Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/T7 promoter variants/t7prom/making
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Gene-Specific PCR) |
(→Extension PCR: Part I) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Extension PCR: Part I == | == Extension PCR: Part I == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The PCR product from the gene-specific PCR becomes the DNA template for the second PCR, which is oftentimes called the "Extension PCR". To find out more about the protocol for this PCR, click [[https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Protocols/T7-ext|here]]. This PCR adds the T7 promoter (or some variant thereof). | ||
[[File:t7_rbs_lysis_term.png]] | [[File:t7_rbs_lysis_term.png]] | ||
Revision as of 23:02, 21 September 2011
The Making of a T7 Promoter Variant
Gene-Specific PCR
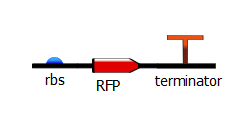
The first PCR that is used to build a full T7 promoter variant is called a "gene-specific" PCR. The primers are chosen so as to add a ribosome-binding site (rbs) upstream of the reporter gene (here RFP or Lysis) and a terminator downstream of the gene. It is in effect a typical PCR.
Extension PCR: Part I
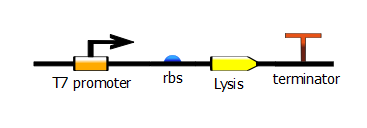
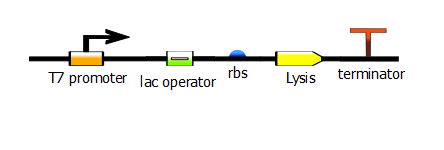
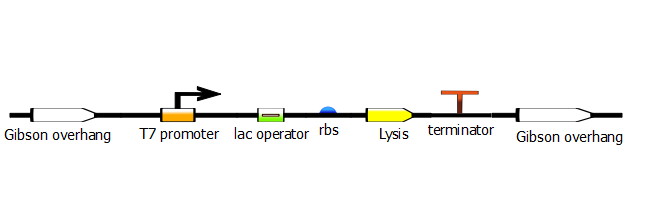
The PCR product from the gene-specific PCR becomes the DNA template for the second PCR, which is oftentimes called the "Extension PCR". To find out more about the protocol for this PCR, click [[1]]. This PCR adds the T7 promoter (or some variant thereof).
Extension PCR: Part II
 "
"