Team:EPF-Lausanne/Notebook/July2011
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
Since we were running out of the P23019 plasmid DNA to try new PCRs, we thought it would be a good idea to transform it. We used both Lilia's and Alina's cells, adding a negative control. The incubation for chloramphenicol required a two hour recovery period in the incubator, since the antibiotic is stronger. After Tuesday's meeting, we went ahead and plated the result and let the plates incubate overnight. | Since we were running out of the P23019 plasmid DNA to try new PCRs, we thought it would be a good idea to transform it. We used both Lilia's and Alina's cells, adding a negative control. The incubation for chloramphenicol required a two hour recovery period in the incubator, since the antibiotic is stronger. After Tuesday's meeting, we went ahead and plated the result and let the plates incubate overnight. | ||
| - | Meanwhile, moving on with the Gibson assembly of the J61002 plasmid, Vincent tried to obtain the final Gibson sequence. This sequence would be used to see if PstI and SpeI would cut differently on the assembled plasmid versus the normal J61002 plasmid: we hoped this would allow us to check that Gibson had worked successfully if we ran the ligated plasmids on a gel. Ideally, the J61002 original plasmid would cut at two locations while the Gibson plasmid would only cut in a single location (the biobrick scar would make it impossible to cut at the previous cut location). On a gel, we would see a single piece of about 3000 bp for the Gibson plasmid and two bands of approximately 2200 and 700 bp respectively for the normal plasmid. | + | Meanwhile, moving on with the Gibson assembly of the J61002 plasmid, Vincent tried to obtain the final Gibson sequence. This sequence would be used to see if PstI and SpeI would cut differently on the assembled plasmid versus the normal J61002 plasmid: we hoped this would allow us to check that Gibson had worked successfully if we ran the ligated plasmids on a gel. Ideally, the J61002 original plasmid would cut at two locations while the Gibson plasmid would only cut in a single location (the biobrick scar would make it impossible to cut at the previous cut location). On a gel, we would see a single piece of about 3000 bp for the Gibson plasmid and two bands of approximately 2200 and 700 bp respectively for the normal plasmid. |
| + | |||
| + | Using the plates with the four Gibson colonies, Vincent made cultures which he put in the incubator overnight. | ||
| + | == Wednesday, 6th of July 2011== | ||
| + | With the Gibson cultures in hand, Vincent made glycerol stocks (500 microL glycerol, 500 microL cells) and then mini-prepped the four cultures using the standard protocol. The resulting DNA plasmids were ready for enzyme ligase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vincent also looked at the results of the transformation of the P23019 using two different sets of competent cells and negative controls. No colonies grew, leaving us quite perplexed as to what was in the original P23019 well. Determined to find a substitute for the P23019 plasmid that would serve as a vector for the TetR sequence, we searched through the database looking for a plasmid with resistance to something other than ampicillin as well as a P15a origin of replication. We found four distinct possibilities, only two of which were available in the plates from the standard registry: pSB3K1 which has kanamycin resistance, and pSB3C5 which has chloramphenicol resistance (very similar to p23019). | ||
| Line 79: | Line 85: | ||
Colonies 1 and 4 have the expected band over 3kb, which is coherent with the observation made that they did express RFP. But colonies 2 and 3 have only one band... It is likely that in these cells the plasmid recombined in a shorter way, without RFP but with the resistance; otherwise the plasmid sequence is not what we think. We'll check tomorrow on the J61002 plasmid if we do get 2 bands on the starting plasmid. | Colonies 1 and 4 have the expected band over 3kb, which is coherent with the observation made that they did express RFP. But colonies 2 and 3 have only one band... It is likely that in these cells the plasmid recombined in a shorter way, without RFP but with the resistance; otherwise the plasmid sequence is not what we think. We'll check tomorrow on the J61002 plasmid if we do get 2 bands on the starting plasmid. | ||
Also, we have some light smaller bands in colonies 1 and 4, indicating that the miniprep is perhaps not so pure. | Also, we have some light smaller bands in colonies 1 and 4, indicating that the miniprep is perhaps not so pure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vincent and Alessandro transformed the J61002 original plasmid, since we were running out of DNA with which to compare to the Gibson assembly. In addition, they transformed the results of the previous day's registry search for convenient substitute plasmids (for p23019) using Alina's cells. These were plated appropriately and put in the incubator overnight. | ||
== Friday, 8th of July 2011 == | == Friday, 8th of July 2011 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thanks to Henrike's expert eyes, we were able to harvest many colonies from the chloramphenicol pSB3C5 plasmid as well as many for the J61002 plasmid and the kanamycin plasmid. Since the chloramphenicol plasmid seemed closest to the p23019 plasmid for which we already had primers, it made sense to pursue the Gibson strategy for that plasmid. Alessandro and Vincent made culture tubes and put those in the incubator overnight. In the meanwhile, primers were designed for the next phase of Gibson assembly (i.e. the new pSB3C5 plasmid with the old TetR piece). | ||
| + | |||
[[File:EPFL-08-07_igem_tetRvariants_1.jpg|thumb|right|Gel from the tetR mutants PCR. 1000kb ladder.]] | [[File:EPFL-08-07_igem_tetRvariants_1.jpg|thumb|right|Gel from the tetR mutants PCR. 1000kb ladder.]] | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 9 July 2011
Notebook: July 2011
Contents |
Friday, 1st of July 2011
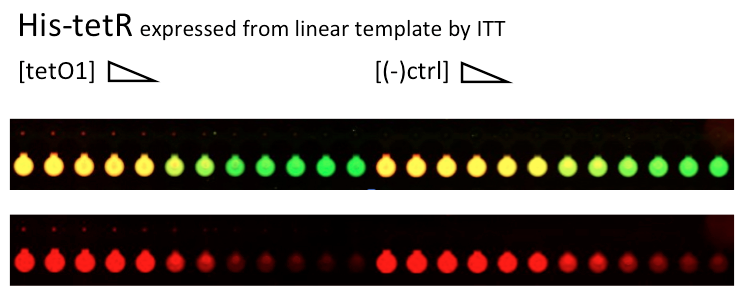
Alina and Lilia did MITOMI on His-tetR expressed from linear template, it was loaded on chip in ITT expression mix. DNA was spotted on June 29 in different concentrations for both: consensus (tetO1) sequence and a random sequence ((-)control).
Images: Green fluorescence comes from green-lysine and red fluorescence comes from DNA (cy-5 labeled).
Although we don't observe much protein bound to the anti His-tag antibody, we can still see that it does bound TetO1 sequence and did not bind any (-)control sequence. Some possible reasons for low protein fluorescence under the buttons: the expression yield from the linear template with T7 promoter might be too low, the His-tag to antibody binding is not strong enough or the concentration of antibody is too low.
Friday, 1st of July 2011
Alina and Lilia amplified the His-tetR linear template. After PCR sample was loaded on 1% agarose gel with Rad Safe, “1Kb Plus DNA Ladder” was used.
We also prepared about thirty LB-agar plates with ampicilin, they are in the BM fridge.
Colonies from Gibson
After an overnight incubation, we found four colonies on the Ampicillin plates that had cells containing the plasmids from the Gibson assembly. The low number of colonies is attributed to the low competence of the cells. Of the four colonies, two were pink and two were yellow.
Tween experiment
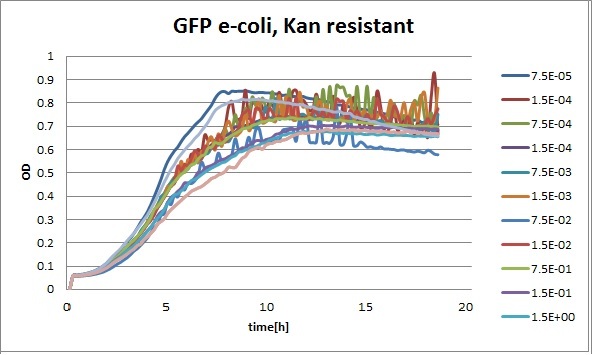
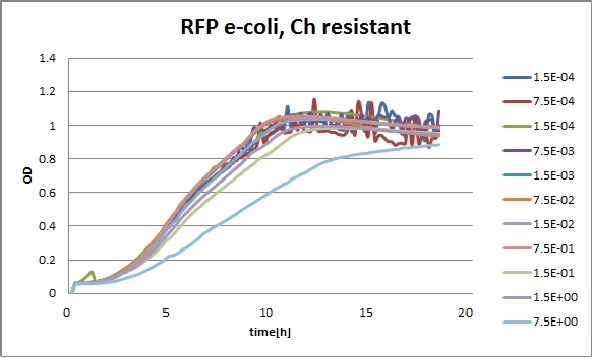
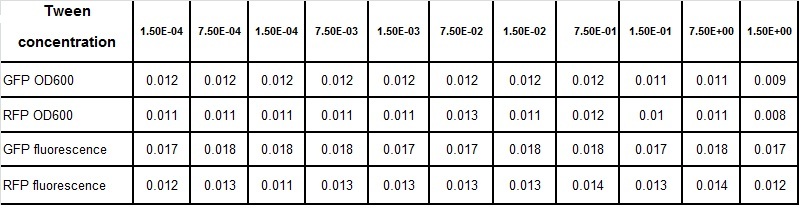
Clara and Henrike tested the right dose of Tween 20 that can be used for the "chemostat" experiment without affecting the cell growth. Tween is a detergent that would prevent the cells from sticking and thus clogging the microfluidic channels. We tested 12 different dilutions of Tween 12 both for GFP and RFP e-coli which can be potentially used for the "chemostat" experiment. We read the OD(absorption @600nm) and fluorescence every 10 minutes, for 18 hours at 37°C.
Growth curves for all the different concentrations vs time
The legend shows the percentage of tween 20 that was added to the medium.
- We can observe that the growth factor is smaller for Chloramphenicol resistant e-coli due to the fact that Chloramphenicol is stronger than Kanamycin.
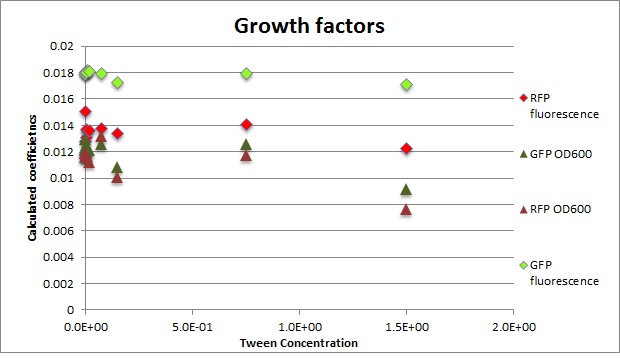
Calculated growth factor for the previous curves(Lilia)
Growth factor
We can observe that tween did not have a major effect on the cells' growth.
I suggest we use 0.075% tween in media for the experiments
Monday, 4th of July 2011
Alina and Vincent made plates (large and small) with chloramphenicol (concentration of 34 mg/mL). We used .74 mL of chloramphenicol for a liter of LB agar and plated them directly under the flame.
To figure out what was going wrong with the P23019 plasmid, we used the Nanodrop to determine that the sample (Plate 4, well 14E) was at a concentration of 97.4 ng/microL. This result seemed to indicate that there was DNA in the sample of the plate (as opposed to just red dye without DNA).
Tuesday, 5th of July 2011
Since we were running out of the P23019 plasmid DNA to try new PCRs, we thought it would be a good idea to transform it. We used both Lilia's and Alina's cells, adding a negative control. The incubation for chloramphenicol required a two hour recovery period in the incubator, since the antibiotic is stronger. After Tuesday's meeting, we went ahead and plated the result and let the plates incubate overnight.
Meanwhile, moving on with the Gibson assembly of the J61002 plasmid, Vincent tried to obtain the final Gibson sequence. This sequence would be used to see if PstI and SpeI would cut differently on the assembled plasmid versus the normal J61002 plasmid: we hoped this would allow us to check that Gibson had worked successfully if we ran the ligated plasmids on a gel. Ideally, the J61002 original plasmid would cut at two locations while the Gibson plasmid would only cut in a single location (the biobrick scar would make it impossible to cut at the previous cut location). On a gel, we would see a single piece of about 3000 bp for the Gibson plasmid and two bands of approximately 2200 and 700 bp respectively for the normal plasmid.
Using the plates with the four Gibson colonies, Vincent made cultures which he put in the incubator overnight.
Wednesday, 6th of July 2011
With the Gibson cultures in hand, Vincent made glycerol stocks (500 microL glycerol, 500 microL cells) and then mini-prepped the four cultures using the standard protocol. The resulting DNA plasmids were ready for enzyme ligase.
Vincent also looked at the results of the transformation of the P23019 using two different sets of competent cells and negative controls. No colonies grew, leaving us quite perplexed as to what was in the original P23019 well. Determined to find a substitute for the P23019 plasmid that would serve as a vector for the TetR sequence, we searched through the database looking for a plasmid with resistance to something other than ampicillin as well as a P15a origin of replication. We found four distinct possibilities, only two of which were available in the plates from the standard registry: pSB3K1 which has kanamycin resistance, and pSB3C5 which has chloramphenicol resistance (very similar to p23019).
Thursday, 7th of July 2011
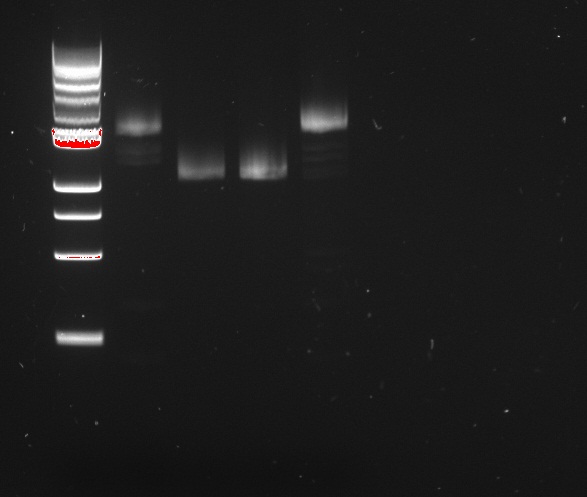
Vincent and Nadine made a digestion on the minipreps from the 4 colonies that were transformed with the Gibson-extended J61002 plasmid. If Gibson was successful, only Pst1 will cut and we should have one band of 3094 bp. If Gibson didn't work, then Pst1 and Spe1 will cut and we should have 2 bands of 890 and 2060 bp. The digestion was made according to last year's protocol, with 1.5 hour incubation. The ladder on the gel is 1kb.
Colonies 1 and 4 have the expected band over 3kb, which is coherent with the observation made that they did express RFP. But colonies 2 and 3 have only one band... It is likely that in these cells the plasmid recombined in a shorter way, without RFP but with the resistance; otherwise the plasmid sequence is not what we think. We'll check tomorrow on the J61002 plasmid if we do get 2 bands on the starting plasmid. Also, we have some light smaller bands in colonies 1 and 4, indicating that the miniprep is perhaps not so pure.
Vincent and Alessandro transformed the J61002 original plasmid, since we were running out of DNA with which to compare to the Gibson assembly. In addition, they transformed the results of the previous day's registry search for convenient substitute plasmids (for p23019) using Alina's cells. These were plated appropriately and put in the incubator overnight.
Friday, 8th of July 2011
Thanks to Henrike's expert eyes, we were able to harvest many colonies from the chloramphenicol pSB3C5 plasmid as well as many for the J61002 plasmid and the kanamycin plasmid. Since the chloramphenicol plasmid seemed closest to the p23019 plasmid for which we already had primers, it made sense to pursue the Gibson strategy for that plasmid. Alessandro and Vincent made culture tubes and put those in the incubator overnight. In the meanwhile, primers were designed for the next phase of Gibson assembly (i.e. the new pSB3C5 plasmid with the old TetR piece).
We ran the PCR on the tetR linear template, using Clara's primers for site-specific mutagenesis.
Six PCRs were run. The first amplified the common sequence of the mutants: everything up to the mutated sites. The six other reactions amplified the second half of the gene, inducing specific mutations in tetR.
The fluorescence traces are insufficiently clear for accurate conclusions, therefore the PCR and gel will be repeated with different concentrations on Monday.
 "
"