Team:Washington/Magnetosomes/Magnet Results
From 2011.igem.org
(→What’s in the Magnetosome Toolkit?) |
(→What’s in the Magnetosome Toolkit?) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* A table compiling individual gene functions from our literature search | * A table compiling individual gene functions from our literature search | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | ----- | + | -----<br> |
== '''Superfolder GFP-magnetosome gene protein fusions'''== | == '''Superfolder GFP-magnetosome gene protein fusions'''== | ||
Revision as of 00:51, 29 September 2011
What’s in the Magnetosome Toolkit?
- A set of 10 gene clusters from the essential mamAB operon of strain AMB-1
- Our favorite genes as translational fusions with superfolder gfp in pGA vectors
- A table compiling individual gene functions from our literature search
Superfolder GFP-magnetosome gene protein fusions
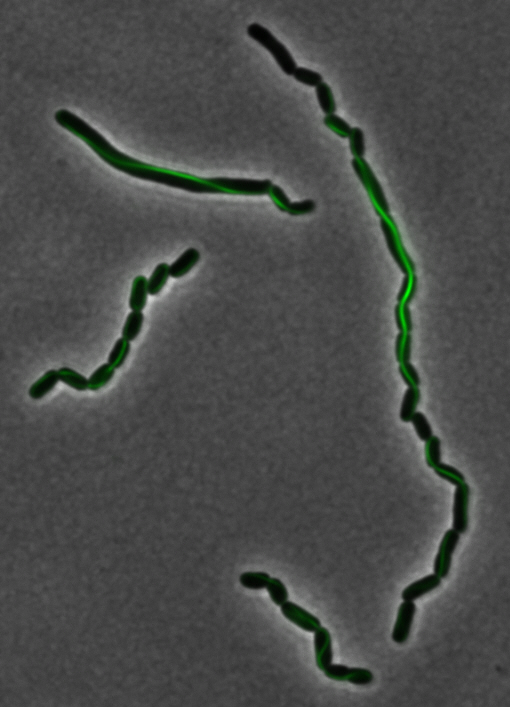
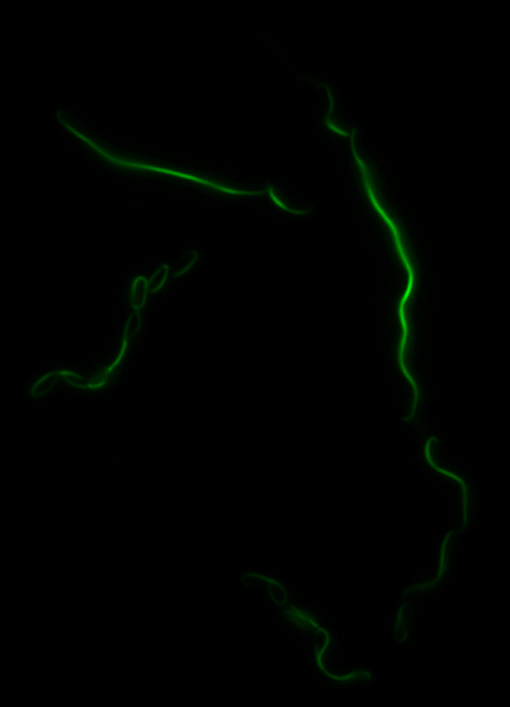
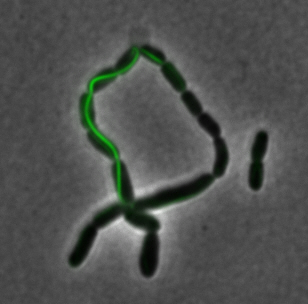
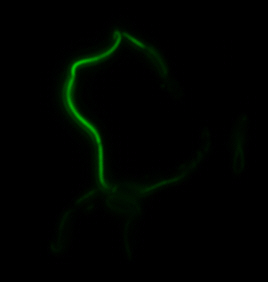
The two genes we characterized as superfolder GFP fusions are ,mamK and mamI. They each perform core functions of magnetosome formation. MamK is a bacterial actin-like cytoskeleton protein required for proper alignment of the magnetosomes in a chain. MamI is a membrane-localized protein required for magnetosome vesicle formation that has also been shown to localize on the MamK filament. For more information, see the mamAB description page. Using our two genes of interest, we created C-terminal sfGFP fusions so we could track the localization of each gene separately within E.coli.
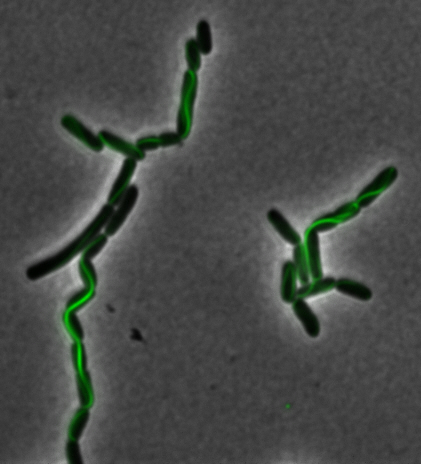
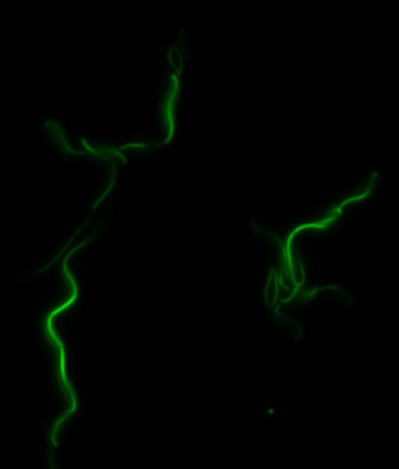
mamK: Filament formation
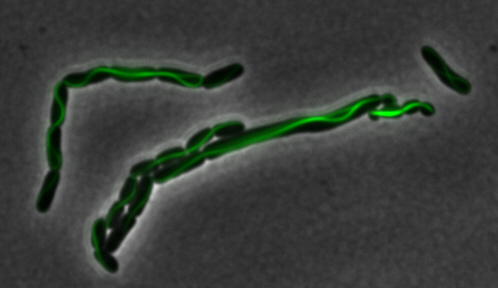
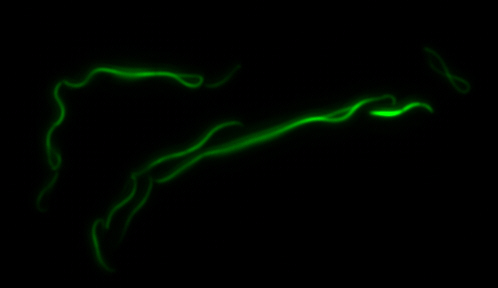
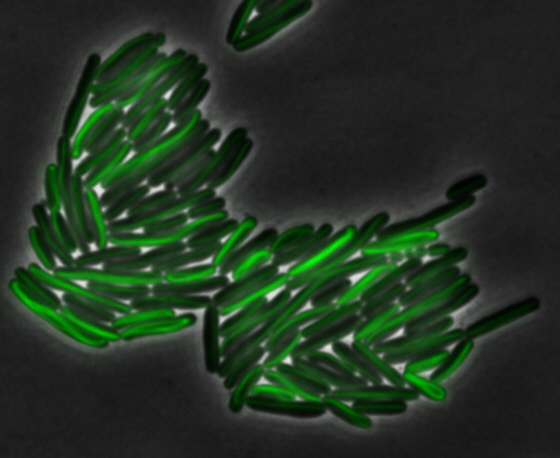
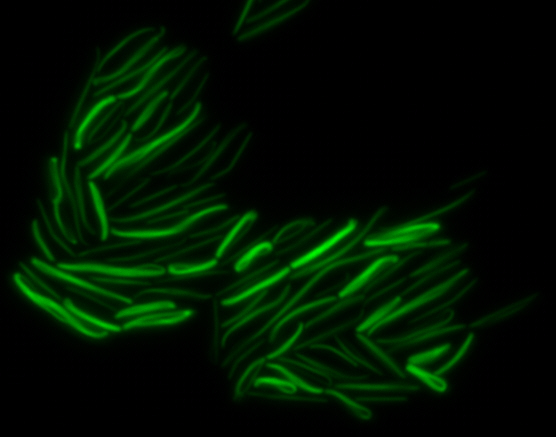
The results we obtained with our sfGFP fusions inside E.coli were comparable to those done through other studies in the host organism Magnetospirillum magneticum. Within AMB-1, mamK is a filament which runs through the length of the bacteria. In the our images of mamK, filamentous structures can be clearly seen running through the length of many bacteria. In our experimental result, there was an over- expression of mamK which connected the E.coli cells together.
mamI: Membrane Localization
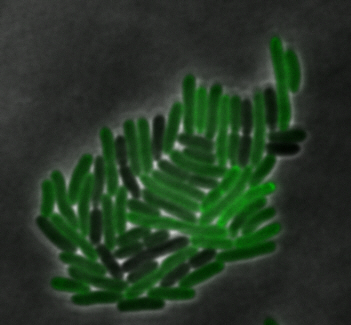
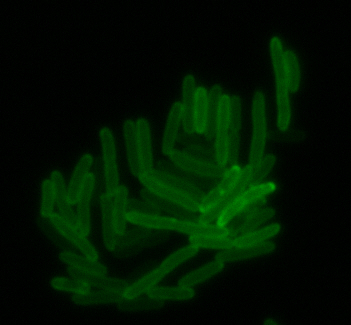
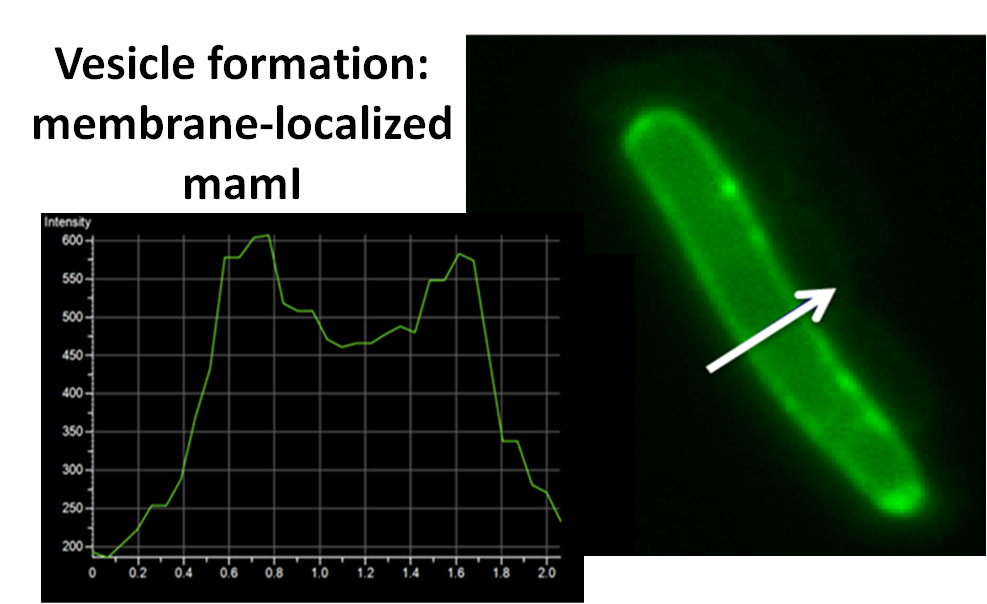
For mamI, the gene product is seen to fluorescent around the bacterial cell membrane of the bacteria but mostly concentrated at the ends. This can be seen in the fluorescence profile analysis that was taken while imaging the cells. The graph shows that as the arrow crosses the cell membrane, the fluorescent peaks are at a maximum, and through the center of the cell, the level of fluorescence decreases.
Construction of the R5 region of the Magnetosome Island in E.coli
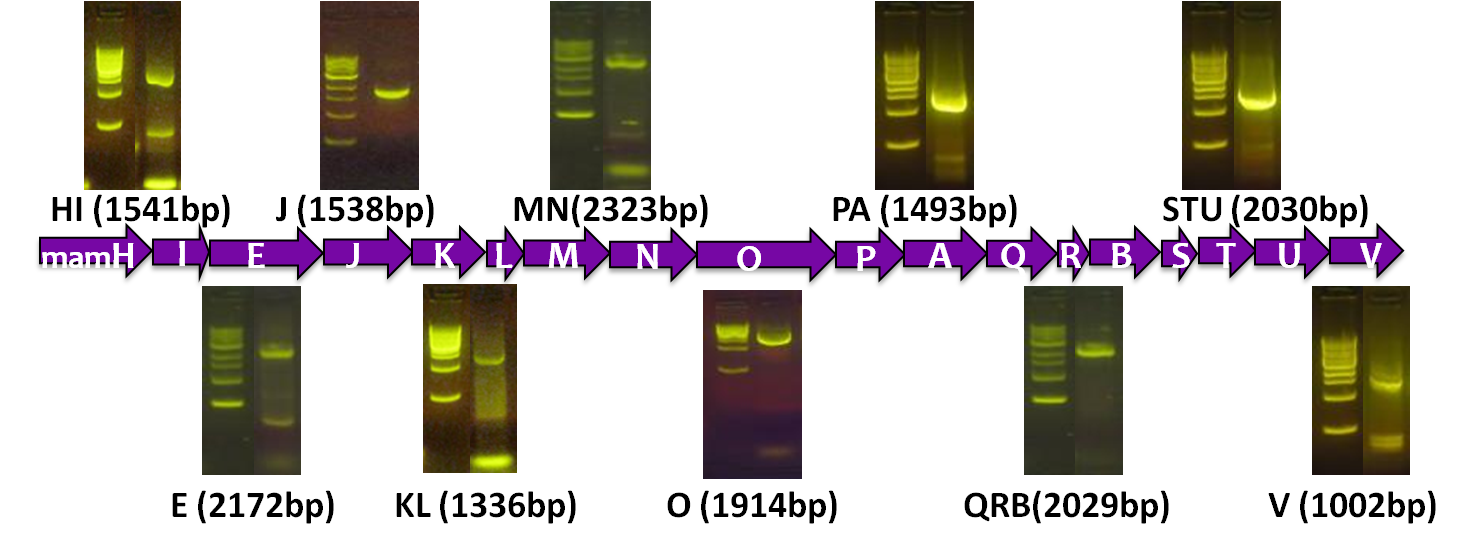
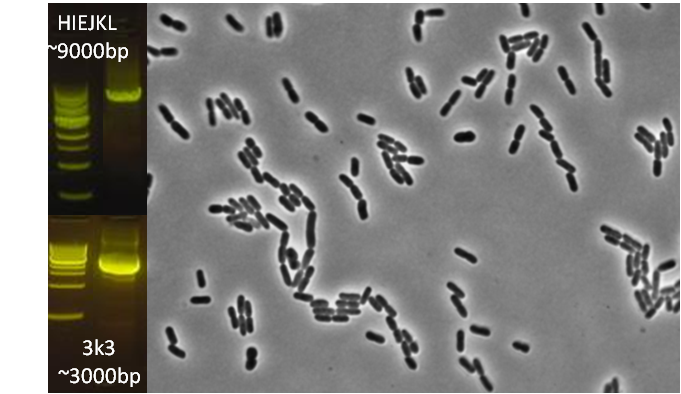
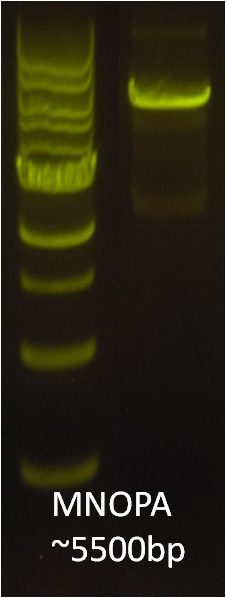
After verifying that the construction of the sfGFP-MamK scaffold worked as expected, we proceeded to create a full assembly of the mamAB operon by building three super-assemblies: mamHIEJKL, mamMNOPA, and mamQRBSTUV. The PCR products of these intermediate assemblies are shown below. The mamHIEJKL and mamQRBSTUV have been partially sequence-confirmed, and we are currently working on designing primers to fill in the gap sequences. Despite these gaps, when cells with the mamHIEJKL construct were imaged, they appeared to be forming chains.
 :
:
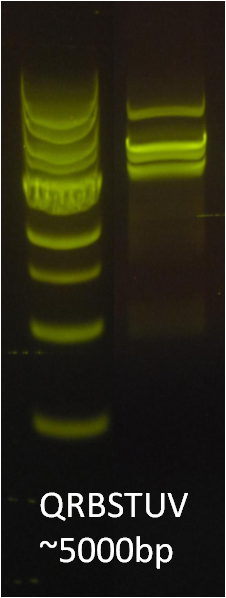
A set of the 18 essential genes for the various steps of magnetosome formation
Before piecing together the 16 kb genome of the mamAB gene cluster within the magnetosome island (MAI), we extracted out the genes in the following groups:
| Gene groups | Length (bp) |
|---|---|
| mamHI | 1541 |
| mamE | 2172 |
| mamJ | 1538 |
| mamKL | 1336 |
| mamMN | 2323 |
| mamO | 1914 |
| mamPA | 1493 |
| mamQRB | 2029 |
| mamSTU | 2030 |
| mamV | 1002 |
A table of individual gene functions
Please see our mamAB genes description page.
 "
"