Team:DTU-Denmark/Bioinformatic
From 2011.igem.org
Alewinska88 (Talk | contribs) (→Approach) |
Alewinska88 (Talk | contribs) (→Results) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Results == | == Results == | ||
| - | From the sequence logo it can be seen that the structure, but not the sequence, is conserved in the first stemloop, whereas both the structure and sequence is conserved in the second stemloop. The length between the two stemloops varies a few nucleotides among the species, which is seen from the introduced gaps in the alignment. Another interesting feature is the conserved A/U stretch around position 40 which resemble the characteristic Hfq binding motif<span class="superscript">[[#References|[5]]]</span>. The sequence which base-pair with the ChiP RBS is perfectly conserved, this might be due to evolutionary selection for a strong RBS rather than functionally constraints (AAAGAGG is not a bad RBS, and is somewhat similar to the RBS BioBricks: BBa_B0030, BBa_B0034, BBa_B0035, and BBa_B0064 which has a relative strength of 0.35-1.124). Consequently we expect that complementary mutations can freely be made to match the RBS in any mRNA of interest. | + | From the sequence logo it can be seen that the structure, but not the sequence, is conserved in the first stemloop, whereas both the structure and sequence is conserved in the second stemloop. The length between the two stemloops varies a few nucleotides among the species, which is seen from the introduced gaps in the alignment. Another interesting feature is the conserved A/U stretch around position 40 which resemble the characteristic Hfq binding motif<span class="superscript">[[#References|[5]]]</span>. The sequence which base-pair with the ChiP RBS is perfectly conserved, this might be due to evolutionary selection for a strong RBS rather than functionally constraints (AAAGAGG is not a bad RBS, and is somewhat similar to the RBS BioBricks: BBa_B0030, BBa_B0034, BBa_B0035, and BBa_B0064 which has a relative strength of 0.35-1.124). Consequently, we expect that complementary mutations can freely be made to match the RBS in any mRNA of interest. |
[[File:DTU1 Sequence logo.png|665px|thumb|center|'''RNALogo graph''' generated with RNALogo<span class="superscript">[[#References|[1]]]</span> as well as sequence logo and percentage of A/U (green) and G/C (yellow)nucleotides out of 24 sequences. Notice, that perfectly conserved nucleotides are highlighted with pink in the graph.]] | [[File:DTU1 Sequence logo.png|665px|thumb|center|'''RNALogo graph''' generated with RNALogo<span class="superscript">[[#References|[1]]]</span> as well as sequence logo and percentage of A/U (green) and G/C (yellow)nucleotides out of 24 sequences. Notice, that perfectly conserved nucleotides are highlighted with pink in the graph.]] | ||
| - | '''To conclude''', the study indicates several constrains for engineering a novel sRNA derived from ChiX. First of all must the sRNA contain a Hfq binding motif, a terminal poly-U stretch and two stemloops | + | '''To conclude''', the study indicates several constrains for engineering a novel sRNA derived from ChiX. First of all must the sRNA contain a Hfq binding motif, a terminal poly-U stretch and two stemloops (the first for which only the structure seems important in contrast to the second for which both the structure and the majority of the nucleotides appear essential). Taking these restrictions into account we believe it is possible to rationally design a sRNA to target any gene of interest. |
== Species == | == Species == | ||
Revision as of 08:20, 21 September 2011
Bioinformatics
Contents |
Motivation
A bioinformatic study was performed to investigate the flexibility when engineering sRNA regulation genetically. The aim was to elucidate sequence and structure conservation for relevant sRNA homologs among 24 bacterial species representative of the diversity within Enterobacteriaceae.
Approach
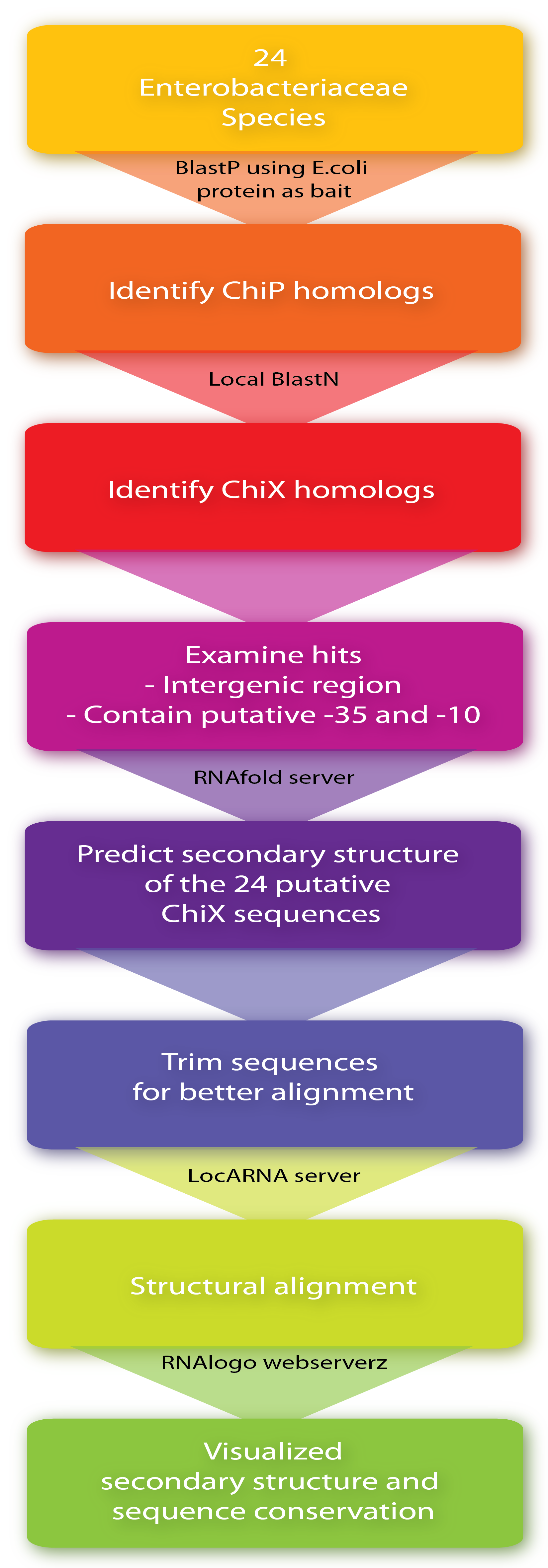
Firstly, ChiP homologs including its ribosome binding site (RBS) were identified in the 24 species by BlastP using the E. coli protein as bait. Then, to identify putative ChiXs a local BlastN search was performed with the sequence flanking the RBS as query and the given genome as target (window size of 7). Hits in coding genes were excluded since we restrict ChiX-homologs to be in intergenic regions as is the case in E.coli and Salmonella[4][2]. In addition, hits which did not seem to have a putative -35 and -10 region in a reasonable distance from the putative start-site were also excluded, leaving one hit for each of the 24 sequences. Next, the secondary structure of the 24 putative ChiX homologs were analysed by RNAfold (default parameter setting) from the Vienna RNA package version 2.0.0[3] and sequence lengths were selected for further analysis so they start with one or two nucleotides upstream of the first stemloop and end with four or five Ts downstream of the second stem-loop. In the next step, a structural alignment was made by the LocARNA server, also from the Vienna RNA package version 2.0.0[3] (using default parameter settings), and finally, the RNA secondary structure and sequence conservation were visualized by RNAlogo webserver[1]. Afterwards, the percentage of G/C and A/T (out of 24) was manually calculated. Note that at gap positions these two numbers do not sum to 100.
Results
From the sequence logo it can be seen that the structure, but not the sequence, is conserved in the first stemloop, whereas both the structure and sequence is conserved in the second stemloop. The length between the two stemloops varies a few nucleotides among the species, which is seen from the introduced gaps in the alignment. Another interesting feature is the conserved A/U stretch around position 40 which resemble the characteristic Hfq binding motif[5]. The sequence which base-pair with the ChiP RBS is perfectly conserved, this might be due to evolutionary selection for a strong RBS rather than functionally constraints (AAAGAGG is not a bad RBS, and is somewhat similar to the RBS BioBricks: BBa_B0030, BBa_B0034, BBa_B0035, and BBa_B0064 which has a relative strength of 0.35-1.124). Consequently, we expect that complementary mutations can freely be made to match the RBS in any mRNA of interest.
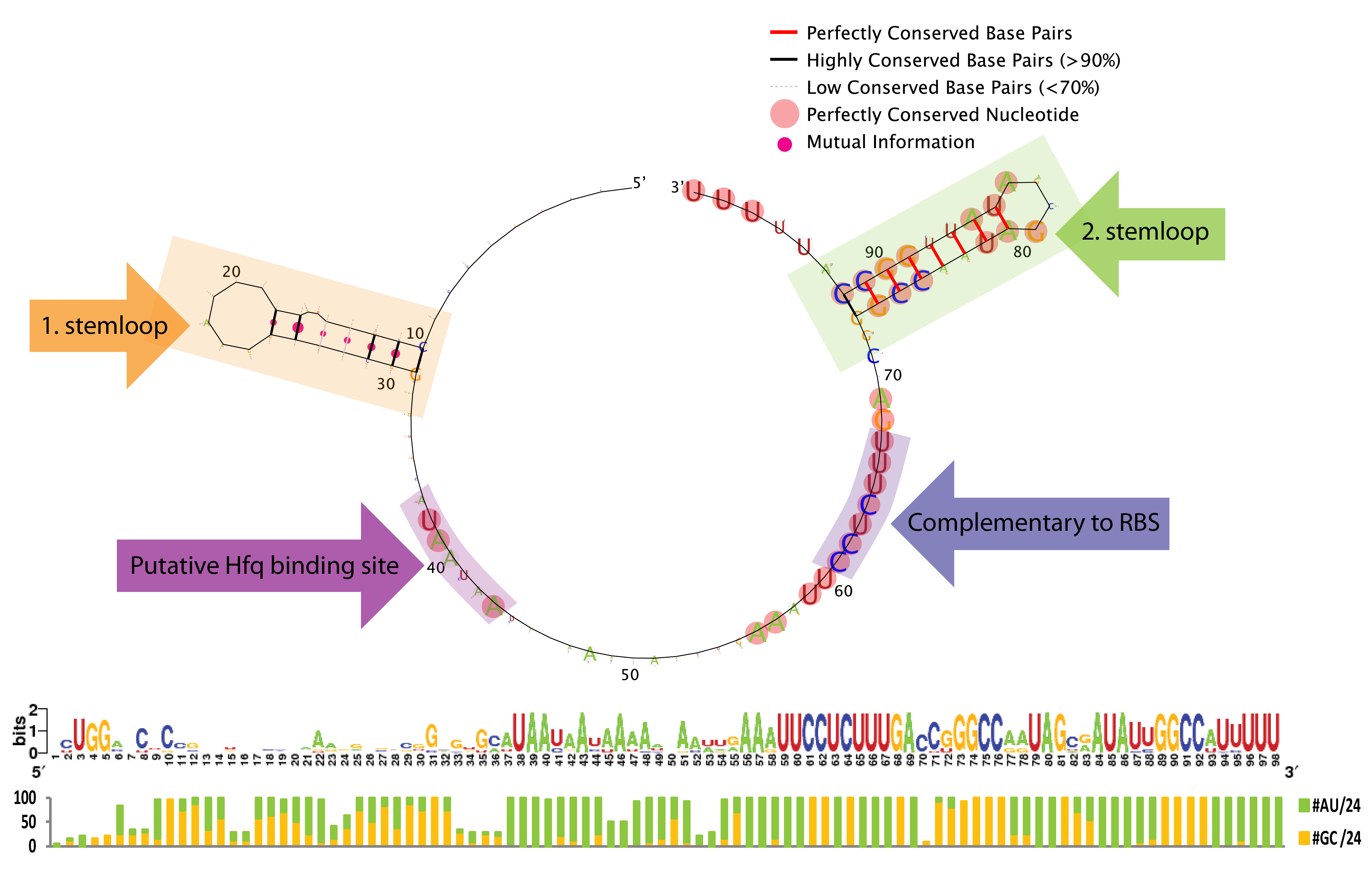
To conclude, the study indicates several constrains for engineering a novel sRNA derived from ChiX. First of all must the sRNA contain a Hfq binding motif, a terminal poly-U stretch and two stemloops (the first for which only the structure seems important in contrast to the second for which both the structure and the majority of the nucleotides appear essential). Taking these restrictions into account we believe it is possible to rationally design a sRNA to target any gene of interest.
Species
Below are the names as accession numbers listed for the 24 species included in the analysis.
| Species | Accession Number |
| Citrobacter koseri | NC_009792 |
| Citrobacter rodentium | NC_013716 |
| Cronobacter sakazakii | CP000783 |
| Cronobacter turicensis | FN543093 |
| Edwardsiella ictaluri | CP001600 |
| Edwardsiella tarda | CP002154 |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | CP002824 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | CP002272 |
| Enterobacter sp. | CP000653 |
| Erwinia billingiae | FP236843 |
| Escherichia coli | AE005174 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | CP002910 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | CP000647 |
| Klebsiella variicola | CP001891 |
| Pantoea sp. | CP002433 |
| Salmonella bongori | FR877557 |
| Salmonella enteric | NC_010067 |
| Serratia proteamaculans | CP000826 |
| Shigella flexneri | AE014073 |
| Shigella sonnei | NC_007384 |
| Yersinia enterocolitica | FR729477 |
| Yersinia pestis | CP000308 |
| Yersinia pestis | NC_005810 |
| Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | NC_006155 |
Alignment
The used structural alignment generated by the LocARNA server from the Vienna RNA package version 2.0.0[3].
Erwinia_billingi -----CCCCG-CUGGCAACCUGAUUGCUACCGG---AUAACUAAAAUCAUA-AAAAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCGAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Pantoea_sp__At_9 AUUGGCCCGCGCCAGCCA-GUAAUGGCUGUGUG---AUAACCAAAAUCAUA-AACAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCGAUAGUAAUAUUGGCCUUCUUU Serratia_proteam -C---UAUUGUAACCGUUAACA--GGGUUACAAUGCGUA-UAACUACAAUACAAGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CUGGCCAGUAGCGAUAUUGGCCACUUUU Yersinia_enteroc -CU-GCUC--AUAUUUUCCGCAAGGAAUGUGAGGGCUUAAUAACUAAAAUAAUGAAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CUGGCCGAUAGCGAUAUCGGCCAUUUUU Yersinia_pesti_1 --UGGCGCUCACAUUAUCCGCAAGGAGUGUGAGUGCUUAAUAACAAAAAUAAUGAAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CUGGCCGGUAGUGAUAUCGGCCAUUUUU Yersinia_pestis_ --UGGCGCUCACAUUAUCCGCAAGGAGUGUGAGUGCUUAAUAACAAAAAUAAUGAAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CUGGCCGGUAGUGAUAUCGGCCAUUUUU Yersinia_pseudot -CUGGUGCUCACAUUAUCCGCAAGGAGUGUGAGUGCUUAAUAACAAAAAUAAUGAAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CUGGCCGGUAGUGAUAUCGGCCAUUUUU Citrobacter_rode --------ACCGUC--GCUUAA-AGCGGCGGC----AUAACAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Cronobacter_saka -----A--ACCGUC--CGCUAAGGCGCACGGC----AUAACGACAAUAACG--AAAAGUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAGUAGCGAUACUGGCCUUCUUU Cronobacter_turi --------ACCGUU--CGCUAACGCGCACGGC----AUAACGAUAAUAACG---AAAGUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAGUAGCGAUACUGGCCUUCUUU Edwardsiella_ict -----ACCGGGCAC--CCCUUGGGGGGCGCCC-GGAAUAAUAAU---AUC---UGAAGUUCCUCUUUGACUG-GCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCUUUUUU Edwardsiella_tar -----A--CCGGGU--CCCUAUGGGGGCCCGGCAUAAUAAUAAU---AUC---UGAAGUUCCUCUUUGACUG-GCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCUUUUUU Enterobacter_aer -----A--UCCGGG--AUGUAU--AUCCCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Enterobacter_clo -----A--UCCGGA--GUGCGA--ACUCCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AACGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGAAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Enterobacter_sp_ -----A--ACCGAG--GGUCU---CCUUCGGC----AUAAUAAU--AACGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGAAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Escherichia_coli -----C--ACCGUC--GCUUAA-AGUGACGGC----AUAAUAAUAAAAAAA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Klebsiella_pne_1 -----A--UCCGGG--AUGCAA--AUCCCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Klebsiella_pneum -----A--UCCGGG--AUGCAA--AUCCCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Klebsiella_varii -----A--UCCGGG--AUGCAA--AUCCCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Salmonella_bongo -----A--UCCGAA--GUGAAA--GCUUCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AAUGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Salmonella_enter -----A--UCCGAA--GCGAAA--GCGUCGGG----AUAAUAAU--AACGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Shigella_flexner --------ACCGUC--GCUUAA-AGUGACGGC----AUAAUAAUAAAAAAA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU Shigella_sonnei_ --------ACCGUC--GCUUAA-AGUGACGGC----AUAAUAAUAAAAAAA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGCGAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU citrobacter_kose -----A--ACCAGG--GCGCUA-CGUCCUGGC----AUAAUAAU--AACGA--UGAAAUUCCUCUUUGA-CGGGCCAAUAGAAAUAUUGGCCAUUUUU
References
[1] Chang, Tzu-Hao, Jorng-Tzong Horng, and Hsien-Da Huang. “RNALogo: a new approach to display structural RNA alignment.” Nucleic Acids Research 36, no. Suppl. S (2008): W91-W96.
[2] Figueroa-Bossi, Nara, Martina Valentini, Laurette Malleret, and Lionello Bossi. “Caught at its own game: regulatory small RNA inactivated by an inducible transcript mimicking its target.” Genes & Development 23, no. 17 (2009): 2004 -2015. http://genesdev.cshlp.org/content/23/17/2004.abstract.
[3] Hofacker, Ivo L. “Vienna RNA secondary structure server.” Nucleic Acids Research 31, no. 13 (July 2003): 3429 -3431. http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/13/3429.abstract.
[4] Overgaard, Martin, Jesper Johansen, Jakob Møller‐Jensen, and Poul Valentin‐Hansen. “Switching off small RNA regulation with trap‐mRNA.” Molecular Microbiology 73, no. 5 (September 2009): 790-800. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06807.x/abstract.
[5] Vogel, Jörg, and Ben F Luisi. “Hfq and its constellation of RNA.” Nature reviews. Microbiology 9, no. 8 (2011): 578-589.
 "
"