Team:Washington/Magnetosomes/Results
From 2011.igem.org
(→What' in the toolkit and How We Assembled It) |
|||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
! Gene Function | ! Gene Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | mamH |
| - | | | + | | amb0961 |
| - | + | | mamAB | |
| + | | Related | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | mamI | ||
| + | | amb0962 | ||
| + | | mamAB | ||
| + | | Specific | ||
| + | |- | ||
| mamE | | mamE | ||
| - | | | + | | amb0963 |
| + | | mamAB | ||
| + | | Related | ||
|- | |- | ||
| mamJ | | mamJ | ||
Revision as of 01:04, 19 September 2011
About the Magnetosome Toolkit:
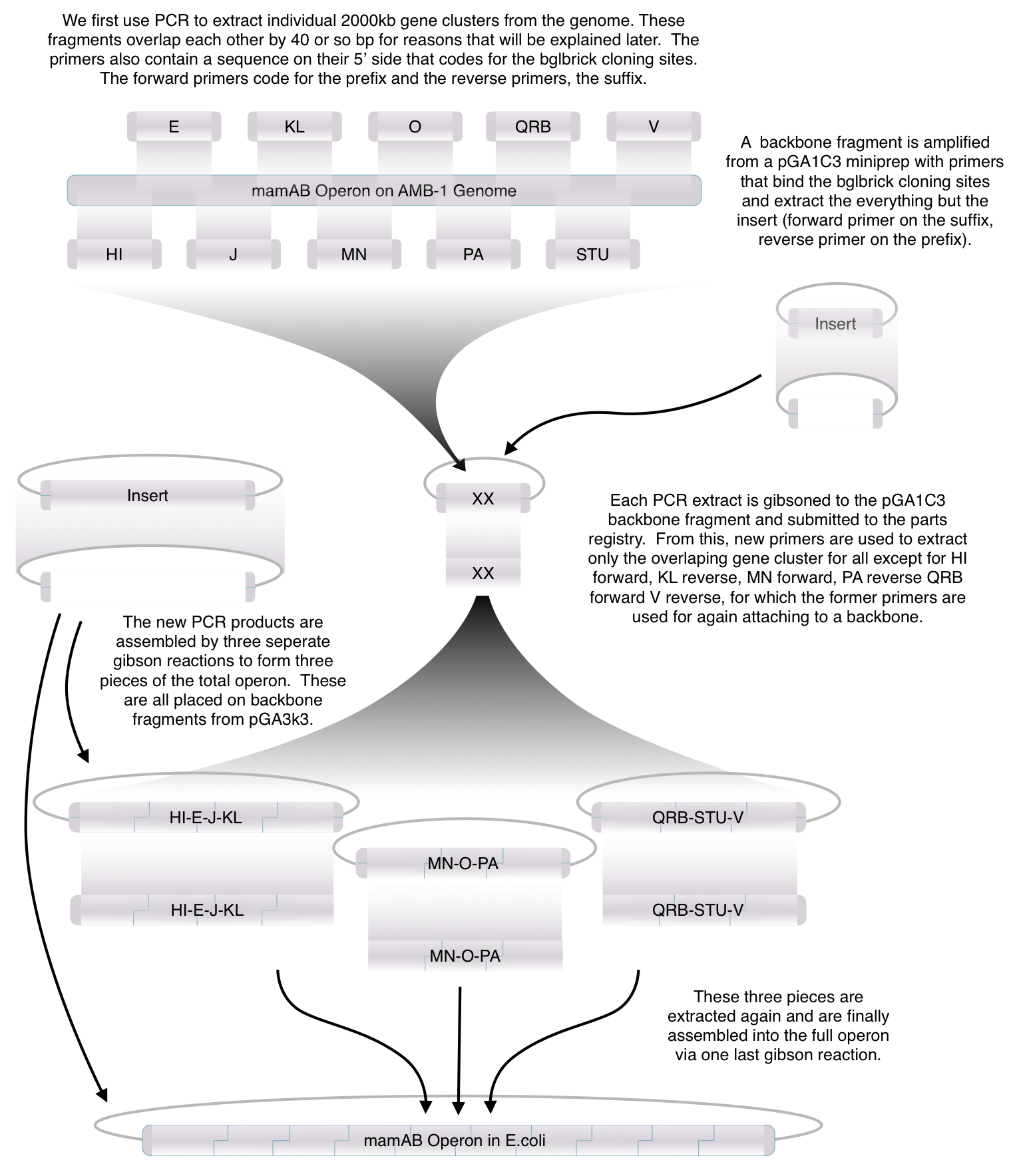
Using standard synthetic biology protocols and the vectors we created in our Gibson Assembly Toolkit, our team was able to create a "Magnetosome Toolkit" consisting of the most basic parts required for magnetosome formation. Providing this toolkit allows future iGem teams to manipulate and understand magnetosome formation to one day create magnets in various types of bacteria.
What' in the toolkit and How We Assembled It
After piecing together the 16 kb genome of the mamAB gene cluster within the magnetosome island (MAI), we extracted out the genes in the following group:
| Gene groups | Length (bp) |
|---|---|
| mamHI | 1541 |
| mamE | 2172 |
| mamJ | 1538 |
| mamKL | 1336 |
| mamMN | 2323 |
| mamO | 1914 |
| mamPA | 1493 |
| mamQRB | 2029 |
| mamSTU | 2030 |
| mamV | 1002 |
Using standard PCR protocols, these genes were extracted and..... These genes were visualized on gels and sequence confirmed; therefore, we can be sure that these are some of the many genes required for proper magnetosome formation.
As previously noted, magnetosome formation within the host-organism, Magnetospirillium magneticum, strain AMB-1, is a highly regulated step-wise process. As shown in (link: figure #), genes encode for an invagination in the inner membrane, there are genes which help align the magnetosomes into their characteristics chains, and there are genes which regulate the biomineralization of magnetic particles. Our team chose to focus on genes specifically related to magnetosome scaffolding/alignment, since it has many practical uses in synthetic biology (??? maybe we could make a link to the alkenes future if they wanted to use mamI....)
Our genes of interest were mamK and mamI as they have functions related to localization of the magnetosome. Specifically, mamK is a bacterial actin-like cytoskeleton protein required for proper alignment of the magnetosomes in a chain. mamK is also shown to localize the mamI, which is loss inhibits membrane formation.
For more information, please refer to the table below:
| Gene | AMB Number | Cluster Membership | Member of 28 genes list? (specific*/related**) | Function Summary (Vesicle chain formation, and/or biomineralization) | Gene Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mamH | amb0961 | mamAB | Related | ||
| mamI | amb0962 | mamAB | Specific | ||
| mamE | amb0963 | mamAB | Related | ||
| mamJ | 1538 | ||||
| mamKL | 1336 | ||||
| mamMN | 2323 | ||||
| mamO | 1914 | ||||
| mamPA | 1493 | ||||
| mamQRB | 2029 | ||||
| mamSTU | 2030 | ||||
| mamV | 1002 |
 "
"