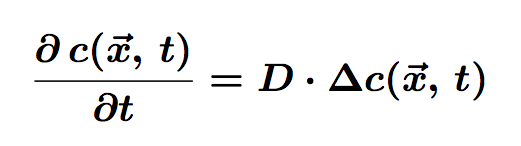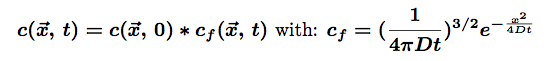Team:Paris Bettencourt/Modeling
From 2011.igem.org
(→Brownian motion and diffusion) |
(→Diffusion without boundary conditions) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
=== Diffusion without boundary conditions === | === Diffusion without boundary conditions === | ||
The first step was to study the general principle of diffusion and to apply them to a single molecule. We expected to estimate the order of magnitude for diffusion time of molecules with this model, not to have a precise understanding of the movement of molecules in a cell. Most of our experimental designs rely on time measurement to characterize the nanotubes, it was therefore crucial to see if diffusion time could add a significant delay to the response of receiver cells.<br> | The first step was to study the general principle of diffusion and to apply them to a single molecule. We expected to estimate the order of magnitude for diffusion time of molecules with this model, not to have a precise understanding of the movement of molecules in a cell. Most of our experimental designs rely on time measurement to characterize the nanotubes, it was therefore crucial to see if diffusion time could add a significant delay to the response of receiver cells.<br> | ||
| - | The principle of this first model is quite simple. We use the statistical diffusion equation with a new normalisation constant so that it describes the behaviour of one molecule. Rather than obtaining a concentration field, we end up for each spatial position with a distribution of the probability | + | The principle of this first model is quite simple. We use the statistical diffusion equation with a new normalisation constant so that it describes the behaviour of one molecule. Rather than obtaining a concentration field, we end up for each spatial position with a distribution of the density of probability to find the molecule in space and time fixed. We did not use any kind of limit conditions, we therefore only have the "movements" of one molecule floating in an infinite water medium.<br> |
The equation of diffusion is the following:<br> | The equation of diffusion is the following:<br> | ||
[[File:diffusion_equation.png|thumb|center]] | [[File:diffusion_equation.png|thumb|center]] | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 26 July 2011

Contents |
Modeling
Direct observation
Characterization
T7 system
tRNA amber system
The amber suppressor tRNA diffusion. The idea of the system is to pass tRNA amber molecules through the nanotubes. At every moment of time in the receiver cell there is a certain amount of transcribed mRNA-T7 among the others mRNA. The behavior of tRNA amber that arrived in a receiver cell is random, so in order to describe its interaction with mRNA-T7 and its further translation we can reason in terms of probability.
We can reason in two steps : first a tRNA amber molecule gets close to a mRNA molecule. Then, it binds it's anti-codon with a codon of the mRNA. This reasoning is similar to the problem of boxes and balls. There are two types of boxes: 'a' of the first type and 'b' of the second (which corresponds to the set of mRNA-T7 and mRNA-non-T7), and there are 't' balls(tRNA amber). All the balls are randomly distributed in the boxes. If there are two or more balls in some box of the first type (two or more tRNA amber per mRNA-T7) then a T7 molecule will be produced with a chance P_0.
This system can be modelled after making some important assumptions :
- All the molecules in the cell are uniformly distributed.
- The number of tRNA amber diffused through the nanotubes is much more smaller than the one of the mRNA. Thus the chance that three or more tRNA amber will "find" one mRNA-T7 is negligible comparing to the one of two tRNA amber (finding a mRNA-T7). In our model we will consider that at one moment of time each mRNA interacts with 0, 1 or 2 tRNA amber.
Master/Slave
Bi-directional communication
Brownian motion and diffusion
A significant part of our designs relies on diffusion of very few molecules activating the amplification and reporter systems. For instance, we know that in the T7 design, we need less than ten T7 RNA polymerases to trigger the amplification. Knowing how a molecule moves in a cell just after its transport through nanotubes was necessary. To model this kind of behaviour we had to look into the mechanisms of diffusion for single molecules in cells. This meant studying the motions of diffusion.
Please note that we are not talking here about the movement of molecules inside the nanotubes, which requires other types of model.
Diffusion without boundary conditions
The first step was to study the general principle of diffusion and to apply them to a single molecule. We expected to estimate the order of magnitude for diffusion time of molecules with this model, not to have a precise understanding of the movement of molecules in a cell. Most of our experimental designs rely on time measurement to characterize the nanotubes, it was therefore crucial to see if diffusion time could add a significant delay to the response of receiver cells.
The principle of this first model is quite simple. We use the statistical diffusion equation with a new normalisation constant so that it describes the behaviour of one molecule. Rather than obtaining a concentration field, we end up for each spatial position with a distribution of the density of probability to find the molecule in space and time fixed. We did not use any kind of limit conditions, we therefore only have the "movements" of one molecule floating in an infinite water medium.
The equation of diffusion is the following:
Where c is the concentration of particles in the cell, function of <math>\vec{x}</math> (position) and t (time). D is the diffusion coefficient.
The solution for such an equation is:
The star * represents the convolution of the two functions. The first part represents the initial conditions which are in our case a Dirac function centered on the origin of space (there is only one molecule at (0,0,0) at t=0). the second part of this solution is the so-called fundamental solution.
 "
"