Team:Washington/Celiacs/Methods
From 2011.igem.org
Redesigning Kumamolisin to Have Higher Activity at Low pH
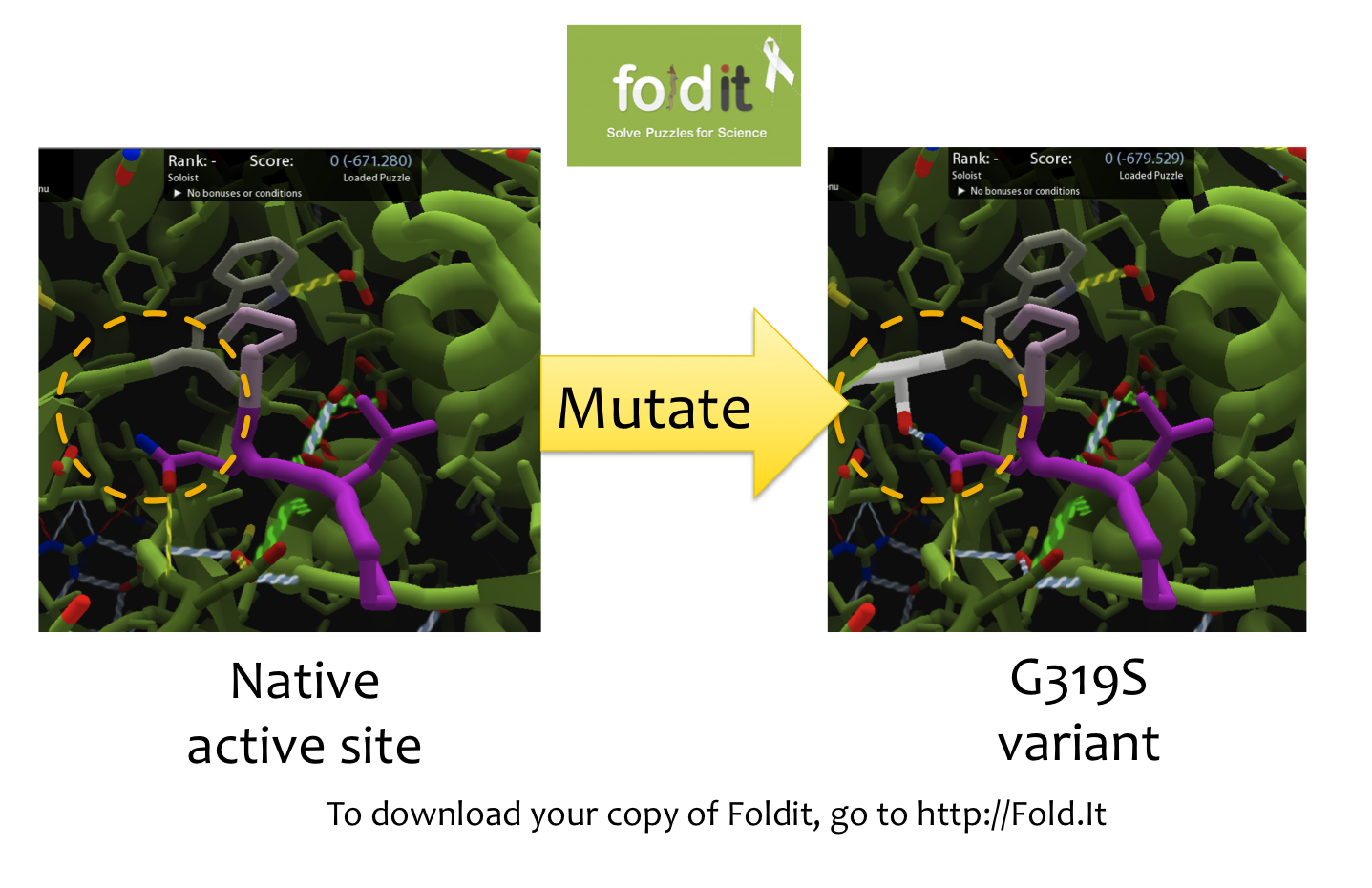
Using Foldit to Design Mutations
In order to design mutations to wild-type Kumamolisin that would increase the enzyme’s proteolytic activity on gluten, we used a computational enzyme editing program called Foldit, which allows the user to hypothetically modify the amino acid sequence of a protein by creating point mutations at any location within the protein’s crystal structure.
Within Foldit, we loaded Kumamolisin’s crystal structure in complex with a model PQLP peptide that recurs frequently in gluten, thus mimicking gluten as a substrate. We then modified the amino acid residues around the active site of Kumamolisin in the crystal structure, attempting to decrease the free energy of, and thus stabilize, the system. Estimations of free energy were based on algorithms run by Foldit.
Using this method, we designed over 100 novel mutants, each of which could potentially increase Kumamolisin’s proteolytic activity on gluten.
Mutagenizing Kumamolisin
Kunkel mutagenesis is a classic procedure for incorporating targeted mutations into a piece of DNA, so it was ideal for changing our wild-type Kumamolisin gene to code instead for specifically designed variant enzymes.
Kunkel Mutagenesis
The first step to producing our specially designed enzymes was to change the wild-type gene that codes for Kumamolisin to code instead for variant enzymes with our desired amino acid substitutions.
We designed mutagenic oligonucleotide primers that would anneal to the wild-type Kumamolisin gene and incorporate point mutations that, when expressed, would result in a variant of Kumamolisin with the desired amino acid shift.
To incorporate these mutations, we first isolated single stranded DNA (ssDNA) of our vector harboring the wild-type Kumamolisin gene. To do this we infected cells with bacteriophage M13, which packages its own ssDNA genome identified by length, and so in tandem packaged our vector in single stranded form. We then harvested the phage from the lysed culture of E. coli, and extracted our single stranded vector DNA.
Next, we annealed and extended our mutagenic oligos to incorporate the specified mutations into the newly synthesized antisense strand. This hybrid vector was transformed into E. coli that degraded the original uracil-containing DNA and replaced it with sections complementary to the mutagenized strand.
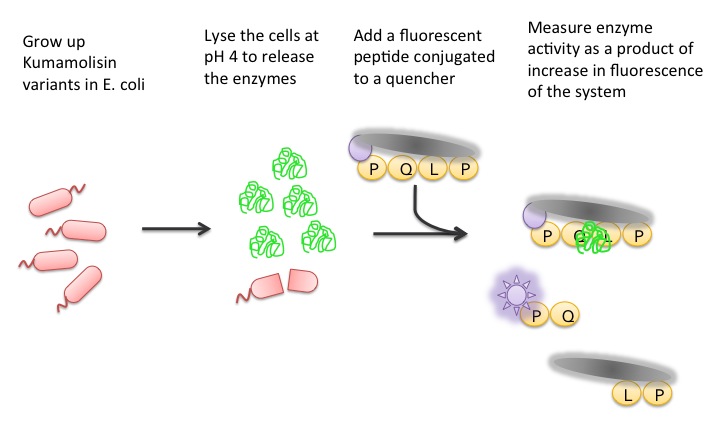
Using a Whole Cell Lysate Assay to Test Activity of Mutants
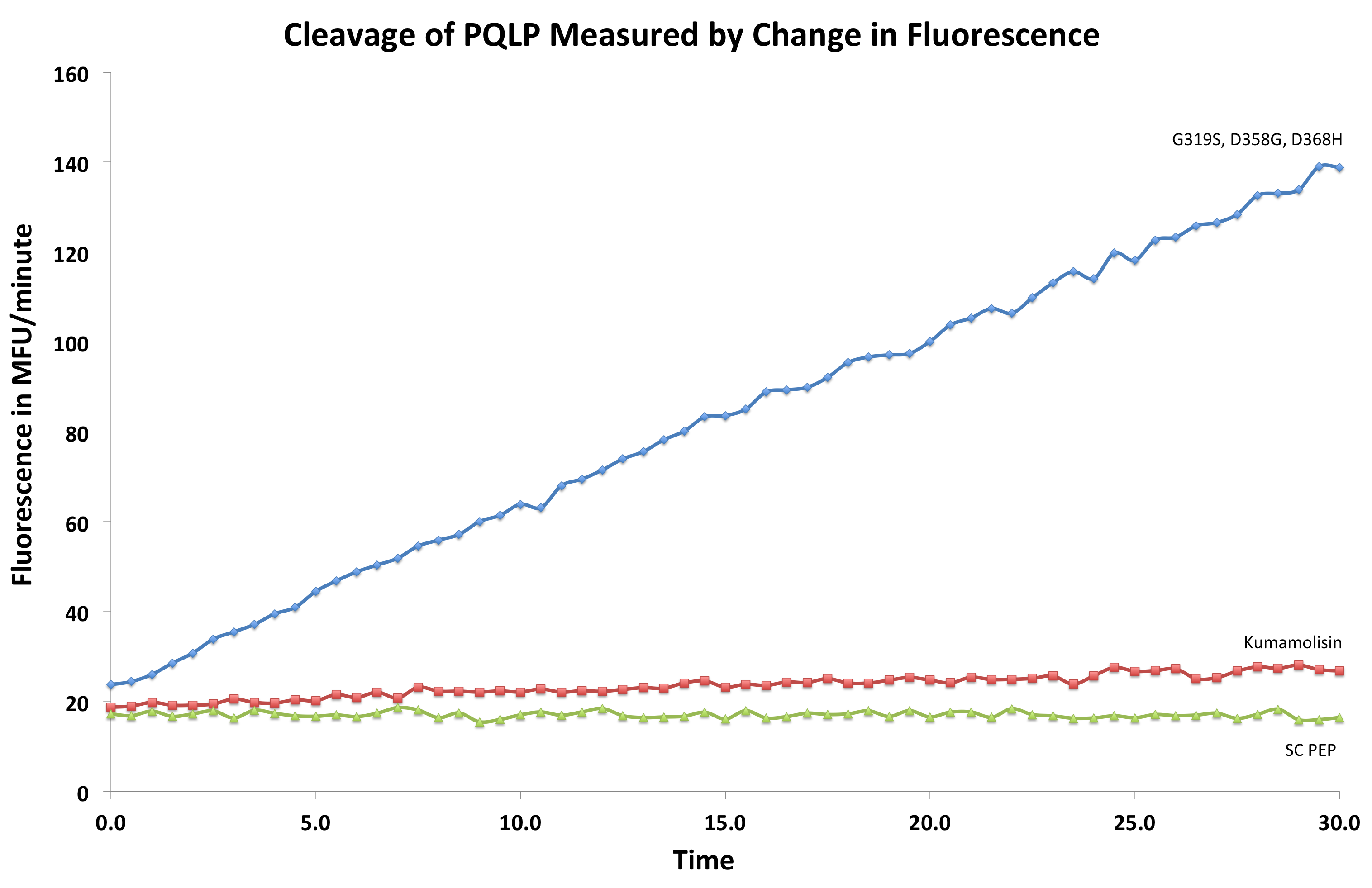
To test our designs, we developed a whole cell lysate assay that allowed us to perform a rough screen of a large number of mutants. In this assay, we expressed our mutant enzymes in E. coli, lysed the cells and separated the enzymes from large cell particulate. We then performed the assay at pH 4, mimicking the gastric environment. We added our model PQLP peptide, conjugated to both a fluorophore and a quencher so that no fluorescence would be achieved until after the peptide had been enzymatically cleaved. We then measured the fluorescence of each reaction at 30 second intervals, and were thereby able to estimate relative activity on breaking down PQLP by increase in fluorescence of the system.
Testing Purified Mutants to Accurately Assess Activity
Purification
After compiling a set of mutants which showed a relative increase in activity we proceeded to purify our mutant proteins. This step is crucial because it allows us to determine how our mutant compares with the wild-type on a quantitative level, as high activity without purification could simply be the result of high protein concentration. Growth, induction, and lysation of single colonies allowed the enzymes to be released from the cells, followed by collection of the purified proteins.
Assay
Concentrations were taken of the purified proteins, and diluted to the same concentration, to produce an assay resulting in accurate data representing which mutants had higher activity than kumamolisin and by how much their activity was greater.
 "
"