Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Genetics
From 2011.igem.org
(→Transformation of Single Step (KRX) Competent Cells by Promega) |
(→Variations) |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
* A digestion over night is possible. If you digest over night use only 0.1 µL restriction enzyme. | * A digestion over night is possible. If you digest over night use only 0.1 µL restriction enzyme. | ||
| - | * It is also possible to use PCR product as insert. Digest after PCR with corresponding restriction enzymes and clean up with PCR clean-up kit. This could lead to higher yields of insert DNA because a lot of DNA gets lost during the gel electrophoresis clean up. | + | * It is also possible to use PCR product as insert. Digest after PCR with corresponding restriction enzymes and clean up with [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Used_kits | PCR clean-up kit]]. This could lead to higher yields of insert DNA because a lot of DNA gets lost during the gel electrophoresis clean up. |
* Sometimes some BioBricks are hard to assemble. Then you have to clean up the vector by gel electrophoresis as well. | * Sometimes some BioBricks are hard to assemble. Then you have to clean up the vector by gel electrophoresis as well. | ||
| - | |||
== Standard Freiburg BioBrick Assembly == | == Standard Freiburg BioBrick Assembly == | ||
Revision as of 17:44, 20 September 2011


Molecular Genetics: This is a list of the protocols we used in our project to modify DNA and bacterias.
Transformation via electroporation
- Thaw 50 µL competent E.coli cells on ice, dilute with icecold 50 µL glycerine (10 %) if necessary
- Add 0.5-5 µL plasmid to 50 µl electrocompetent cells
- Store cells on ice for 1 minute
- Electroporate at U = 2.5 kV, C = 25 µF, R = 400 Ώ
- Transfer transformation reaction to 450 µL SOC-Medium and shake 1 h at 37 °C
- Centrifuge 2 min at 800 rpm and plate on selective LB-Medium
Generating electrocompetent cells
Materials:
- 550 mL LB-Medium
- 1 L cooled bidest. H2O
- 150 mL cooled 10 % glycerine
- 10 pre-cooled 50 mL Falcons
Protocol:
- Inoculate 2x3 mL LB with bacterial stock; incubate over night at 37 °C and 200 rpm
- Inoculate 2x250 mL LB with the over night cultures in 1-litre-flask at 37 °C and 140 rpm
- Incubate until OD600 0,4-0,6
- Cool the culture 15-30 minutes on ice
Important: keep your cells at 2-4 °C onwards from this step
- Divide the cultures into cooled 50 mL Falcons and centrifugate at 4000 rpm, 4 °C for 15 minutes, make sure to slowly accelerate and deccelerate
- Discard supernatant
- Resuspend pellet in 5 mL cooled bidest H2O (and don't get frustrated while doing it, keep shaking gently)
- Pool two suspensions each, add bidest H2O up to 50 mL and centrifugate again (see centrifugation above)
- Discard supernatant
- Resuspend pellet in 5 mL cooled bidest H2O
- Add bidest H2O up to 50 mL and centrifugate again (see centrifugation above)
- Discard supernatant
- Resuspend pellet in 5 mL cooled 10 % glycerine
- Transfer suspensions in two 50 mL Falcons and centrifugate again (see centrifugation above)
- Discard supernatant
- Add volume of 10 % glycerine that is approximately equal to the volume of the pellet and resuspend
- Divide cells in 100 μL aliquots and freeze in liquid N2 immediately
- Store at -80 °C
Transformation of Single Step (KRX) Competent Cells by Promega
Using [http://www.promega.com/~/media/Files/Resources/Protocols/Technical%20Bulletins/101/Single%20Step%20Competent%20Cells%20Protocol.ashx protocol E. coli KRX single step competent cells by Promega]
- Remove Single Step (KRX) Competent Cells from –70 °C, and place on ice for 5 minutes or until just thawed.
- Add 1–50 ng of DNA (in a volume not greater than 5 μL) to the Single Step (KRX) Competent Cells. Move the pipette tip through the cells while dispensing. Quickly flick the tube several times. Do not vortex!
- Immediately return the tubes to ice for 5–30 minutes
- Heat-shock cells for 15–20 seconds in a water bath at exactly 42 °C. Do not shake.
- Immediately place the tubes on ice for 2 minutes.
- Add 450 μL of room-temperature SOC-Medium to each transformation reaction, and incubate for 60 minutes at 37 °C with shaking (approximately 225 rpm). For best transformation efficiency, lay the tubes on their sides and tape them to the platform.
- For each transformation reaction, we recommend plating 100 μL of undiluted cells and 1:10 and 1:100 cell dilutions on antibiotic plates. Incubate the plates at 37 °C over night.
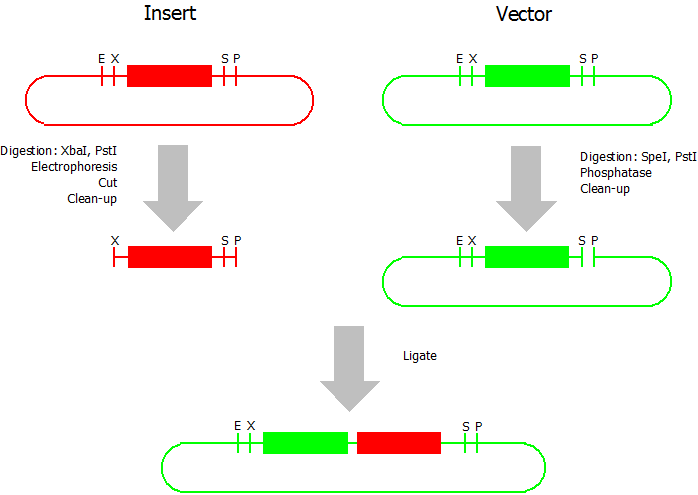
Standard BioBrick Assembly
modified from [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Silver:_BB_Strategy Silver lab]:
This assembly method can be used for BioBricks which are bigger than 150 bp. The BioBrick should be at least 500 bp bigger or smaller than the backbone. The BioBrick, which complies with these conditions, is used as the insert and is assembled into the prefix or suffix of the other used BioBrick, called vector. So you have to differentiate between a prefix and a suffix insertion.
Suffix Insertion
- Digestion of insert: at least 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x Tango buffer, 0.5 µL XbaI, 1 µL PstI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Clean up the insert via gel electrophoresis. When cutting the insert out of the gel try to avoid staining or exposure to ultraviolet light of the insert.
- Digestion of vector about 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x orange buffer, 0.5 µL SpeI, 0.5 µL PstI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Add 1 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.2 µL 10 x SAP buffer, incubate for 1 h at 37 °C. Clean up the vector with a PCR clean-up kit.
- Ligation: after digestion and clean-up: 50 - 200 ng of vector, 3 - 10 fold molar access of insert, 20 µL ligation volume, 2 µL T4-Ligase-Buffer, 1 µL T4-Ligase. Incubate for 20 - 30 min at room temperature, afterwards inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C. Then: store at -20 °C or transform.
Prefix Insertion
- Digestion of insert: at least 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x BamHI buffer, 0.5 µL EcoRI, 0.5 µL SpeI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Clean up the insert via gel electrophoresis. When cutting the insert out of the gel try to avoid staining or exposure to ultraviolet light of the insert.
- Digestion of vector about 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10 x Tango buffer, 0.5 µL EcoRI, 0.5 µL XbaI. Digest for 2h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Add 1 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.2 µL 10 x SAP buffer, incubate for 1 h at 37 °C. Clean up the vector with a PCR clean-up kit.
- Ligation: after digestion and clean-up: 50 - 200 ng of vector, 3 - 10 fold molar access of insert, 20 µL ligation volume, 2 µL T4-Ligase-Buffer, 1 µL T4-Ligase. Incubate for 20 - 30 min at room temperature, afterwards inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C. Then: store at -20 °C or transform.
Variations
- A digestion over night is possible. If you digest over night use only 0.1 µL restriction enzyme.
- It is also possible to use PCR product as insert. Digest after PCR with corresponding restriction enzymes and clean up with PCR clean-up kit. This could lead to higher yields of insert DNA because a lot of DNA gets lost during the gel electrophoresis clean up.
- Sometimes some BioBricks are hard to assemble. Then you have to clean up the vector by gel electrophoresis as well.
Standard Freiburg BioBrick Assembly
Modified from [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Silver:_BB_Strategy Silver lab] and [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Assembly standard 25]:
This assembly method can be used for fusion protein assemblies with BioBricks which are bigger than 150 bp. The BioBrick should be at least 500 bp bigger or smaller than the backbone. The BioBrick, which complies with these conditions, is used as the insert and is assembled into the prefix or suffix of the other used BioBrick, which is called vector and needs to be available in the BioBrick [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Assembly standard 25]. You have to differentiate between a prefix and a suffix insertion.
Suffix Insertion
- Digestion of insert: at least 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x NEB buffer 4 + 0.1 µL 100x BSA, 0.5 µL NgoMIV (NEB), 1 µL PstI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Clean up the insert via gel electrophoresis. When cutting the insert out of the gel try to avoid staining or exposure to ultraviolet light of the insert.
- Digestion of vector about 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x orange buffer, 0.5 µL AgeI, 0.5 µL PstI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Add 1 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.2 µL 10x SAP buffer, incubate for 1 h at 37 °C. Clean up the vector with a PCR clean-up kit.
- Ligation: after digestion and clean-up: 50 - 200 ng of vector, 3 - 10 fold molar access of insert, 20 µL ligation volume, 2 µL T4-Ligase-Buffer, 1 µL T4-Ligase. Incubate for 20 - 30 min at room temperature, afterwards inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C. Then: store at -20 °C or transform.
Prefix Insertion
- Digestion of insert: at least 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x orange buffer, 0.5 µL EcoRI, 0.5 µL AgeI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Clean up the insert via gel electrophoresis. When cutting the insert out of the gel try to avoid staining or exposure to ultraviolet light of the insert.
- Digestion of vector about 700 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10 x NEB buffer 4, 0.5 µL EcoRI, 0.5 µL NgoMIV (NEB). Digest for 2h at 37 °C, afterwards inactivation for 20 min at 80 °C. Add 1 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.2 µL 10 x SAP buffer, incubate for 1 h at 37 °C. Clean up the vector with a PCR clean-up kit.
- Ligation: after digestion and clean-up: 50 - 200 ng of vector, 3 - 10 fold molar access of insert, 20 µL ligation volume, 2 µL T4-Ligase-Buffer, 1 µL T4-Ligase. Incubate for 20 - 30 min at room temperature, afterwards inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C. Then: store at -20 °C or transform.
Variations
- A digestion over night is possible. If you digest over night use only 0.1 µL restriction enzyme.
- It is also possible to use PCR product as insert. Digest after PCR with corresponding restriction enzymes and clean up with PCR clean-up kit. This could lead to higher yields of insert DNA because a lot of DNA gets lost during the gel electrophoresis clean up.
- Sometimes some BioBricks are hard to assemble. Then you have to clean up the vector by gel electrophoresis as well.
Standard 3A assembly
Modified from [http://ginkgobioworks.com/support/BioBrick_Assembly_Manual.pdf BioBrick Assembly Manual by Ginkgo BioWorks]
Digestion
- Thaw DNA from upstream and downstream part and the destination plasmid on ice.
- Destination plasmid has to carry the ccdB gene <partinfo>P1010</partinfo> as insert and has to have a different antibiotic resistance than the plasmids carrying the upstream and downstream parts
- DNA has to be cleaned (by MiniPrep or after a PCR)
- 500 ng DNA / digestion mix for upstream part, downstream part and destination plasmid (total volume of mix 10 µL, dilute with ddH20 if necessary)
- Add 1 µL of 10x buffer and restriction enzymes as shown in the following table:
| Upstream part | Downstream part | Destination plasmid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| enzyme 1 | 0.5 µL EcoRI | 0.5 µL XbaI | 0.5 µL EcoRI |
| enzyme 2 | 0.5 µL SpeI | 1 µL PstI | 0.5 µL PstI |
| buffer | BamHI | Tango | Orange |
- Incubation of the digestion mixes at 37 °C
- After 2 h: add 0.5 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.15 µL 10x SAP buffer to destination plasmid mix, continue incubation at 37 °C
- After another hour: heat inactivation of all mixes for 20 min at 80 °C
- Continue with ligation or freeze the mixes
Ligation
- Ligation mix:
- 2 µL ddH2O
- 5 µL of every digestion mix (so 15 µL in total)
- 2 µL T4-DNA-ligase buffer (thaw on ice!)
- 1 µL T4-DNA-ligase
- Incubate at least 20 min at room temperature, afterwards heat inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C (optional)
- Freeze ligation mix or continue with transformation (heatshock or electroporation)
Freiburg 3A assembly
Modified from [http://ginkgobioworks.com/support/BioBrick_Assembly_Manual.pdf BioBrick Assembly Manual by Ginkgo BioWorks] and [http://partsregistry.org/Assembly_standard_25 Assembly standard 25]
Digestion
- Thaw DNA from upstream and downstream part (=N-terminal and C-terminal protein domain) and the destination plasmid on ice.
- Destination plasmid has to carry the ccdB gene <partinfo>P1010</partinfo> as insert and has to have a different antibiotic resistance than the plasmids carrying the upstream and downstream parts
- DNA has to be cleaned (by MiniPrep or after a PCR)
- 500 ng DNA / digestion mix for upstream part, downstream part and destination plasmid (total volume of mix 10 µL, dilute with ddH20 if necessary)
- Add 1 µL of 10x buffer and restriction enzymes as shown in the following table:
| Upstream part | Downstream part | Destination plasmid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| enzyme 1 | 0.5 µL EcoRI | 0.5 µL NgoMIV | 0.5 µL EcoRI |
| enzyme 2 | 0.5 µL AgeI | 1 µL PstI | 0.5 µL PstI |
| buffer | Orange | NEB buffer 4 + BSA | Orange |
- Incubation of the digestion mixes at 37 °C
- After 2 h: add 0.5 µL SAP (shrimp alcaline phosphatase) and 1.15 µL 10x SAP buffer to destination plasmid mix, continue incubation at 37 °C
- After another hour: heat inactivation of all mixes for 20 min at 80 °C
- Continue with ligation or freeze the mixes
Ligation
- Ligation mix:
- 2 µL ddH2O
- 5 µL of every digestion mix (so 15 µL in total)
- 2 µL T4-DNA-ligase buffer (thaw on ice!)
- 1 µL T4-DNA-ligase
- Incubate at least 20 min at room temperature, afterwards heat inactivation for 5 min at 70 °C (optional)
- Freeze ligation mix or continue with transformation (heatshock or electroporation)
Gibson assembly
Modified from [http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v6/n5/full/nmeth.1318.html Gibson et al. (2009)]
This assembly method is an isothermal, single-reaction method for assembling multiple overlapping DNA molecules. By coordinating the activity of a 5‘ exonuclease, a DNA polymerase and a DNA ligase two adjacent DNA fragments with complementary terminal sequence overlaps can be joined into a covalently sealed molecule, without the use of any restriction endonuclease.
Preparation of DNA molecules for in vitro recombination
- Generate the complementary sequence overlaps by PCR using the Phusion DNA-polymerase. If necessary add 5 M Betain in the reaction mix by reducing the amount of H2O to decrease the number of false PCR products.
- Identify the PCR products of interest by gel electrophoresis with known DNA standards.
- Extract the PCR products from the gel by cutting out the DNA fragments and clean them up by using a commercial clean up kit.
In vitro recombination
- assembly mixture (6 mL)
- 320 µL 5x isothermal reaction buffer
- 0.64 µL of 10 U mL-1 T5 exonuclease (for DNA molecules overlapping by greater than 150 bp add 3.2 µL of 10 U ml–1 T5 exonuclease)
- 20 µL of 2 U mL-1 Phusion DNA polymerase
- 160 µL of 40 U mL-1 taq DNA ligase
- add ddH2O water up to a final volume of 1.2 mL
- aliquote 15 µL of the reagent-enzyme mix and store it at –20 ˚C
- Thaw 15 µL assembly mixture aliquot and keep it on ice until use.
- Add 5 µL of the purified DNA molecules in equimolar amounts (between 10 and 100 ng of each DNA fragment).
- Incubate the resulting mixture at 50 ˚C for 15 to 60 min, with 60 min being optimal.
- Transformation (heatshock or electroporation) without cleaning up the assembly product.
Restriction analysis
- Digest BioBrick of interest: about 400 ng DNA / 10 µL volume, 1 µL 10x orange buffer, 0.5 µL NotI or PstI. Digest for 2 h at 37 °C. NotI is used to determine the length of the BioBrick and the plasmid backbone, PstI ist used to determine the length of the BioBrick in the plasmid backbone.
- Gel electrophoresis: add 2 µL loading buffer to every digestion mix, apply about 100 - 200 ng DNA / pocket in gel. Don't forget to apply the uncut BioBrick as well. A good agarose concentration for BioBricks between 0.2 and 3 kb is 1.5 %. The smaller your BioBrick of interest is the higher the agarose concentration should be and vice versa. The gel electrophoresis is made with TAE-buffer. Be sure that you melt your agarose gel in the same buffer you use for the electrophoresis later.
Colony PCR
- Pick one colony with a sterile tip and elute it in 100 µL ddH20 or medium
- Store the colony in 4 °C while colony PCR is running
- One reaction mix contains:
- 10 µL 5x buffer
- 2 µL MgCl2 (25 mM stock)
- 1 µL dNTPs
- 0.5 µL primer mix (prefix/suffix primers or sequencing primers)
- 35.25 µL ddH2O
- 0.25 µL GoTaq polymerase (Promega)
- 1 µL template
- PCR program:
- Start: 3 min, 98 °C
- 30 cycles of:
- 30 s, 98 °C
- 30 s, 55 °C
- 30 s / 1 kb template, 72 °C
- Finish: 5 min, 72 °C
- Gel electrophoresis: check the fragment size
- Plate the correct colony
Site Directed Mutagenesis
- Design Primers using the QuickChange Primer Design tool
- Run mutagenesis PCR
- One reaction mix contains:
- 5 µL 10x buffer
- 0.4 µL Pfu polymerase
- 1 µL dNTPs
- 39.6 µL H2O
- 1 µL DMSO
- 2 µL primermix
- 1 µL template
- PCR program:
- Start: 2 min, 94 °C
- 16 cycles of:
- 45 s, 95 °C
- 30 s, 55 °C
- 2 min/kb, 73 °C
- Finish: 5 min, 72 °C
- One reaction mix contains:
- Control the amplified PCR-fragments by gel electrophoresis
- Digest the template plasmide by adding 1 µL of DpnI and incubate for 2-3 hours
- Purify the PCR produkt with a PCR clean-up kit
- Transform 3 µL of the purified PCR product into elektrokompetent XL1 blue cells
- Screen the transformants using restiction digest and sequencing
 "
"