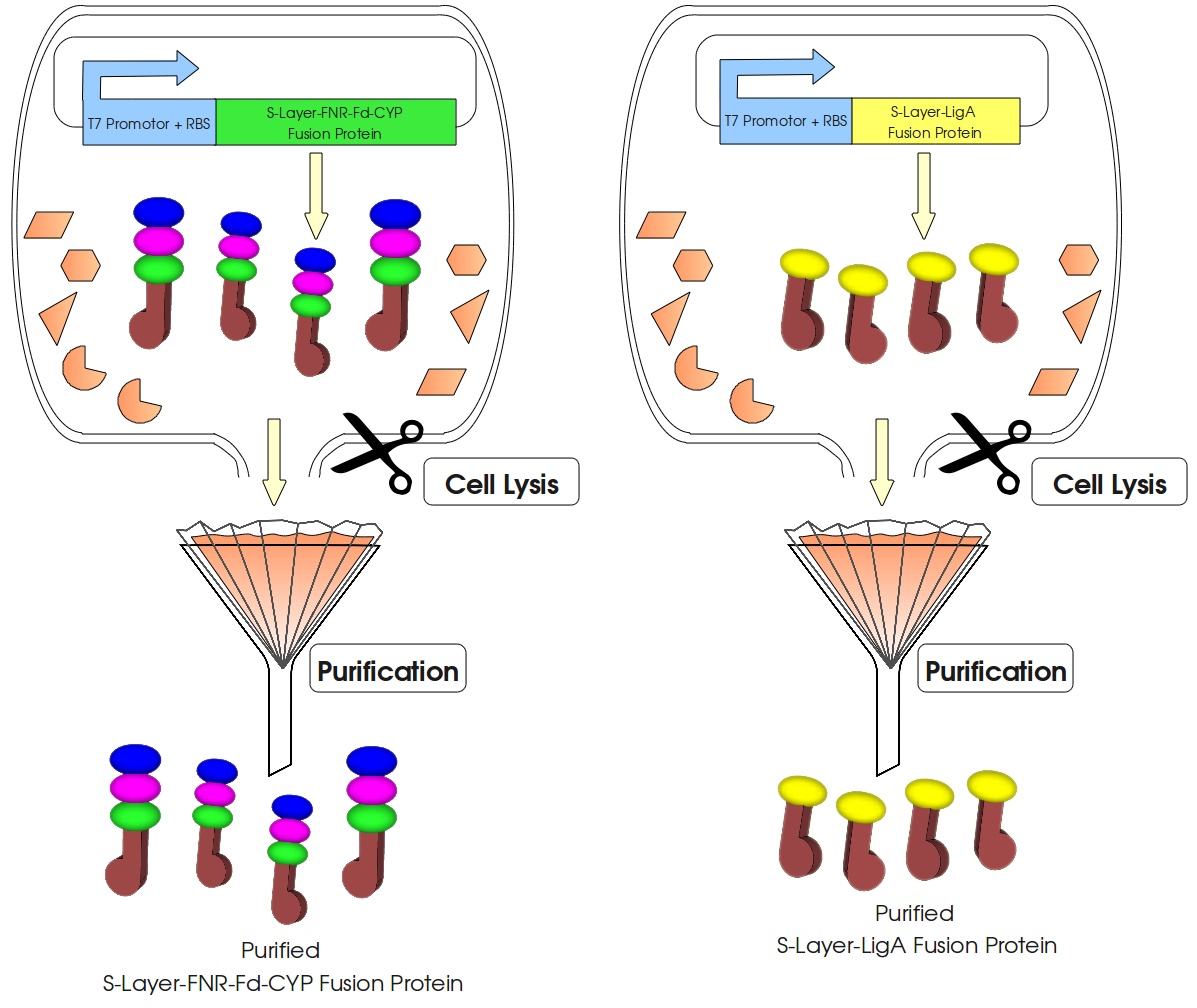
Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Data Page
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
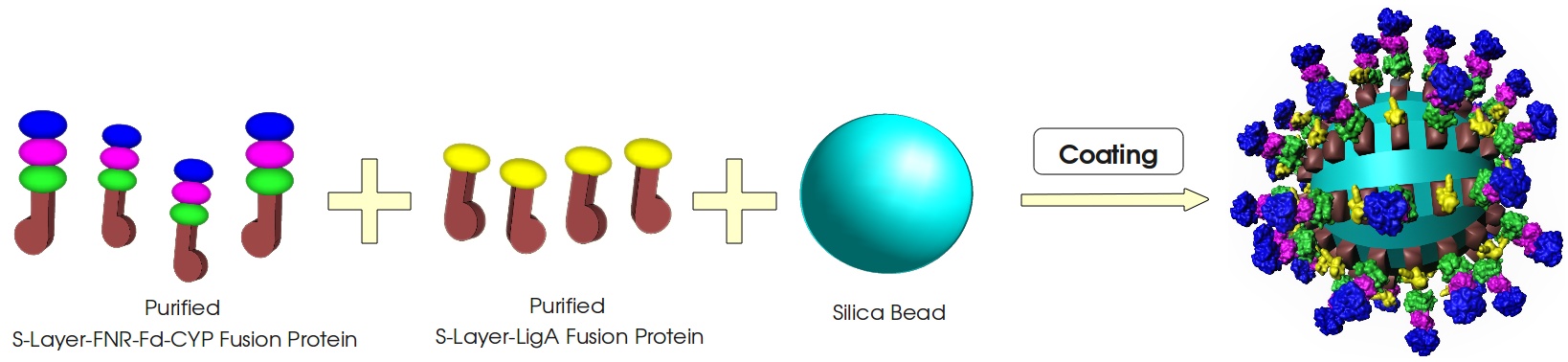
[[Image:Bielefeld_2011_Bead-Coating_v1.jpg|center|700px|thumb|'''Fig. 2: Coating of the silica beads with two different S-Layer fusion proteins.''']] | [[Image:Bielefeld_2011_Bead-Coating_v1.jpg|center|700px|thumb|'''Fig. 2: Coating of the silica beads with two different S-Layer fusion proteins.''']] | ||
| - | [[Image:IGEM_Bielefeld_Project.jpg|center|700px|thumb|'''Fig. 3: Visualization of our cellfree Bisphenol A sensor system with all essential components. The molecular beacon (hairpin structure) binds two short DNA-oligos. The NAD<sup>+</sup> dependent ligase (LigA) ligates the two oligos so that the hairpin structure opens and the fluorophore is able to emit light. | + | [[Image:IGEM_Bielefeld_Project.jpg|center|700px|thumb|'''Fig. 3: Visualization of our cellfree Bisphenol A sensor system with all essential components.''' Bisphenol A (BPA) is reduced by the electrons from NADH transfered by reductase (Red), ferredoxin (Fd) and cytochrome P450. The molecular beacon (hairpin structure) binds two short DNA-oligos. The NAD<sup>+</sup> dependent ligase (LigA) ligates the two oligos so that the hairpin structure opens up and the fluorophore is able to emit light.]] |
Revision as of 17:35, 17 September 2011

Contents |
How our System works
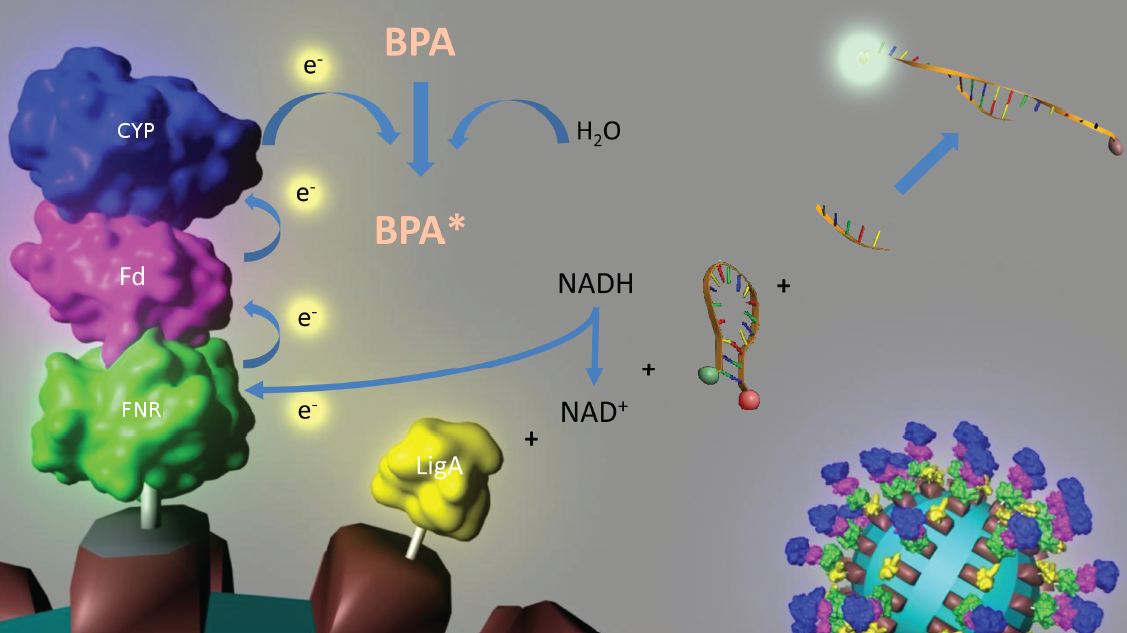
Fig. 3: Visualization of our cellfree Bisphenol A sensor system with all essential components. Bisphenol A (BPA) is reduced by the electrons from NADH transfered by reductase (Red), ferredoxin (Fd) and cytochrome P450. The molecular beacon (hairpin structure) binds two short DNA-oligos. The NAD+ dependent ligase (LigA) ligates the two oligos so that the hairpin structure opens up and the fluorophore is able to emit light.
Data For Our Favorite New Parts
- Main Page - Fusion Protein of S-Layer SgsE and mCitrine: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize purification methods and to demonstrate the S-layer's ability to self-assemble on surfaces.
- Main Page - Fusion Protein of BisdA and BisdB (expressed): This fusion protein improves the bisphenol A degradation in E. coli compared to the so far in the partsregistry existing BPA degrading BioBricks.
- Main Page - NAD+-dependent DNA ligase from E. coli : This enzyme enables determination of NAD+ even in very low concentrations by coupling it with a molecular beacon based assay.
Data For Pre-existing Parts
- Experience - BisdA degrades Bisphenol A when used with BisdB, BBa_K123000 (University of Alberta, iGEM 2008): Complete degradation of 120 mg L-1 Bisphenol A with polycistronic bisdAB gene in 30-33 h. Even faster (21-24 h) when using a fusion protein of BisdA and BisdB.
- Experience - BisdB degrades Bisphenol A when used with BisdA, BBa_K123001 (University of Alberta, iGEM 2008): Complete degradation of 120 mg L-1 Bisphenol A with polycistronic bisdAB gene in 30-33 h. Even faster (21-24 h) when using a fusion protein of BisdA and BisdB.
We've Also Characterized the Following Parts
- Main Page - Fusion Protein of S-Layer SbpA and mCitrine: This fluorescent S-layer fusion protein is used to characterize purification methods and to demonstrate the S-layer's ability to self-assemble on surfaces.
- Main Page - Polycistronic expression of BisdA and BisdB: This is the version of BPA degrading BioBricks found in the partsregistry - comparison to our fusion protein <partinfo>K525515</partinfo>.
 "
"