Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/Assembly
From 2011.igem.org
(→Reporter Plasmids) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Reporter Plasmids == | == Reporter Plasmids == | ||
| - | The reporter | + | The reporter plasmids contain a selection gene under LacI regulation, to be coupled with the TetR plasmid containing the LacI inverter. In presence of TetR the reporter gene is ''activated''. Two reporter plasmids are built: one that contains and RFP reporter and one that contains a lysis gene (also called lysis plasmid), to lyse the cells that contain valid combinations of TetR and pTet mutants, in order to recover their DNA. Their structure is illustrated below. |
[[File:EPFL-Reporter_plasmids_both.png|700px|center]] | [[File:EPFL-Reporter_plasmids_both.png|700px|center]] | ||
| - | |||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
The product of this assembly is the J61002-pTet-RFP 'backbone' plasmid. It contains an ampicillin resistance gene, a middle copy-number p15A origin, as well as RFP repressed by pTet. This plasmid is used as a template for the second step of assembly, in which the LacI inverter and reporter genes are introduced. | The product of this assembly is the J61002-pTet-RFP 'backbone' plasmid. It contains an ampicillin resistance gene, a middle copy-number p15A origin, as well as RFP repressed by pTet. This plasmid is used as a template for the second step of assembly, in which the LacI inverter and reporter genes are introduced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=== Adding the reporter === | === Adding the reporter === | ||
| Line 81: | Line 82: | ||
The resulting plasmids express either RFP or the lysis genes under Plac control. For the '''lysis''' plasmid, we transformed the Gibson-assembled plasmids into Bl21 <i>E.coli</i> strain. They constitutively express LacI, which represses the lysis cassette and allow the correct mutants to grow.For the '''RFP''' plasmid -and all the other assemblies- we used the DH5alpha strain. | The resulting plasmids express either RFP or the lysis genes under Plac control. For the '''lysis''' plasmid, we transformed the Gibson-assembled plasmids into Bl21 <i>E.coli</i> strain. They constitutively express LacI, which represses the lysis cassette and allow the correct mutants to grow.For the '''RFP''' plasmid -and all the other assemblies- we used the DH5alpha strain. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== TetR plasmid == | == TetR plasmid == | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 12 September 2011
Assembly Sequence
TODO: describe here the sequence of assembly for our plasmids: what plasmids we build; where the parts came from; what had to be done. For example, why did we have to rebuild J61002 from scratch?
This page will probably become very technical, in which case we will move it and replace by a succinct outline. The goal of this page is to keep everybody on the assembly team up to date on the ugly details of everybody's work. Leave nothing out!
Contents |
Reporter Plasmids
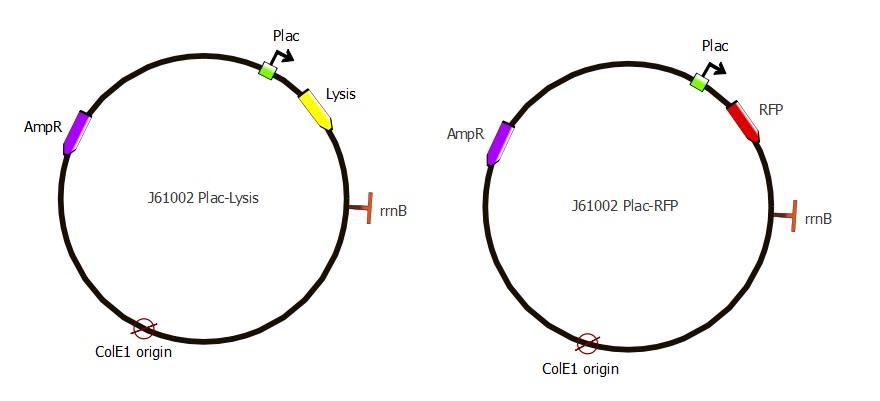
The reporter plasmids contain a selection gene under LacI regulation, to be coupled with the TetR plasmid containing the LacI inverter. In presence of TetR the reporter gene is activated. Two reporter plasmids are built: one that contains and RFP reporter and one that contains a lysis gene (also called lysis plasmid), to lyse the cells that contain valid combinations of TetR and pTet mutants, in order to recover their DNA. Their structure is illustrated below.
Backbone template assembly
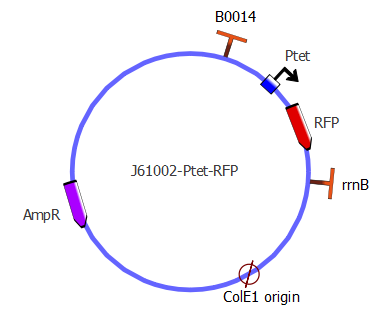
The first step of assembly was to make a J61002 backbone, containing pTet and RFP. We took the J61002 plasmid from the registry, containing ampicillin resistance, RFP and a ColE1 replication origin (medium copy number). By PCR, we then added the pTet promoter in front of RFP. Finally, the pTet-RFP and the backbone (plasmid without RFP) were assembled thank to Gibson.( vincent, please confirm this!). This was our first successful Gibson assembly.
Vincent, please document this step. What template did you use, what primers, etc? Please include links to the sequences of the template, of the expected product, and if possible a table that summarizes that all, like Nadine did.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| J61002 backbone | J61002 plasmid - from delivery kit | Terminator B0014 |
| Ptet-RFP | J61002 plasmid - from delivery kit | Ptet, RBS and spacer |
The product of this assembly is the J61002-pTet-RFP 'backbone' plasmid. It contains an ampicillin resistance gene, a middle copy-number p15A origin, as well as RFP repressed by pTet. This plasmid is used as a template for the second step of assembly, in which the LacI inverter and reporter genes are introduced.
Adding the reporter
The second step is to add the reporter gene, either RFP or lysis cassette, under Plac promoter in the J61002 backbone. Let's run through the elements one by one. We need:
- The backbone, which already contains the pTet promoter (but we don't need it anymore...)
- a pLac promoter...
- ...that represses expression of a reporter gene either RFP or the Lysis cassette.
TODO: - illustrate which parts are copied from where.
- lookup biobrick numbers.
- illustrate Gibson overhangs
The backbone is copied from the previously-assembled J61002-pTet-RFP. The RFP gene is not included in this copy; this allows the same PCR primers and products to be used for the assembly of both plasmids. In the case of the RFP plasmid, RFP is copied from the J61002-pTet-RFP plasmid, making a fragment separate from the backbone. In the case of the Lysis plasmid, the lysis device is copied from the T4 Lysis device plasmid, from the iGEM gene distribution. In both cases, the Plac promoter is introduced with the primer.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| J61002 backbone | J61002 pTet-RFP plasmid - from previous assembly | none |
| Plac-RFP | J61002 pTet-RFP plasmid - from previous assembly | Plac (already containing RBS and spacer) |
| Plac-lysis | T4 lysis plasmid | Plac (already containing RBS and spacer) |
The resulting plasmids express either RFP or the lysis genes under Plac control. For the lysis plasmid, we transformed the Gibson-assembled plasmids into Bl21 E.coli strain. They constitutively express LacI, which represses the lysis cassette and allow the correct mutants to grow.For the RFP plasmid -and all the other assemblies- we used the DH5alpha strain.
TetR plasmid
Inserting TetR under constitutive promoter
This assembly was quite tricky, as we had to test 3 plasmids before succeeding.
- We first took the J23019 plasmid from the registry and designed plasmids, but we never succeeded in amplifying it during PCRs. We assumed that probably the plasmid is not exactly the one described in the registry and went on with plasmid number 2.
- Our second choice was pSB3C5, as we could partially reuse the primers designed for J23019. But the PCR results were very weak and the assembly failed.
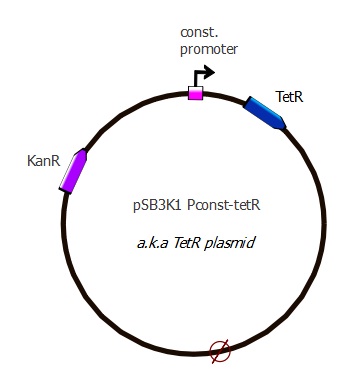
- So finally we used pSB3K1, which is really similar to pSB3C5, designed new primers and succeeded in doing the Gibson assembly!
We amplified this backbone, and added TetR under constitutive promoter to it.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| pSB3K1 backbone | pSB3K1 plasmid - from registry | none |
| Pconst-TetR | Repressilator plasmid | Constitutive promoter (Pconst), RBS and spacer |
Cutting out RFP
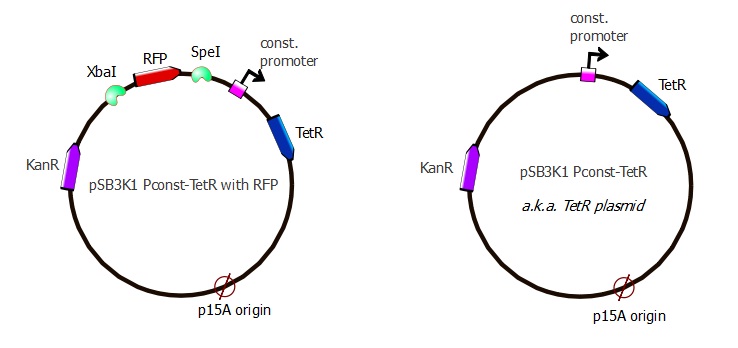
We were surprised to see that the colonies recovered after Gibson assembly were red, indicating that the pSB3K1 plasmid contains RFP. By looking at it more carefully, we discovered that we had included the Biobrick region with our primers, which explains why RFP was present in our pSB3K1 backbone. taking advantage of the BioBrick format, we digested our pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR plasmid with SpeI and XbaI and then successfully religated.
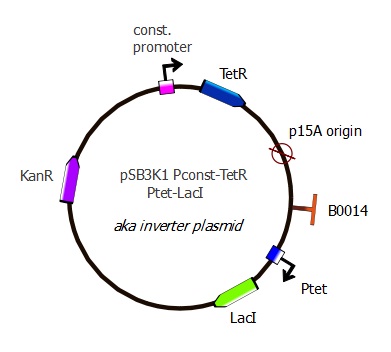
Adding Ptet-LacI
In order to test our lysis device, we added LacI under Ptet promoter to pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR (after RFP has been cut out).
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR backbone | pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR plasmid - from previous digestion | Terminator B0014 |
| Ptet-LacI | Repressilator plasmid | Ptet, RBS and spacer |
 "
"