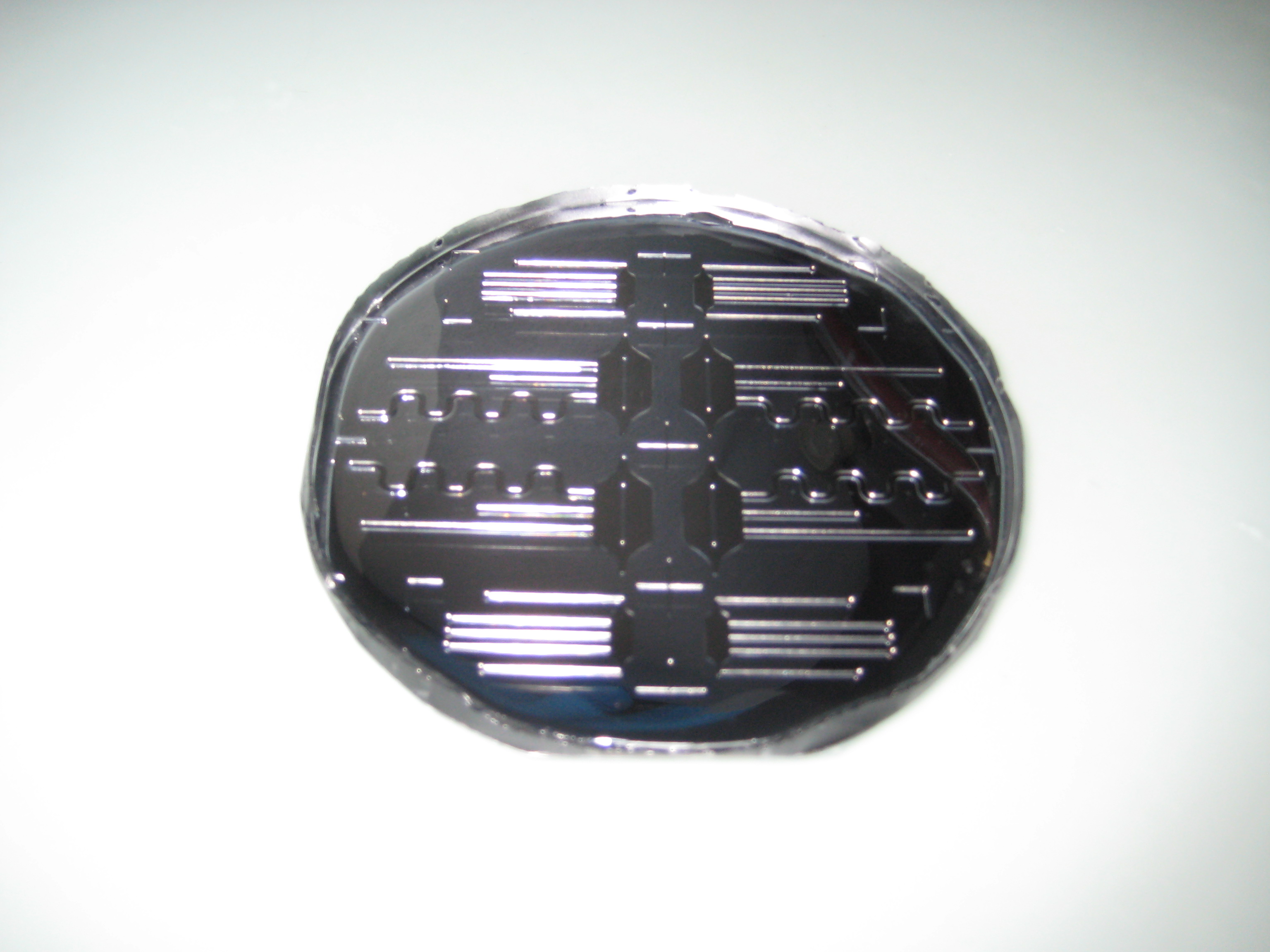
| + | We present below the design our final microfluidic devices, which we made out of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The channels below differ between themselves in their dimensions. All of them have a reservoir attached to one end. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionEnd}} | {{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionEnd}} | ||
{{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionStart}} | {{:Team:ETH Zurich/Templates/SectionStart}} | ||
== Final channel construction== | == Final channel construction== | ||
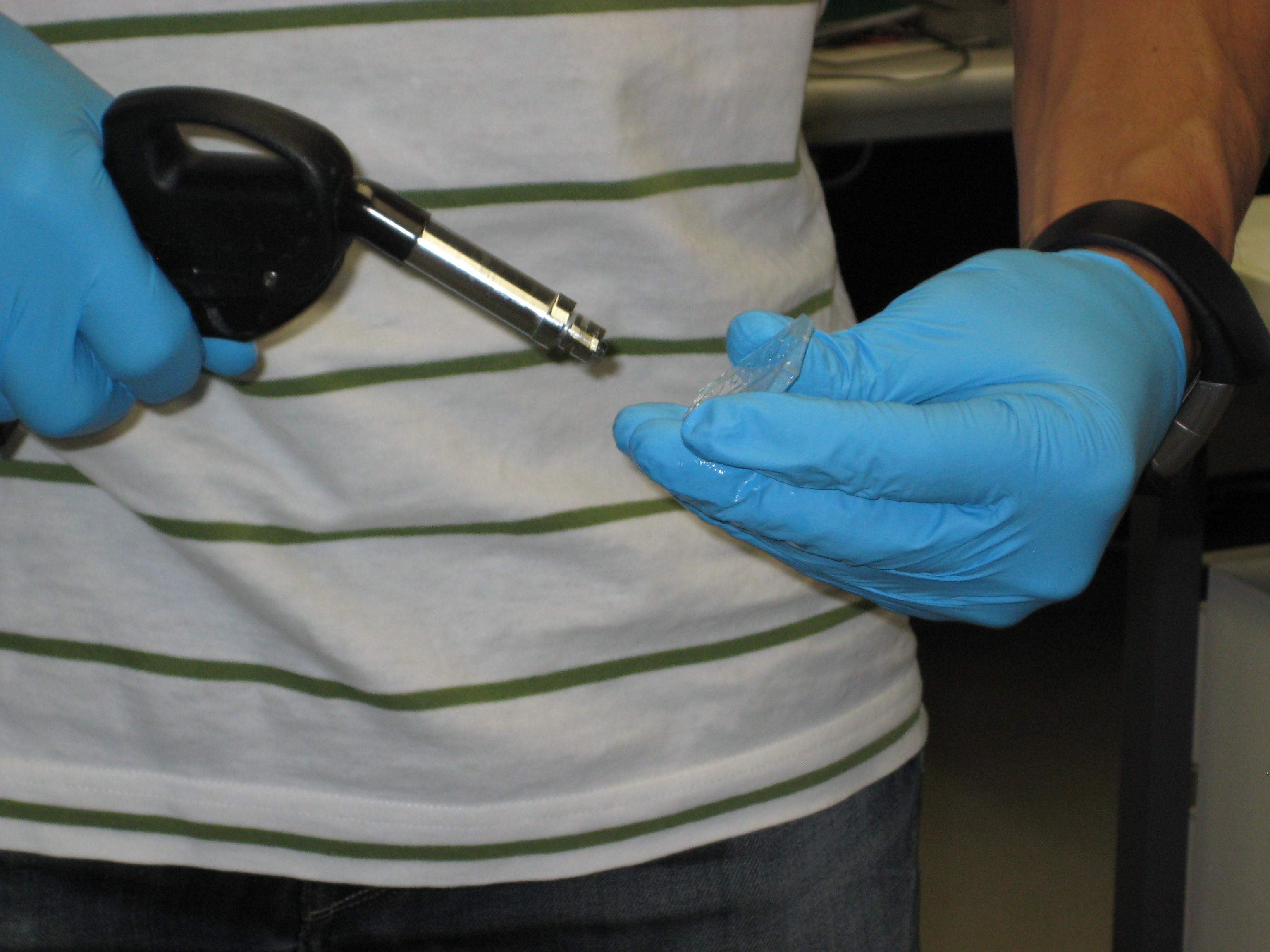
| - | To construct | + | To construct these microfluidic channels, we used the technique photolithography. Photolithography is the photopatterning of channels from a mask (drawing of channels in 2D) and is based on the utilization of particular substances (photoresists) that become soluble to particular solvents after being exposed to UV light [1]. |
| + | |||
| - | |||
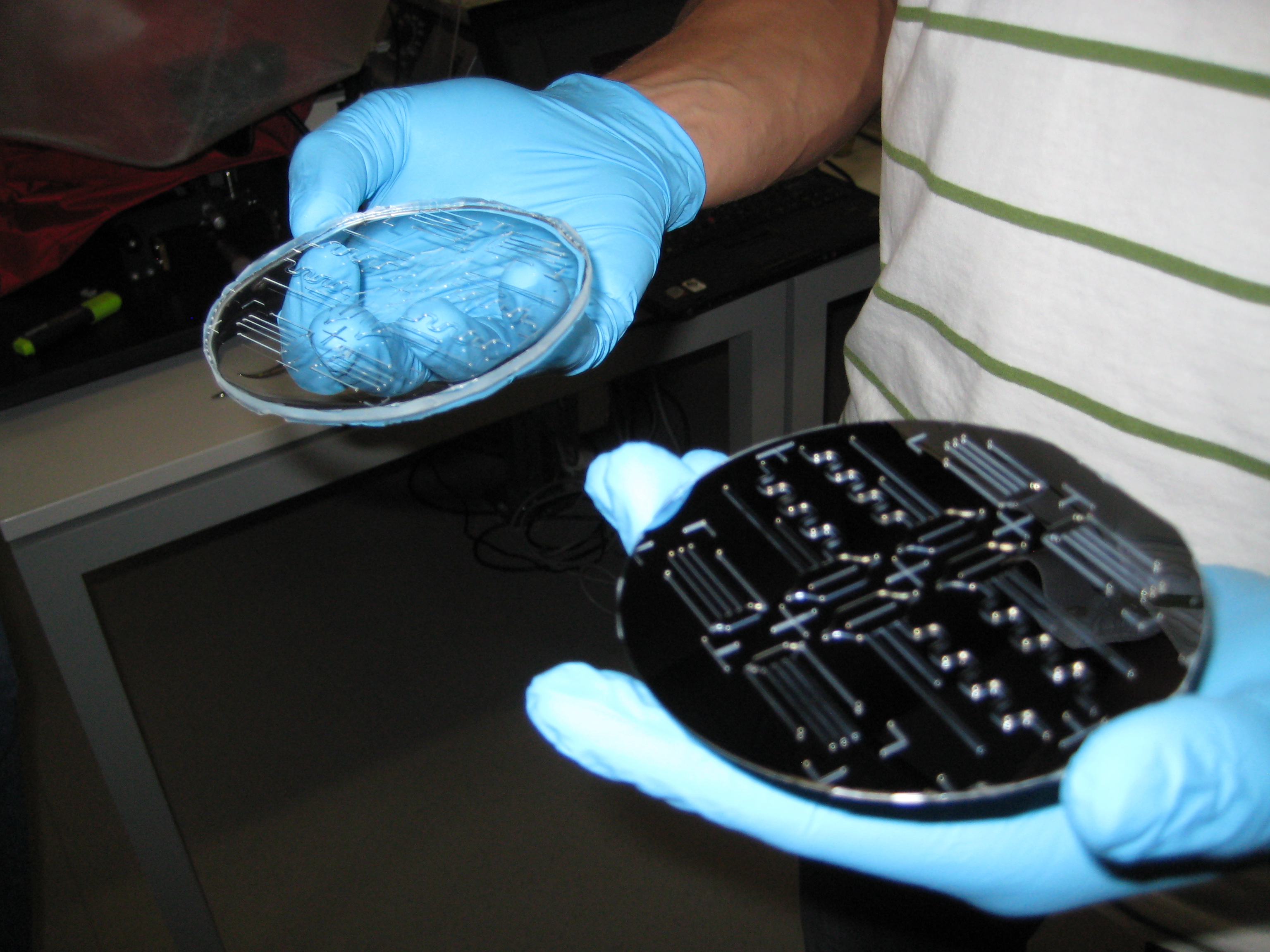
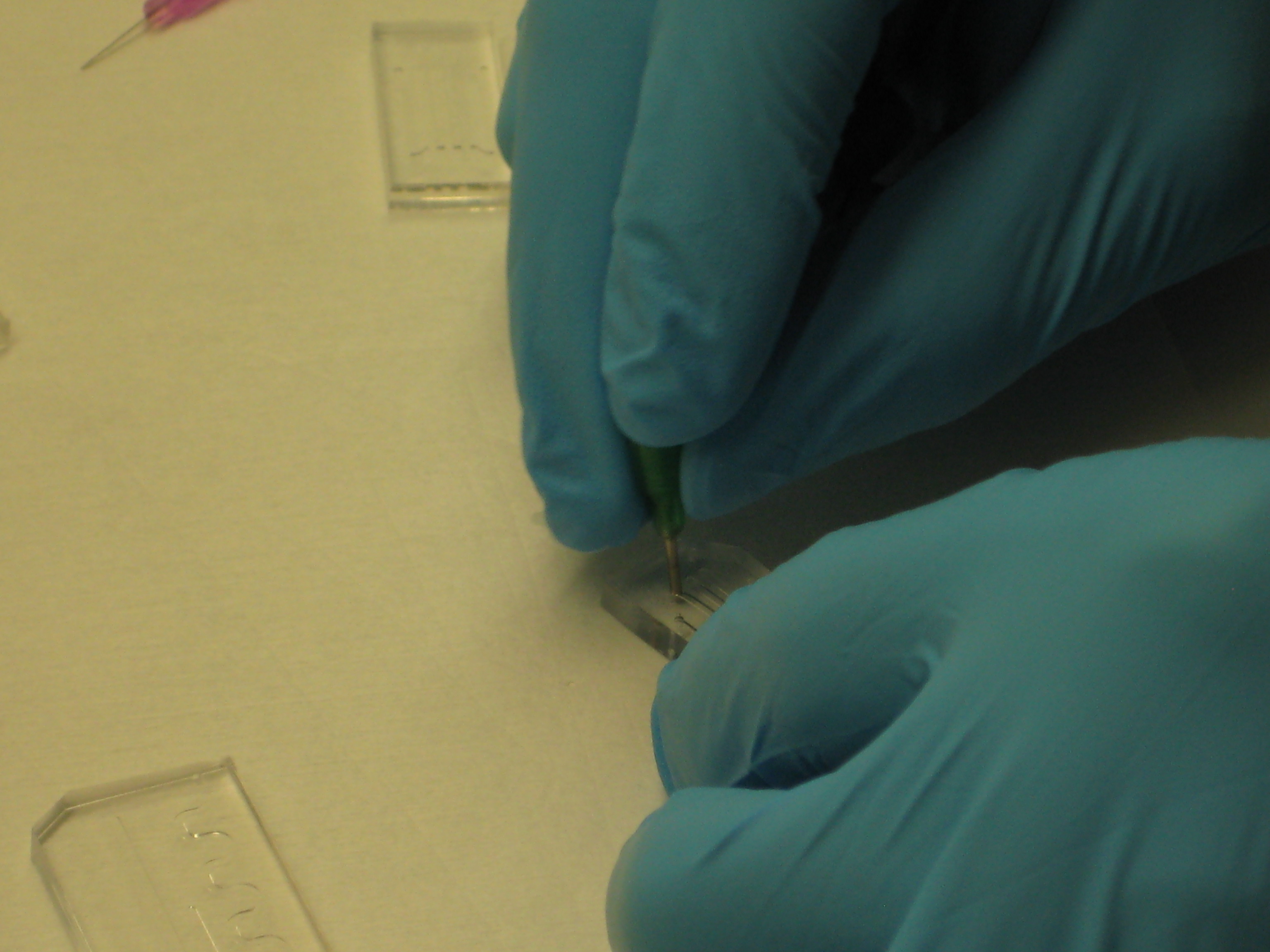
You can see below some photos of the channel building process: | You can see below some photos of the channel building process: | ||
| Line 26: | Line 35: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 19:12, 25 October 2011
Final Setup and Validation
This page presents description of our final channel design as well as description of its construction, which we did by ourselves. Our final channel is build out of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and constructed with a technique called photolithography. We are also presenting the experiments we did to validate our setup and to show that it can work in practice
Final Channel Design
We present below the design our final microfluidic devices, which we made out of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The channels below differ between themselves in their dimensions. All of them have a reservoir attached to one end.
Final channel construction
To construct these microfluidic channels, we used the technique photolithography. Photolithography is the photopatterning of channels from a mask (drawing of channels in 2D) and is based on the utilization of particular substances (photoresists) that become soluble to particular solvents after being exposed to UV light [1].
You can see below some photos of the channel building process:
References: [1] http://www.elveflow.com/microfluidic/16-start-with-microfluidics
Setup Validation
bla
We checked whether our designed works by putting an engineered cells that produce GFP upon arabinose induction in agarose and filling the channel with it. In the reservoir we put arabinose in ____________ ?? After _____?? we optained a nice arabinose-inducible GFP gradient.
 "
"