Team:EPF-Lausanne/Tools/MITOMI
From 2011.igem.org
MITOMI
MITOMI stays for "mechanicaly induced trapping of molecular interactions", it is a high troughput method using microfluidic technology designed to mesure low affinity molecular interactions.
Purpose: We used MITOMI technique during our project to characterize transcription factor binding energy landscapes in absolute terms by determining dissociation constants (Kd) for a comprehensive set of target DNA sequences.
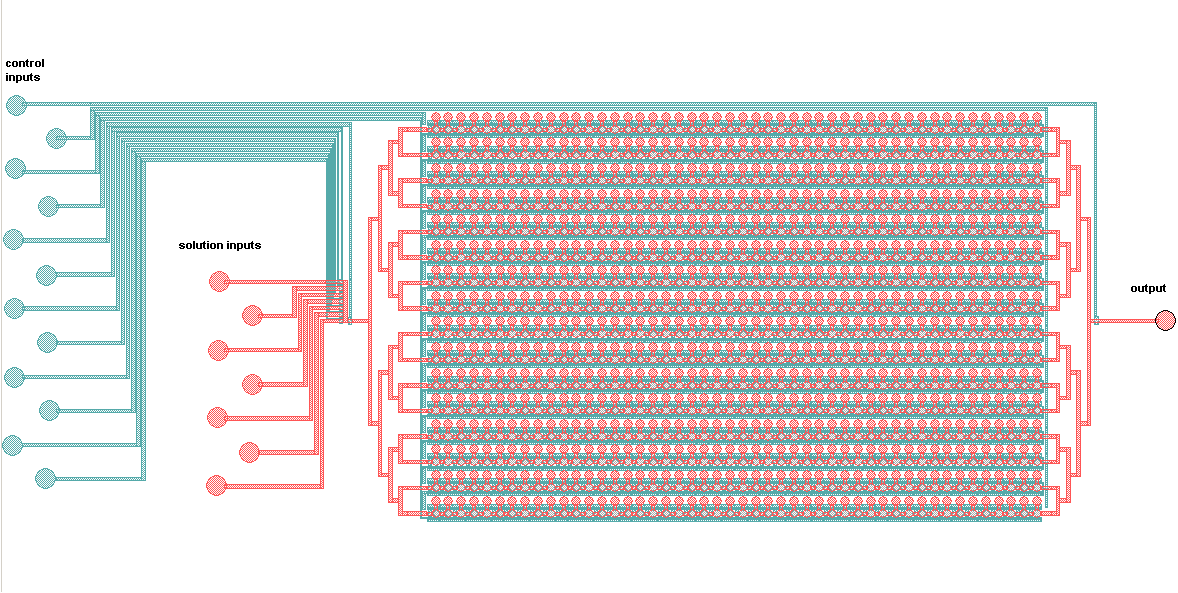
Schematic of the MITOMI platform:
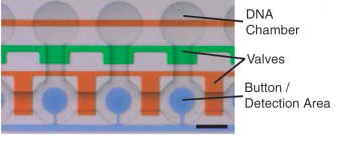
The control inputs control the valves that close the units or separate the chamber from the mixing space. Detailed view of the chambers and of the movable membrane used for mechanical trapping, referred to as the 'Button' .
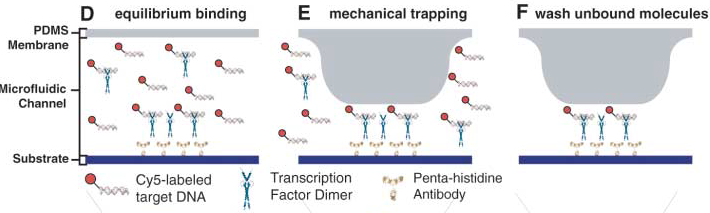
Advantages: The movable membrane shown in the scheme below enables measurements of transient interactions, exhibiting sub micromolar affinities which are generally problematic to observe.
Maerkl, S.J. and S.R. Quake, A systems approach to measuring the binding energy landscapes of transcription factors. Science, 2007. 315(5809): p. 233-237.
Maerkl, S.J. and S.R. Quake, Experimental determination of the evolvability of a transcription factor. PNAS, 2009. 106(44):p. 18650-5.
Running a MITOMI experiment
The protocol can be found here .
MITOMI scans explanation
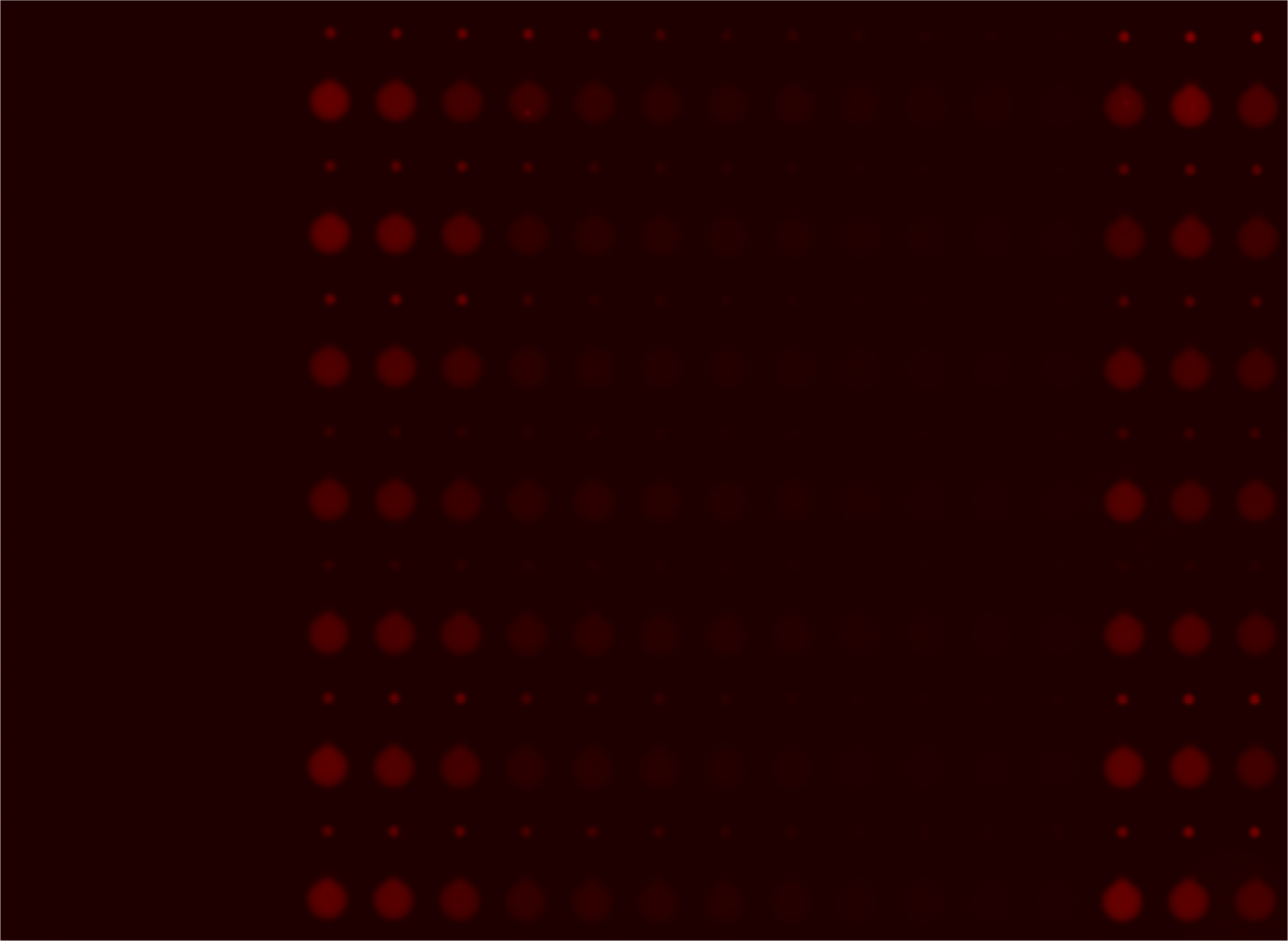
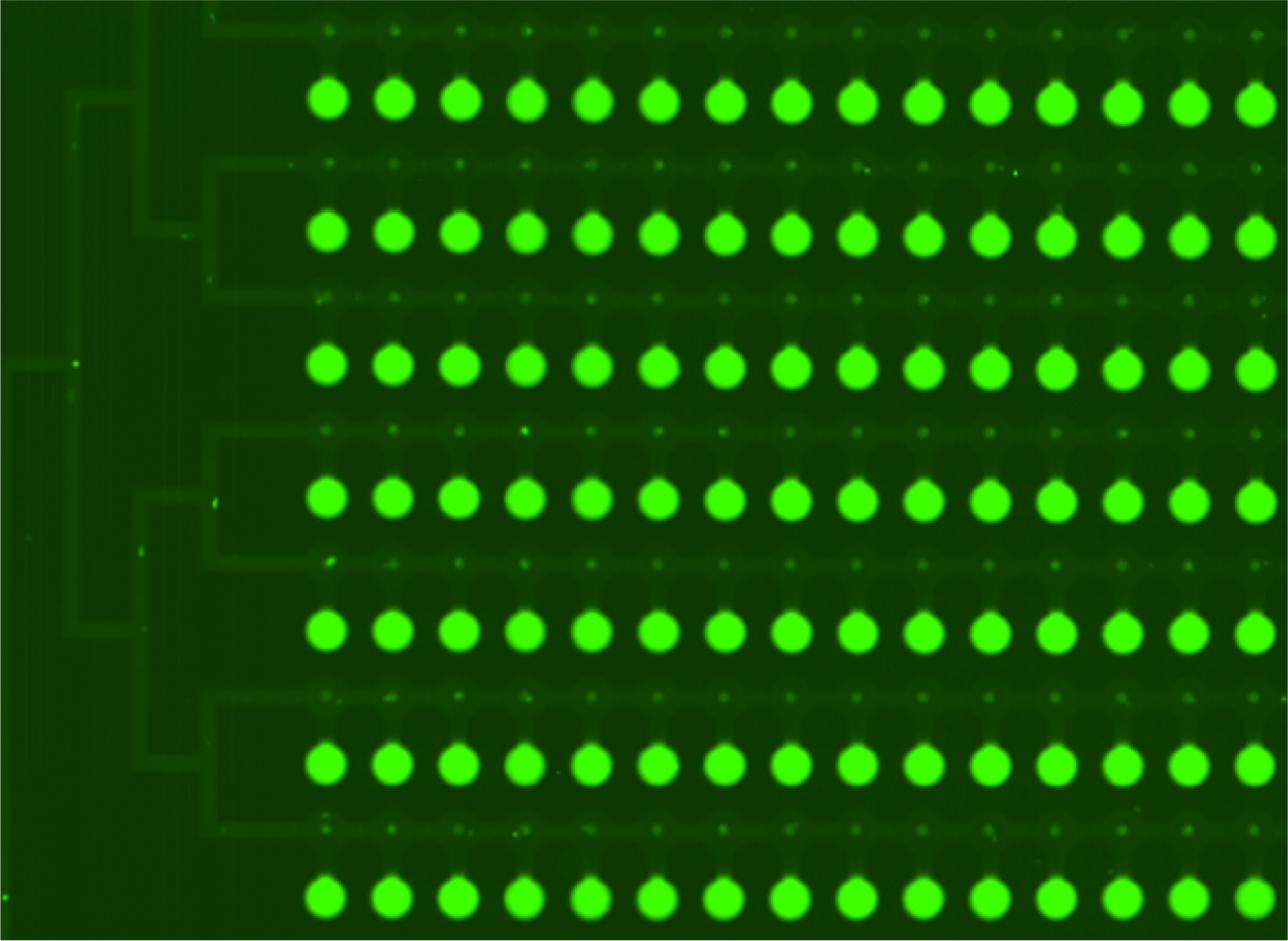
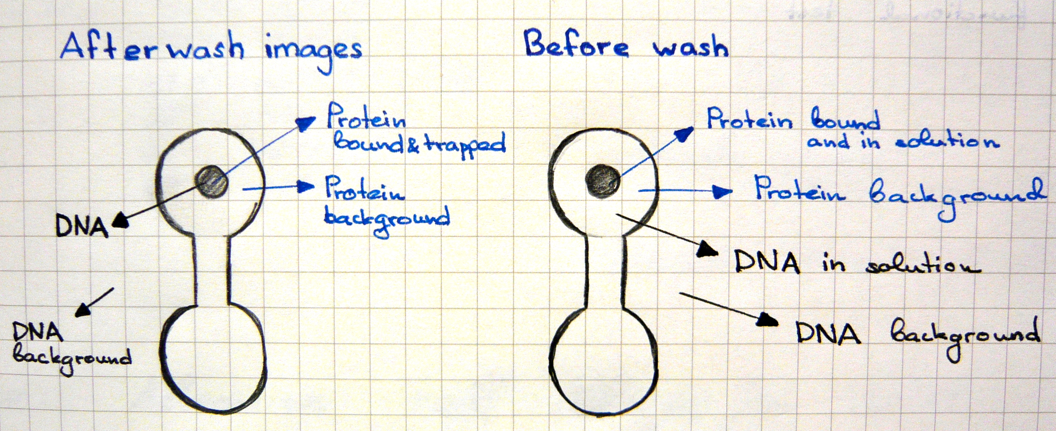
Two scans of the chip are necessary for the analysis of the molecular interactions.
- First scan is taken after 30-60 minutes of incubation, when the protein-DNA interactions reach thermodynamic stability. At this point the chamber containing DNA is open to allow diffusion and the valves separating each of the 756 units are closed, which prevents contamination.
- Second scan is taken after 10-15 minutes of wash with PBS.
For data collection the fluorescence intensity measured under the button is normalised to the background and the DNA/protein ratio is calculated. This ratio is ploted against the intensity of the fluorescence of DNA in solution to make the saturation curves. And the Kd for each sequence is calculated from these curves.
 "
"