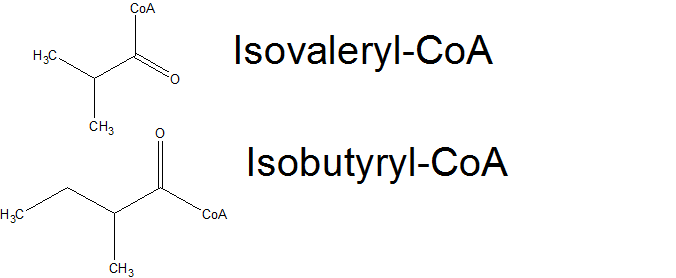Team:Washington/Alkanes/Future/FabH2
From 2011.igem.org
(→Current Results) |
(→FabH2 is toxic to E. coli) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:Washington growthcurve.png|center|450px|thumb|Growth curve showing that cells expressing FabH2 are growth deficient. [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590026 ADC] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590027 AAR] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 DrR] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 FabH2] | [[File:Washington growthcurve.png|center|450px|thumb|Growth curve showing that cells expressing FabH2 are growth deficient. [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590026 ADC] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590027 AAR] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 DrR] [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 FabH2] | ||
]] | ]] | ||
| - | After 24 hours, FabH2 producing cells had barely grown at all, indicating a severe growth deficiency. The cells were able to rapidly grow after 24 hours, presumably due to a mutation that counteracted the negative effects of FabH2. This toxicity could be due to branched chain fatty acid production, or due to the activity of FabH2 on straight chain substrates affecting cellular metabolism. This severe growth deficiency implies that FabH2 is being expressed, and has activity that is detrimental to cell growth. Due to FabH2's toxicity, any time that we | + | After 24 hours, FabH2 producing cells had barely grown at all, indicating a severe growth deficiency. The cells were able to rapidly grow after 24 hours, presumably due to a mutation that counteracted the negative effects of FabH2. This toxicity could be due to branched chain fatty acid production, or due to the activity of FabH2 on straight chain substrates affecting cellular metabolism. This severe growth deficiency implies that FabH2 is being expressed, and has activity that is detrimental to cell growth. Due to FabH2's toxicity, any time that we coexpressed fabH2 and the PetroBrick on a high copy number, strong promter expression vector, total alkane yield was decimated. In cells expressing the normal PetroBrick, we were able to consistently Reduction of this toxicity should allow us to determine the effects of FabH2 production on alkane biosynthesis. |
=Reducing the Toxicity of FabH2.= | =Reducing the Toxicity of FabH2.= | ||
Revision as of 17:25, 21 October 2011
Background
The basic alkane production system is incapable of making branched chain alkanes, as E. coli normally only makes straight chain fatty acids. In addition, our basic system is only able to make odd chain length alkanes, as E. coli only normally make even chain length fatty acids. We thought that if we could introduce an enzyme into PetroBrick expressing E. coli that results in the production of branched chain or odd chain length Fatty acids, we could cause the PetroBrick to produce branched chain or even change length alkanes. One protein whose expression has been previously shown ( [1]) to cause E. coli to produce branched chain and odd chain length fatty acids is FabH2 from Bacillus subtilis. The FabH family of proteins initiates fatty acid elongation by converting an Acyl-CoA into an Acyl-ACP, with is extended by 2 carbon units to form longer chain length fatty acids. Normally, FabH proteins use a simple 2-carbon acetyl-CoA to start fatty acid biosynthesis, resulting in even chain length linear fatty acids. However, FabH2 has been hypothesized to initiate fatty acid biosynthesis using Isobutyryl-CoA and Isovaleryl-CoA( products from Valine and Leucine degredation), resulting in 2-methyl branched fatty acid production, as well as using a 3-carbon propanoyl-CoA, resulting in odd chain length fatty acids. If we could use FabH2 and the Petrobrick to get E. coli to produce both alkanes and branched chain or odd chain length fatty acids, we should theoretically be able to produce 2-methyl branched alkanes or even chain length fatty acids.
Methods
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590034 FabH2 ] was constructed from oligos( refer to protocol). FabH2 was then amplified to add an [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 Elowitz standard RBS]. This RBS-FabH2 construct was cloned into the 3' end of [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590025 the PetroBrick] to express [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 FabH2 as well as AAR and ADC]. In addition, we cloned fabH2 into a [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K314103 low copy number IPTG inducible vector].
FabH2 is toxic to E. coli
Throughout our experiments, we observed that cells expressing FabH2 grew significantly slower than any of our other alkane producing cells. In order to quantify this effect, we measured OD600 for alkane production constructs every 24 hours for a 72 hour period, producing a growth curve.
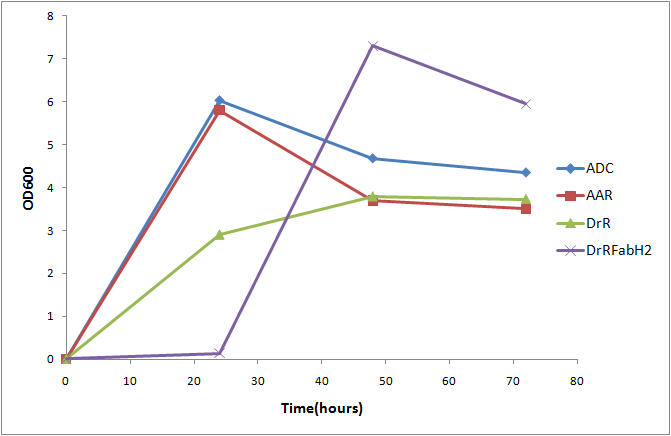
After 24 hours, FabH2 producing cells had barely grown at all, indicating a severe growth deficiency. The cells were able to rapidly grow after 24 hours, presumably due to a mutation that counteracted the negative effects of FabH2. This toxicity could be due to branched chain fatty acid production, or due to the activity of FabH2 on straight chain substrates affecting cellular metabolism. This severe growth deficiency implies that FabH2 is being expressed, and has activity that is detrimental to cell growth. Due to FabH2's toxicity, any time that we coexpressed fabH2 and the PetroBrick on a high copy number, strong promter expression vector, total alkane yield was decimated. In cells expressing the normal PetroBrick, we were able to consistently Reduction of this toxicity should allow us to determine the effects of FabH2 production on alkane biosynthesis.
Reducing the Toxicity of FabH2.
We hypothesized that if we could reduce the toxicity of FabH2, we could see the production of alternative alkane products. The original FabH2 system placed the FabH2 gene under the control of a strong constituitive promoter. We thought that if we could reduce FabH2 expression, we could decrease toxicity and be able to see the effects of FabH2 production on the alkanes produced by the PetroBrick. We cloned FabH2 into a [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K314103 low copy number 3k3 IPTG inducible vector]. By reducing copy number appproximetly 10 fold, and by having the ability
References
1.Beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) is a determining factor in branched-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Choi KH, Heath RJ, Rock CO. J Bacteriol. 2000 Jan;182(2):365-70.
2. http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?AD=ADA317177&Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf
3. Branched-chain fatty acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Smirnova N, Reynolds KA. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Oct;27(4):246-51.
Parts Submitted
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590034 FabH2] This part contains the FabH2 coding sequence, codon optimized for E. coli
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K590030 FabH2-ADC-AAR] This part expresses FabH2, as well as AAR and ADC, the two genes responsible for alkane production.
 "
"