Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/Data
From 2011.igem.org
(→T7 Promoter variants) |
(→Summary) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{:Team:EPF-Lausanne/Templates/Header|title=Data}} | {{:Team:EPF-Lausanne/Templates/Header|title=Data}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 5: | ||
=== Summary === | === Summary === | ||
| - | + | [[File:EPFL-Summary_drawing.png|right|thumb|250px]] | |
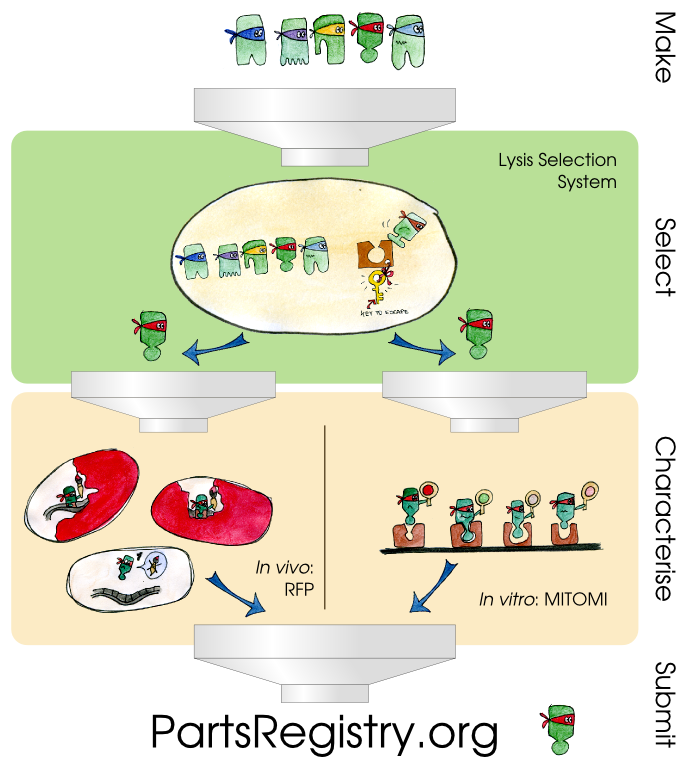
| - | In developing these three pillars, a number of parts were made. We have listed all of them and have highlighted our favorites. | + | Three components constitute our transcription factor development pipeline. The first is a selection system which lyses cells containing strong matches between a mutated transcription factor and its promoter and allows for the speedy recovery of the relevant DNA. The second component is an ''in vivo'' characterization system that uses two different reporter systems as a way to document the binding affinities of the TetR transcription factor and its promoter pTet. The third component is an ''in vitro'' characterization system called MITOMI that allows high-throughput quantitative analysis of DNA-protein interaction strengths. |
| + | |||
| + | In developing these three pillars, a number of parts were made. We have listed all of them here and have highlighted our favorites. | ||
=== Systems === | === Systems === | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
'''In Vivo Characterization''': We cloned an RFP gene under control of T7 promoter variants (parts BBa_K613001 through BBa_K613012) into a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). We also cloned TetR mutants (parts BBa_K613013 through BBa_K613019) into a a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). Both sets of plasmids were thoroughly characterized using IPTG platereader experiments. | '''In Vivo Characterization''': We cloned an RFP gene under control of T7 promoter variants (parts BBa_K613001 through BBa_K613012) into a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). We also cloned TetR mutants (parts BBa_K613013 through BBa_K613019) into a a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). Both sets of plasmids were thoroughly characterized using IPTG platereader experiments. | ||
| - | + | '''In Vitro Characterization''': We characterized TetR mutants (parts BBa_K613013, BBa_K613015, BBa_K613016, BBa_K613017, BBa_K613019) in the low copy number plasmid pSB3K1 (formerly BBa_I739202). | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | '''In Vitro Characterization''': | + | |
== Favourite parts == | == Favourite parts == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 44: | ||
=== T7 Promoter variants === | === T7 Promoter variants === | ||
| - | We submitted a family of T7 promoters with varying strength. Our lysis selection device uses what we refer to as the wild-type (100% strength) T7 Promoter: | + | We submitted a family of T7 promoters with varying strength. Our lysis selection device uses what we refer to as the wild-type (100% reported strength) T7 Promoter: |
| - | * [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613001 K613001] '''T7 Promoter''', 100% strength | + | * [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613001 K613001] '''T7 Promoter''', 100% reported strength |
In addition, we submitted the following mutants: | In addition, we submitted the following mutants: | ||
Latest revision as of 22:05, 28 October 2011
Data
Contents |
Overview
Summary
Three components constitute our transcription factor development pipeline. The first is a selection system which lyses cells containing strong matches between a mutated transcription factor and its promoter and allows for the speedy recovery of the relevant DNA. The second component is an in vivo characterization system that uses two different reporter systems as a way to document the binding affinities of the TetR transcription factor and its promoter pTet. The third component is an in vitro characterization system called MITOMI that allows high-throughput quantitative analysis of DNA-protein interaction strengths.
In developing these three pillars, a number of parts were made. We have listed all of them here and have highlighted our favorites.
Systems
Selection System: We cloned the Berkeley Lysis cassette (BBa_K112808) under control of the T7 promoter into a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202).
In Vivo Characterization: We cloned an RFP gene under control of T7 promoter variants (parts BBa_K613001 through BBa_K613012) into a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). We also cloned TetR mutants (parts BBa_K613013 through BBa_K613019) into a a low copy number plasmid (pSB3K1, formerly BBa_I739202). Both sets of plasmids were thoroughly characterized using IPTG platereader experiments.
In Vitro Characterization: We characterized TetR mutants (parts BBa_K613013, BBa_K613015, BBa_K613016, BBa_K613017, BBa_K613019) in the low copy number plasmid pSB3K1 (formerly BBa_I739202).
Favourite parts
Our three favourite parts are TetR mutants, characterised in-vivo using our reporter systems, and in-vitro by MITOMI.
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613015 BBa_K613015] TetR E37A W43S T141A mutant
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613016 BBa_K613016] TetR P39K mutant
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613017 BBa_K613017] TetR Y42F mutant
Pre-existing parts characterised
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K112808:Experience BBa_K112808 Experience Page] - The Berkeley Lysis Device: In developing our Lysis selection device, we characterised induction, and ran proof-of-principle experiments.
All other parts submitted
TetR Mutants
In addition to our three favourite tetR mutants, we created these four:
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613013 K613013] V36F mutant
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613014 K613014] V36F W43S mutant
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613018 K613018] Y42F K108E mutant
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613019 K613019] P39Q Y42M mutant
T7 Promoter variants
We submitted a family of T7 promoters with varying strength. Our lysis selection device uses what we refer to as the wild-type (100% reported strength) T7 Promoter:
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613001 K613001] T7 Promoter, 100% reported strength
In addition, we submitted the following mutants:
Variants without additional lac operator (constitutive):
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613002 BBa_K613002] T7 Promoter, 14% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613003 BBa_K613003] T7 Promoter, 30% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613004 BBa_K613004] T7 Promoter, 54% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613005 BBa_K613005] T7 Promoter, 80% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613006 BBa_K613006] T7 Promoter, 111% reported strength
Variants with additional lac operator (LacI repressed):
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613007 BBa_K613007] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 100% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613008 BBa_K613008] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 14% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613009 BBa_K613009] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 30% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613010 BBa_K613010] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 54% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613011 BBa_K613011] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 80% reported strength
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613012 BBa_K613012] T7 Promoter, LacI repressed, 111% reported strength
Medium-strength Plac
We submitted a new Plac promoter of medium strength. We characterized it with ATC inductions, using RFP as a readout.
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613000 BBa_K613000] pLac promoter, medium strength
 "
"