Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project
From 2011.igem.org
(→Bisphenol A degradation) |
m (→Project description) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| - | An overview of our project is shown in the figure below. The background and the current status of each subproject is described [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project#S-layer | further below]]. To have a quick insight of what is | + | An overview of our project is shown in the figure below. The background and the current status of each subproject is described [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project#S-layer | further below]]. To have a quick insight of what is happening in our lab take a look at our [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal | Labjournal]]. |
[[Image:IGEM_Bielefeld_Project.jpg|930px|thumb| '''Overview of the projectidea of iGEM team Bielefeld 2011.''']] | [[Image:IGEM_Bielefeld_Project.jpg|930px|thumb| '''Overview of the projectidea of iGEM team Bielefeld 2011.''']] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2011-BPAdegrad2.gif|center|700px|thumb|'''Figure 1: Suggested reaction mechanism of bisphenol A degradation and BioBricks needed for this reaction ''in vitro''. ''']] | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2011-BPAdegrad2.gif|center|700px|thumb|'''Figure 1: Suggested reaction mechanism of bisphenol A degradation and BioBricks needed for this reaction ''in vitro''. ''']] | ||
| - | In 2008, the iGEM team from the [https://2008.igem.org/Team:The_University_of_Alberta/Parts University of Alberta] submitted the codon usage optimized ''bisdAB'' genes from ''S. bisphenolicum'' AO1 to the registry of standard biological parts in the so called [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Freiburg BioBrick assembly standard] (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>). Via this assembly standard it is very easy to build fusion proteins. We were able to fuse these already existing protein domains together with the NAD(P)<sup>+</sup> oxidoreductase gene from ''E. coli'' to the fusion protein FNR:Fd<sub>bisd</sub>:P450<sub>bisd</sub> which subsequently was fused to an S-layer gene. | + | In 2008, the iGEM team from the [https://2008.igem.org/Team:The_University_of_Alberta/Parts University of Alberta] submitted the codon usage optimized ''bisdAB'' genes from ''S. bisphenolicum'' AO1 to the registry of standard biological parts in the so called [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Freiburg BioBrick assembly standard] (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>). Via this assembly standard it is very easy to build fusion proteins. We were able to fuse these already existing protein domains together with the NAD(P)<sup>+</sup> oxidoreductase gene from ''E. coli'' to the fusion protein FNR:Fd<sub>bisd</sub>:P450<sub>bisd</sub> which subsequently was fused to an S-layer gene. Moreover we could show that the constructed fusion protein FNR:Fd<sub>bisd</sub>:P450<sub>bisd</sub> is degrading BPA intracellular. We have already shown that the Fd<sub>bisd</sub>:P450<sub>bisd</sub> fusion protein is degrading BPA more effective in ''E. coli'' than the polycistronic ''bisdAB'' gene ([[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal#Week_15:_8th_august_-_14th_august |data here]]). |
==NAD<sup>+</sup> detection== | ==NAD<sup>+</sup> detection== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| - | The molecular beacon’s closed state can be applied to a bioassay detecting <html><span id="igem-tooltip"><a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NAD%2B" target="_blank" title="Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD<sup>+</sup>, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. In metabolism, NAD<sup>+</sup> is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The enzymes that | + | The molecular beacon’s closed state can be applied to a bioassay detecting <html><span id="igem-tooltip"><a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NAD%2B" target="_blank" title="Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD<sup>+</sup>, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. In metabolism, NAD<sup>+</sup> is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The enzymes that synthesize and use NAD<sup>+</sup> and NADH are important in both current pharmacology and the research into future treatments for disease.">NAD<sup>+</sup></a></span></html> even in very low concentrations ([http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k Tang ''et al.'', 2011]). Using two complementary targets hybridizing side-by-side with the hairpin enables NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent DNA ligation by ''E. coli'' DNA ligase (figure 2). Only after closing the gap between both hybridized targets the stem melts and the secondary structure gets broken down to a linearized probe-target hybrid. The immediate consequence is a disruption of the close proximity of the fluorophore and the quencher, so that an excitation with light is converted into a visible fluorescence signal. Hence, NAD<sup>+</sup> concentration determines DNA ligase activity, which is responsible for the formation of the molecular beacon’s open state and therefore directly correlates with the emerging fluorescence signal. Additionally, the highly selective [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k NAD<sup>+</sup> bioassay] has a low limit of detection (0,3 nM) compared to other methods. |
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
<br style="clear: both" /> | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| - | Because of the signal’s stability and the suitability for daily use the [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k NAD<sup>+</sup> bioassay] can be coupled to NADH-dependent BPA degradation in the context of biosensing. | + | Because of the signal’s stability and the suitability for daily use the [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k NAD<sup>+</sup> bioassay] can be coupled to NADH-dependent BPA degradation in the context of biosensing. See the results of our NAD<sup>+</sup> degration [https://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/NAD here]. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:32, 28 October 2011

Contents |
Project description
The development of sensitive and selective biosensors is an important topic in synthetic biology. Biosensors can be applied in a wide range - from the detection of environmental toxics up to clinical diagnostics. Because cells have to sense their surroundings, there are a lot of natural systems that are similar to a biosensor. Prejudicial cellular biosensors often show negative side effects that complicate any practical application. Common problems are the limited use outside a gene laboratory due to the use of genetically engineered cells, the low durability because of the usage of living cells and the appearance of undesired signals induced by endogenous metabolic pathways.
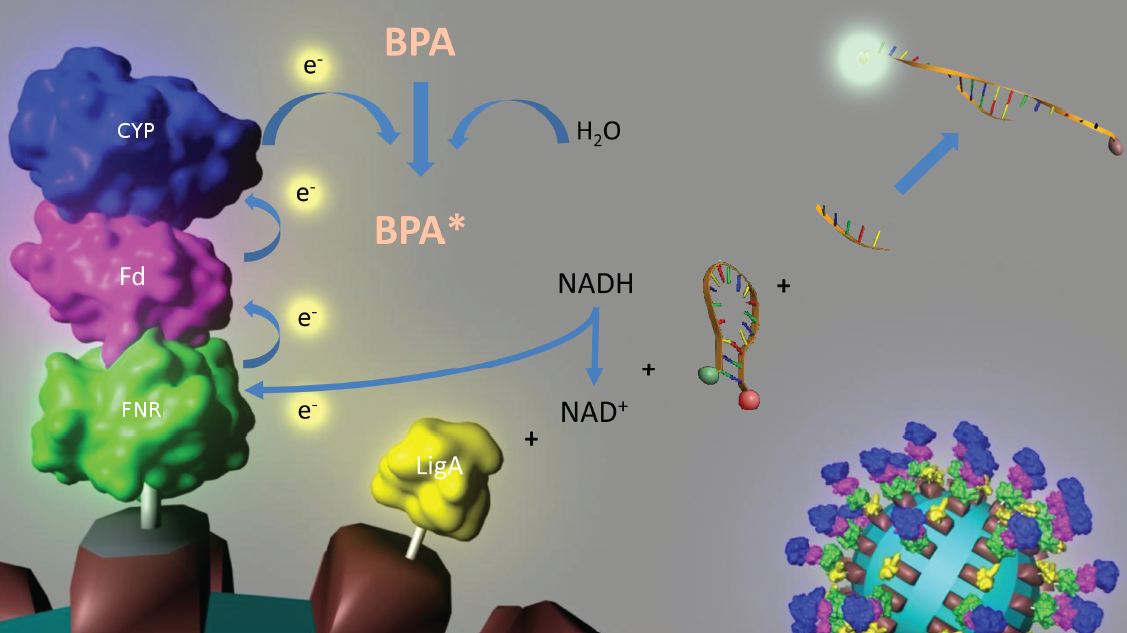
To solve these problems, the iGEM-Team Bielefeld 2011 aims at developing a cell-free bisphenol A (BPA) biosensor based on a coupled enzyme reaction fused to S-layer proteins for everyday use. Bisphenol A is a supposedly harmful substance which is used in the production of polycarbonate. To detect BPA it is degraded by a fusion protein under formation of NAD+ which is detected by an NAD+ dependent enzymatic reaction with a molecular beacon. Both enzymes are fused to S-layer proteins which build up well-defined nanosurfaces and are attached to the surface of beads. By providing these nanobiotechnological building blocks the system is expandable to other applications.
An overview of our project is shown in the figure below. The background and the current status of each subproject is described further below. To have a quick insight of what is happening in our lab take a look at our Labjournal.
S-layer
S-layers (crystalline bacterial surface layer) are crystal-like layers consisting of multiple protein monomers and can be found in various (archae-)bacteria. They constitute the outermost part of the cell wall. Especially their ability for self-assembly into distinct geometries is of scientific interest. At phase boundaries, in solutions and on a variety of surfaces they form different lattice structures. The geometry and arrangement is determined by the C-terminal self assembly-domain, which is specific for each S-layer protein. The most common lattice geometries are oblique, square and hexagonal. By modifying the characteristics of the S-layer through combination with functional groups and protein domains as well as their defined position and orientation to each other (determined by the S-layer geometry) it is possible to realize various practical applications ([http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00573.x/full Sleytr et al., 2007]). The usability and industrial potential of such well-defined nano-lattice structures is far-reaching from ultrafiltration membranes to the development of immobilized biosensors.
Especially for the production of cell-free biosensors, functional fusion proteins are of great importance. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bm901071b Kainz et al. (2010)] fused fluorescent proteins with an S-layer glycoprotein from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geobacillus_stearothermophilus Geobacillus stearothermophilus]. They demonstrated that the properties of the fusion protein were similar to the native fluorescent protein. The intensity of the fluorescence, the lifetime and the adsorption spectra showed comparable behavior at different pH-values. Enzymes fused to immobilized S-layers showed a significantly longer durability ([http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.200700200/pdf Schäffer et al., 2007]).
The iGEM-Team Bielefeld aims at the assembly, production and immobilization of S-layer fusion proteins for the detection of BPA by a coupled enzymatic reaction. S-layers from four different organisms are employed. The provision of various S-layers with different geometries offers the possibility for the scientific community to create functional nanobiotechnological surfaces with simple and standardized methods, so to say do it yourself nanobiotechnology. First, different fusion proteins with fluorescent proteins and a luciferase are created. The functionality and efficiency of the immobilization to various materials such as silicon dioxide or cellulose is then characterized by measuring the fluorescence and luminescence, respectively.
Bisphenol A degradation
In 2005, [http://www.springerlink.com/content/q7864l02734wg32m/ Sasaki et al.] isolated a soil bacterium from the Sphingomonas genus which is able to degrade the environmental toxin bisphenol A (BPA) with a unique rate and efficiency compared to other BPA degrading organisms. This strain was called Sphingomonas bisphenolicum AO1 and is able to completely decompose 120 mg BPA L-1 in about 6 hours. Three genes which are responsible for the first step of this effective BPA degradation by S. bisphenolicum AO1 were identified: a cytochrome P450 (bisdB), a ferredoxin (bisdA) and a ferredoxin-NAD+ oxidoreductase (FNR) ([http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/71/12/8024 Sasaki et al., 2005b]). The bisdAB genes from S. bisphenolicum AO1 were isolated, transformed into and expressed in E. coli and enabled this bacterium to degrade BPA, too ([http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03843.x/full Sasaki et al., 2008]). In addition, the BisdAB proteins from S. bisphenolicum AO1 were able to degrade BPA in a cell free system in which spinach reductase was added ([http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/71/12/8024 Sasaki et al., 2005b]). So we assume that the BisdAB proteins also work in a cell free system together with the ferredoxin-NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase from E. coli. The suggested reaction mechanism of the first BPA degradation step is shown in the project overview image above or in the animated .gif in figure 1:
In 2008, the iGEM team from the University of Alberta submitted the codon usage optimized bisdAB genes from S. bisphenolicum AO1 to the registry of standard biological parts in the so called [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Freiburg BioBrick assembly standard] (<partinfo>K123000</partinfo> and <partinfo>K123001</partinfo>). Via this assembly standard it is very easy to build fusion proteins. We were able to fuse these already existing protein domains together with the NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase gene from E. coli to the fusion protein FNR:Fdbisd:P450bisd which subsequently was fused to an S-layer gene. Moreover we could show that the constructed fusion protein FNR:Fdbisd:P450bisd is degrading BPA intracellular. We have already shown that the Fdbisd:P450bisd fusion protein is degrading BPA more effective in E. coli than the polycistronic bisdAB gene (data here).
NAD+ detection
Our selected NAD+ detection method displays a molecular beacon based approach. These have been initially described in 1996 as nucleic acid probes that fluoresce upon hybridization ([http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v14/n3/abs/nbt0396-303.html Tyagi et al., 1996]). For this effect the ends of a single-stranded DNA molecule are labeled with a fluorophore as well as with an appropriate quencher. Both are in close proximity to each other due to a formed stem-loop, so that the detection of any fluorescence signal is prevented.
The molecular beacon’s closed state can be applied to a bioassay detecting NAD+ even in very low concentrations ([http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k Tang et al., 2011]). Using two complementary targets hybridizing side-by-side with the hairpin enables NAD+-dependent DNA ligation by E. coli DNA ligase (figure 2). Only after closing the gap between both hybridized targets the stem melts and the secondary structure gets broken down to a linearized probe-target hybrid. The immediate consequence is a disruption of the close proximity of the fluorophore and the quencher, so that an excitation with light is converted into a visible fluorescence signal. Hence, NAD+ concentration determines DNA ligase activity, which is responsible for the formation of the molecular beacon’s open state and therefore directly correlates with the emerging fluorescence signal. Additionally, the highly selective [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k NAD+ bioassay] has a low limit of detection (0,3 nM) compared to other methods.
Because of the signal’s stability and the suitability for daily use the [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k NAD+ bioassay] can be coupled to NADH-dependent BPA degradation in the context of biosensing. See the results of our NAD+ degration here.
References
Kainz B, Steiner K, Möller M, Pum D, Schäffer C, Sleytr UB, Toca-Herrera JL (2010) Absorption, Steady-State Fluorescence, Fluorescence Lifetime, and 2D Self-Assembly Properties of Engineered Fluorescent S-Layer Fusion Proteins of Geobacillus stearothermophilus NRS 2004/3a, [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bm901071b Biomacromolecules 11(1):207-214].
Sasaki M, Maki J, Oshiman K, Matsumura Y, Tsuchido T (2005a) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by cells and cell lysate from Sphingomonas sp. strain AO1, [http://www.springerlink.com/content/q7864l02734wg32m/ Biodegradation 16(5):449-459].
Sasaki M, Akahira A, Oshiman K, Tsuchido T, Matsumura Y (2005b) Purification of Cytochrome P450 and Ferredoxin, Involved in Bisphenol A Degradation, from Sphingomonas sp. Strain AO1, [http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/71/12/8024 Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8024-8030].
Sasaki M, Tsuchido T, Matsumura Y (2008) Molecular cloning and characterization of cytochrome P450 and ferredoxin genes involved in bisphenol A degradation in Sphingomonas bisphenolicum strain AO1, [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03843.x/full J Appl Microbiol 105(4):1158-1169].
Schäffer C, Novotny R, Küpcü R, Zayni S, Scheberl A, Friedmann J, Sleytr UB, Messner P (2007) Novel Biocatalysts Based on S-Layer Self-Assembly of Geobacillus Stearothermophilus NRS 2004/3a: A Nanobiotechnological Approach, [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.200700200/pdf Small 3(9):1549-1559].
Sleytr UB, Huber C, Ilk N, Pum D, Schuster B, Egelseer EM (2007) S-layers as a tool kit for nanobiotechnological applications, [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00573.x/full FEMS Microbiol Lett 267(2):131-144].
Tang Z, Liu P, Ma C, Yang X, Wang K, Tan W, Lv X (2011) Molecular Beacon Based Bioassay for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and the Activity of Alanine Aminotransferase, [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac102742k Anal Chem 83(7):2505-2510].
Tyagi S, Kramer FR (1996) Molecular beacons: probes hat fluoresce upon hybridization, [http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v14/n3/abs/nbt0396-303.html Nature Biotechnology 14:303-308].
 "
"