|
|
| Line 22: |
Line 22: |
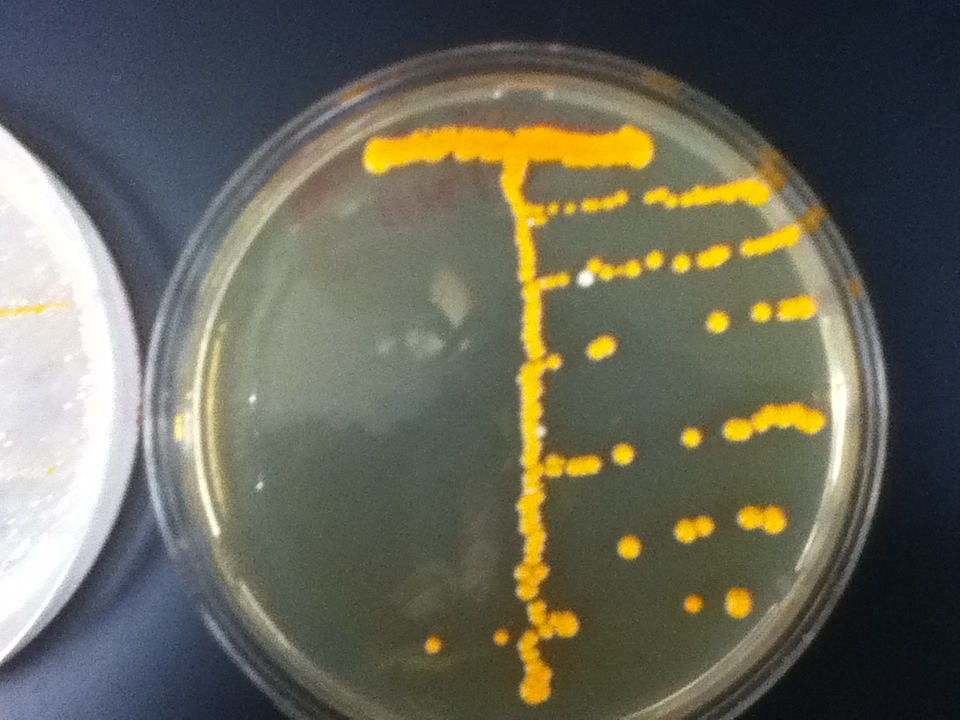
| | The strains transformed with the caretenogenic genes are a bright orange color due to all the beta-carotene they produce, as beta-carotene is an orange pigment. We confirmed its presence via HPLC using a standard. | | The strains transformed with the caretenogenic genes are a bright orange color due to all the beta-carotene they produce, as beta-carotene is an orange pigment. We confirmed its presence via HPLC using a standard. |
| | | | |
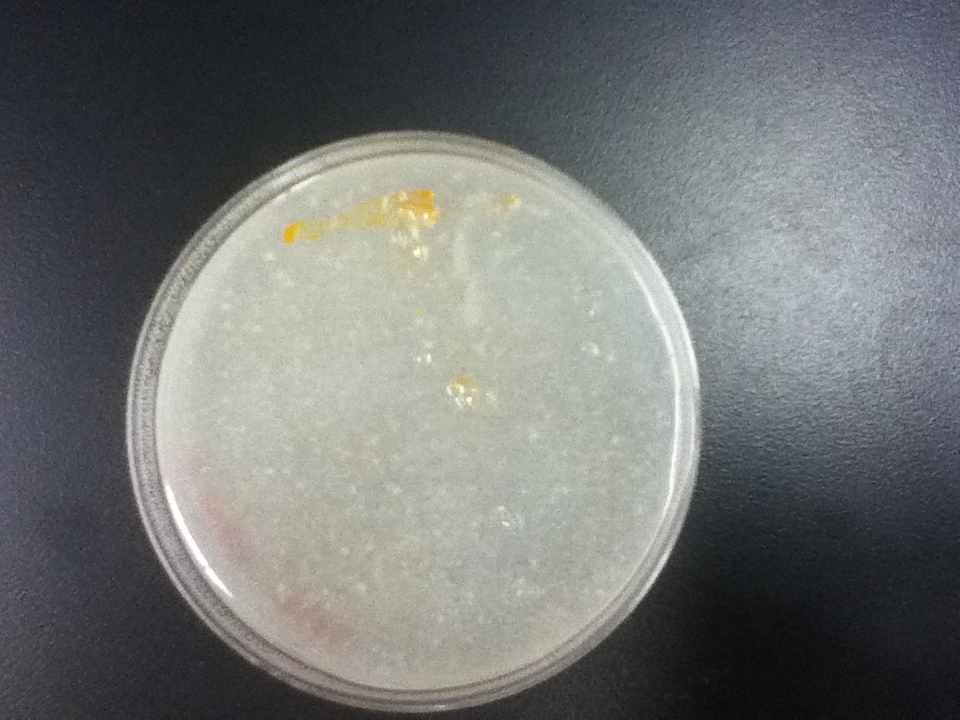
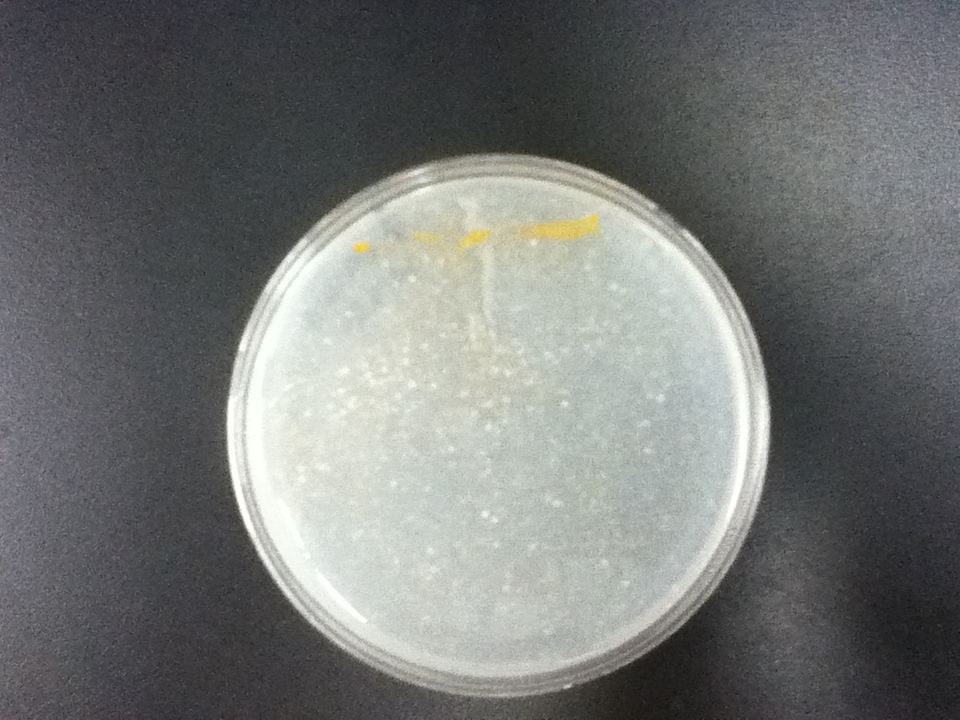
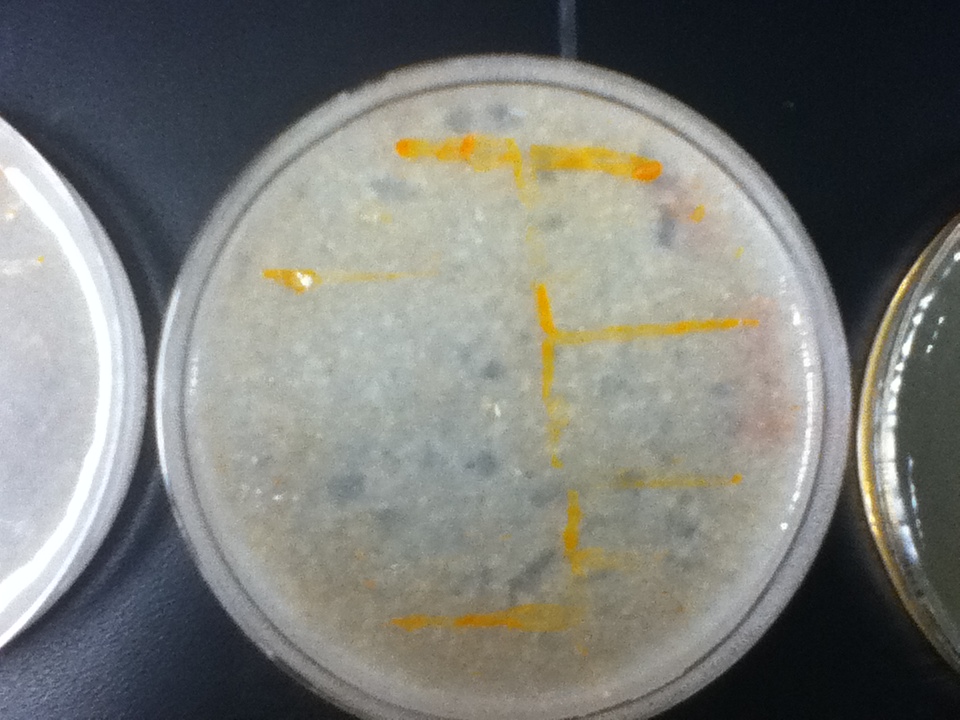
| - | On a first visual comparison of growth on dough media vs YPD we did see a significantly slower growth on dough media than on YPD. This is to be expected considering there is a large excess of nutrients on the YPD plates. There was still significant growth on the dough media plates however, enough to show that it would be viable to use in bread. | + | <gallery widths=70> |
| | + | File:Dough_media-negative_control.jpg |
| | + | File:Dough_media_1.jpg |
| | + | File:Dough_media_2.jpg |
| | + | File:File:Dough_media_3.jpg |
| | + | File:Dough_media_4.jpg |
| | + | File:Dough media-pos ctrl.jpg |
| | + | </gallery> |
| | + | |
| | + | On a first visual comparison of growth on dough media vs YPD we did see a significantly slower growth on dough media than on YPD. This is to be expected considering there is a large excess of nutrients on the YPD plates. There was still significant growth on the dough media plates however, enough to show that it would be viable to use in bread. |
| | + | |
| | + | We then took it one step further and showed that baking bread with the Vitamin A yeast was possible. |
| | | | |
| | =====Spectroscopy and HPLC===== | | =====Spectroscopy and HPLC===== |
Results
The strains transformed with the caretenogenic genes are a bright orange color due to all the beta-carotene they produce, as beta-carotene is an orange pigment. We confirmed its presence via HPLC using a standard.
On a first visual comparison of growth on dough media vs YPD we did see a significantly slower growth on dough media than on YPD. This is to be expected considering there is a large excess of nutrients on the YPD plates. There was still significant growth on the dough media plates however, enough to show that it would be viable to use in bread.
We then took it one step further and showed that baking bread with the Vitamin A yeast was possible.
Spectroscopy and HPLC
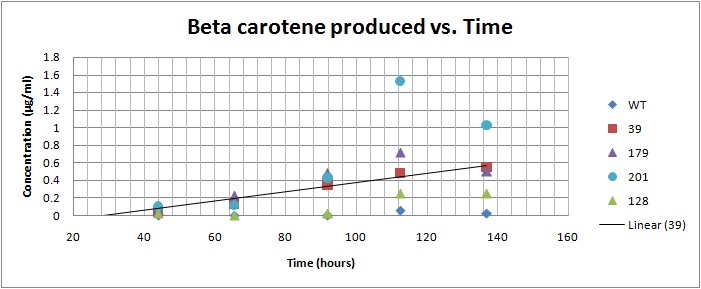
Beta carotene vs. Time for yeast strains 39, 128, 179, 201[1]
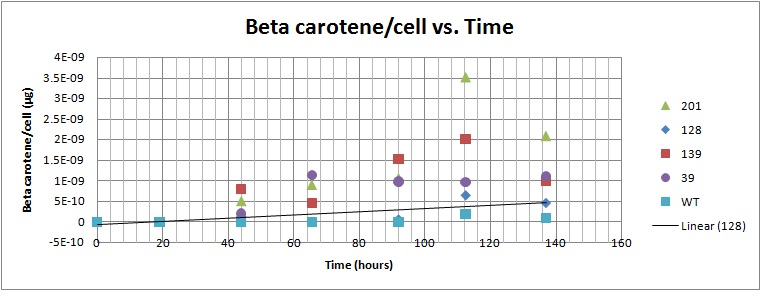
Beta carotene/cell vs. Time for yeast strains 39, 128, 179, 201[1]
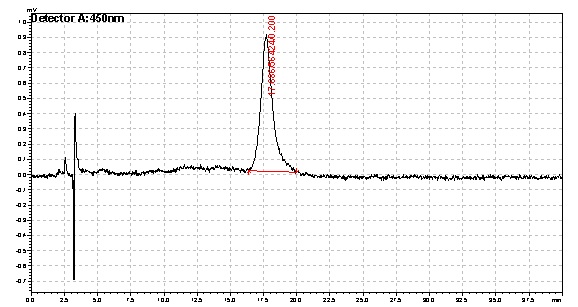
Beta carotene extracted from yeast strain 210
Based on the results of our Spectroscopy experiments measuring beta-carotene versus time and characterization by the use of HPLC, we can see that the production of beta-carotene over time increases at a linear rate. The results of the HPLC confirm that the yeast cells are in fact producing beta carotene, as the absorption peak at 450nm corresponds to the absorption maxima of beta-carotene. Before running the samples on the HPLC, beta carotene was extracted from cell extract using hexane, as it would only isolate highly hydrophobic molecules, such as beta-carotene. As seen in following Spectroscopy and HPLC graphs, beta carotene production and characterization can be quantified.
Protein Purification
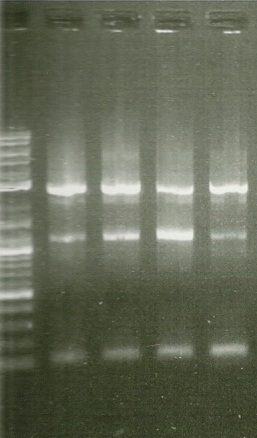
1st round PCR Gel. Lanes from left to right: 2kb ladder, BTS1, crtE, crtI, crtYB
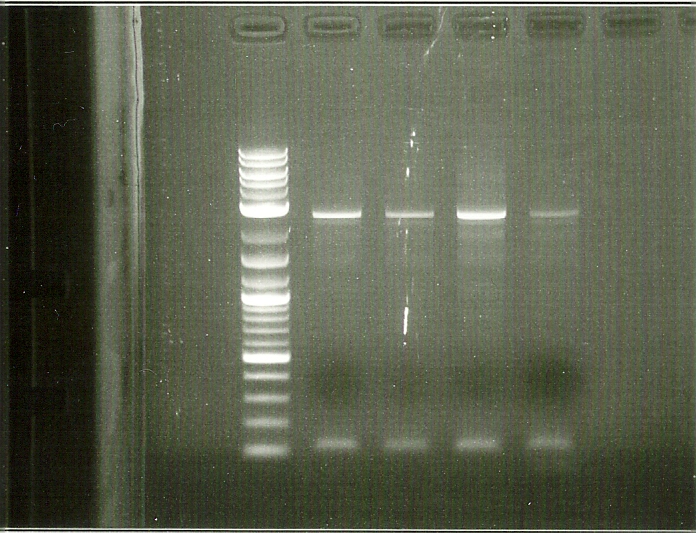
2nd round PCR Gel: Lanes from left to right: 2kb ladder, BTS1, crtE, crtI, crtYB
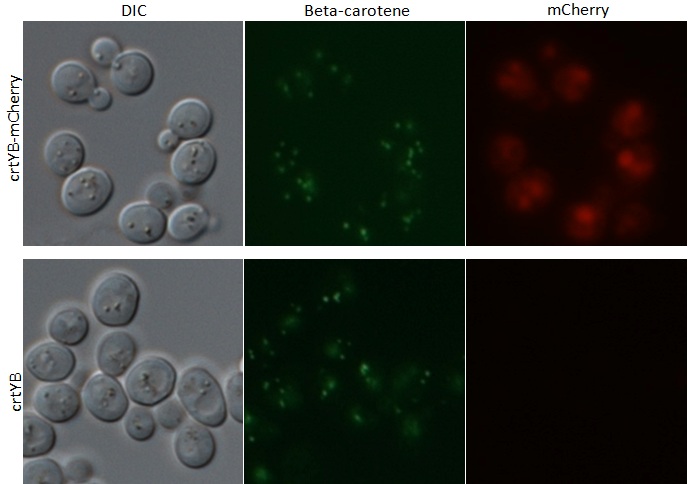
Microscopy Images from tagged crtYB-mCherry tagged yeast and control
References
1. High-Level Production of Beta-Carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Successive Transformation with Carotenogenic Genes from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous
René Verwaal,1, Jing Wang,1 Jean-Paul Meijnen,1 Hans Visser,1,Gerhard Sandmann,2 Johan A. van den Berg,1, and Albert J. J. van Ooyen1*
 "
"