Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/Assembly/Assembly details
From 2011.igem.org
(→First reporter - J61002 Ptet-RFP) |
(→Cutting out RFP) |
||
| (One intermediate revision not shown) | |||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
| - | The resulting plasmid is called the '''Reporter plasmid''', it is used in our [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly#TetR_-_LacI_-_RFP_system second readout system] along with the [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly/Assembly_details#Second_plasmid_-_pSB3K1_Pconst-TetR_Ptet-LacI Inverter plasmid]. | + | The resulting plasmid is called the '''Reporter plasmid''', it is used in our [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly#TetR_-_LacI_-_RFP_system second readout system] along with the [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly/Assembly_details#Second_plasmid_-_pSB3K1_Pconst-TetR_Ptet-LacI Inverter plasmid]. You can access the complete sequence of the plasmid on [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/4/42/EPFL_J61002_Plac-RFP.txt this page]. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== TetR plasmids == | == TetR plasmids == | ||
| Line 144: | Line 142: | ||
[[File:EPFL_TetR_plasmid_cut_out_RFP.jpg|680px]] | [[File:EPFL_TetR_plasmid_cut_out_RFP.jpg|680px]] | ||
| - | Now we have the expected ''TetR plasmid'' that is used in combination with the [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly/Assembly_details#First_reporter_-_J61002_Ptet-RFP J61002 Ptet-RFP plasmid] into our [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly#TetR_-_RFP_system first readout system]. | + | Now we have the expected ''TetR plasmid'' that is used in combination with the [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly/Assembly_details#First_reporter_-_J61002_Ptet-RFP J61002 Ptet-RFP plasmid] into our [https://2011.igem.org/Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our_Project/Assembly#TetR_-_RFP_system first readout system]. The complete sequence of the plasmid is available[https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/5/5a/EPFL_PSB3K1_Pconst-TetR.txt here]. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
=== Second plasmid - pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR Ptet-LacI === | === Second plasmid - pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR Ptet-LacI === | ||
Latest revision as of 16:58, 21 September 2011
Reporter plasmids assembly
Back to Reporter systems || Ptet | Plac | Plasmid detailsWe built two different systems: one containing TetR + RFP and another containing TetR + LacI + RFP.
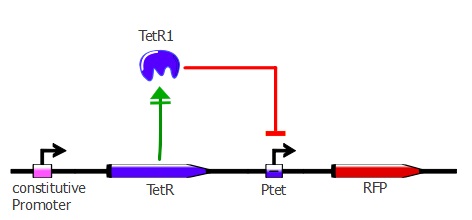
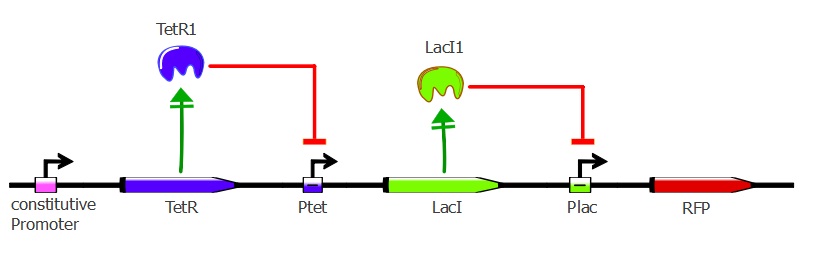
In the first readout system, RFP is repressed when TetR binds to its Ptet recognition sequence. However, the sequential use of two repressors in the second system allows us to have a direct activation of the selection gene when TetR binds its recognition sequence.
We need several plasmids to build our two systems:
- A reporter plasmid for the first system: J61002 Ptet-RFP
- A reporter plasmid for the second system: J61002 Plac-RFP
- A plasmid with TetR for the first system: pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR
- A plasmid containing TetR and LacI for the second system: pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR Ptet-LacI
Contents |
Reporter Plasmids
The reporter plasmids contain RFP under TetR or LacI regulation, depending on which readout system they are used in. Their structure is illustrated below.
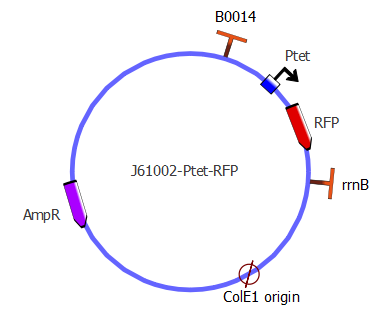
First reporter - J61002 Ptet-RFP
The first step of assembly was to make a J61002 backbone, containing pTet and RFP. We took the J61002 plasmid from the registry, containing ampicillin resistance, RFP and a ColE1 replication origin (medium copy number). By PCR, we then added the pTet promoter in front of RFP. Finally, the pTet-RFP and the backbone (plasmid without RFP) were assembled using the Gibson method. This was our first successful Gibson assembly.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| J61002 backbone | J61002 plasmid - from delivery kit | Terminator B0014 |
| Ptet-RFP | J61002 plasmid - from delivery kit | Ptet, RBS and spacer |
Details of the parts assembled:
- J61002 backbone: from Arkin lab [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61002 "J61002"]
- Terminator B0014: from the Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0014 "B0014"] (sequence copied into our plasmids)
- Ptet promoter: B0040 from the Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0040 "B0040"] (sequence copied into our plasmids)
- RBS: B0034 from the Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0034 "B0034"] (sequence copied into our plasmids)
- RFP gene: sequence from J61002 plasmid [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61002 "J61002"]
The product of this assembly is the J61002-pTet-RFP 'backbone' plasmid. It contains an ampicillin resistance gene, a middle copy-number p15A origin, as well as RFP repressed by Ptet. You can access the complete sequence of the plasmid here. This plasmid is used as a template for the second step of assembly, in which the LacI inverter and reporter genes are introduced.
This plasmid is used in our first readout system, both with the wild-type TetR and with mutants. For the results of this readout system, please refer to this page.
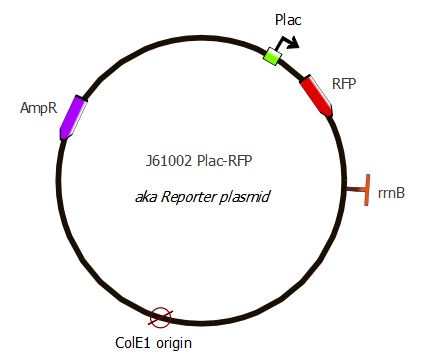
Second reporter - J61002 Plac-RFP
The second step is to add the RFP reporter gene under Plac promoter in the J61002 backbone. Let's run through the elements one by one. We need:
- The backbone, containing the replication origin and Ampicillin resistance
- a pLac promoter...
- ...that represses expression of a RFP reporter gene
The backbone is copied from the previously-assembled J61002-pTet-RFP. RFP is also copied from the J61002-pTet-RFP plasmid, making a fragment separate from the backbone. The Plac promoter is added in the primer sequence.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| J61002 backbone | J61002 pTet-RFP plasmid - from previous assembly | none |
| Plac-RFP | J61002 pTet-RFP plasmid - from previous assembly | Plac (already containing RBS and spacer) |
Details of the parts assembled:
- J61002 backbone: from Arkin lab [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61002 "J61002"]
- Plac promoter: new biobrick
- RFP gene: sequence from J61002 plasmid [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61002 "J61002"]
The resulting plasmid is called the Reporter plasmid, it is used in our second readout system along with the Inverter plasmid. You can access the complete sequence of the plasmid on this page.
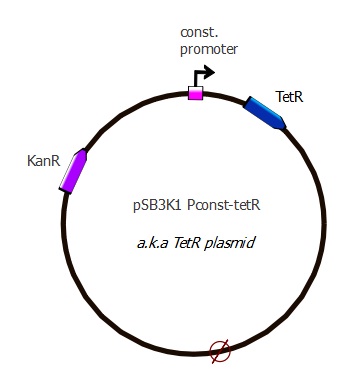
TetR plasmids
First plasmid - pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR
This assembly was quite tricky, as we had to test 3 plasmids before succeeding.
- We first took the J23019 plasmid from the registry and designed plasmids, but we never succeeded in amplifying it during PCRs. We assumed that probably the plasmid is not exactly the one described in the registry and went on with plasmid number 2.
- Our second choice was pSB3C5, as we could partially reuse the primers designed for J23019. But the PCR results were very weak and the assembly failed.
- So finally we used pSB3K1, which is really similar to pSB3C5, designed new primers and succeeded in doing the Gibson assembly!
We amplified this backbone, and added TetR under control of a constitutive promoter.
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| pSB3K1 backbone | pSB3K1 plasmid - from registry | none |
| Pconst-TetR | Repressilator plasmid | Constitutive promoter (Pconst), RBS and spacer |
Details of the parts assembled:
- Plasmid backbone: pSB3K1 from ETHZ 2007 [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:pSB3K1 "pSB3K1"] (taken from the delivery plate)
- Pconst: J23116 from Berkeley 2006 [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23116 "J23116"] (sequence copied into our primers)
- RBS: B0034 from the Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0034 "B0034"] (sequence copied into our primers)
- TetR: "TetR sequence" (623 bp)- The sequence lacks a stop codon, so we added one (TAA) with our primers.
Our TetR plasmid contains a p15A replication origin, the same medium-copy number as in J61002 to ensure that during co-transformations the 2 different plasmids are present in same amounts. The plasmid carries a Kanamycin resistance marker, since co-transformations with J61002 means we need a different selection antibiotic for each plasmid to confirm both are present (J61002 = Ampicillin resistance).
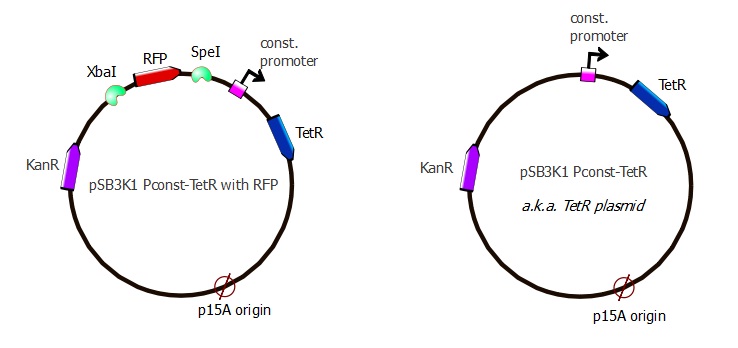
Cutting out RFP
We were surprised to see that the colonies recovered after Gibson assembly were red, indicating that the pSB3K1 plasmid contains RFP. By looking at it more carefully, we discovered that we had included the Biobrick region with our primers, which explains why RFP was present in our pSB3K1 backbone. Taking advantage of the BioBrick format, we digested our pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR plasmid with SpeI and XbaI and then successfully religated.
Now we have the expected TetR plasmid that is used in combination with the J61002 Ptet-RFP plasmid into our first readout system. The complete sequence of the plasmid is availablehere.
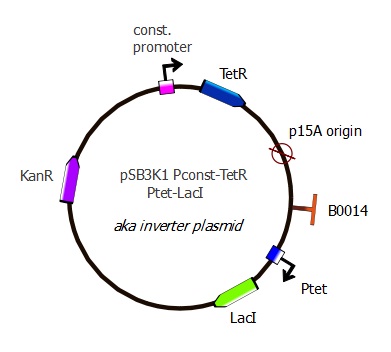
Second plasmid - pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR Ptet-LacI
For the second readout system, we added LacI under Ptet promoter to pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR (after RFP had been cut out).
| Part used for Gibson assembly | Amplified from which template | Features added with the PCR primers |
|---|---|---|
| pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR backbone | pSB3K1 Pconst-TetR plasmid - from previous digestion | Terminator B0014 |
| Ptet-LacI | Repressilator plasmid | Ptet, RBS and spacer |
Details of the parts assembled:
- Plasmid backbone containing Pconst and TetR: see preceding section
- Terminator: B0014 from the Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0014 "B0014"] (sequence copied into our primers)
- Ptet: R0040 from Registry [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0040 "R0040"] (sequence copied into our primers)
- LacI: amplified from Repressilator plasmid "LacI sequence"- The sequence lacks a stop codon, so we added one (TAA) with our primers.
This Inverter plasmid now contains a cascade reaction consisting of TetR constitutively expressed that represses LacI. It still contains p15A origin and a kanamycin resistance marker, making it compatible for cotransformations with the J61002 plasmids.
The Inverter plasmid is used in combination with the Reporter plasmid in our second reporter system. To see the experimental results of this system, please go on this page.
Sequence of the plasmid:
This plasmid was sequence-verified. While Pconst, TetR and LacI were OK, Ptet has been mutated.
 "
"