Team:Washington/Celiacs/Background
From 2011.igem.org
(→Introduction) |
(→What is Gluten Intolerance?) |
||
| (72 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| - | + | <center><big><big><big><big>'''Gluten Destruction: Background'''</big></big></big></big></center><br><br> | |
| - | == | + | ='''What is Gluten Intolerance?'''= |
| - | + | ||
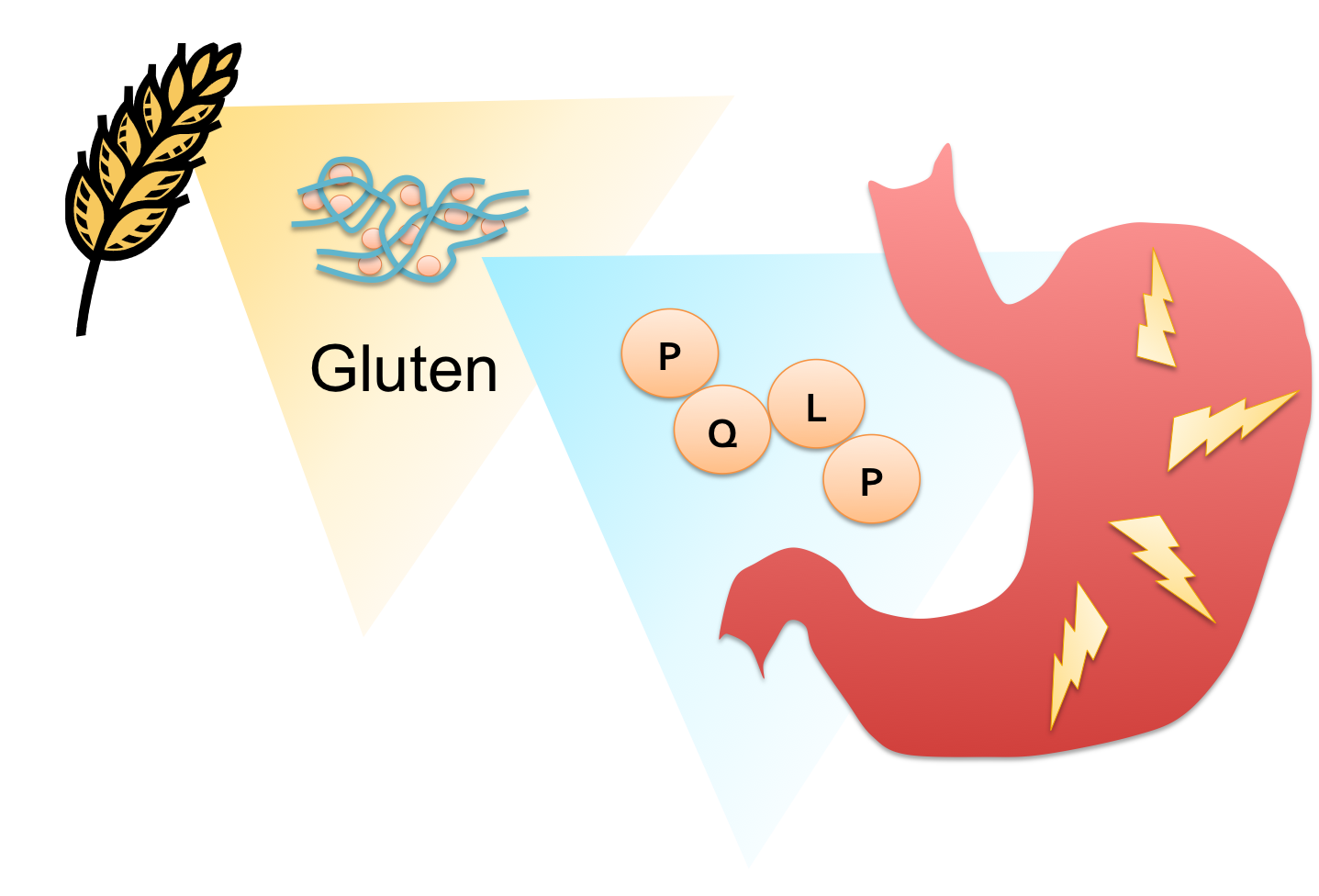
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:Washington CD Diagram.png|right|250px|thumb|Proline(P) and glutamine(Q) -rich peptide fragments of gluten provoke an immune response which causes painful inflammation in the digestive tract of gluten intolerant individuals.]] |
| + | |||
| + | People who suffer from gluten intolerance have an adverse reaction to gluten proteins found in wheat, barley, and rye products. The glutens invoke an immune response in the digestive tract of genetically predisposed individuals resulting in inflammation of the gut, impeding the absorption of nutrients. Symptoms can appear in early childhood or later in life, and range widely in severity, from diarrhea, fatigue and weight loss to abdominal distension, anemia, and neurological symptoms. There are currently no effective therapies for this lifelong disease except the total elimination of glutens from the diet. Although celiac sprue remains largely underdiagnosed, its prevalence in the US and Europe is estimated at 0.5-1.0% of the population. With this in mind, we set out to design an enzyme therapeutic for gluten intolerance that could be taken in pill form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Proline (P)- and glutamine (Q)-rich components of gluten known as ‘gliadins’ appear to be responsible for the bulk of the immune response in most patients. Their high PQ content protects gliadin oligopeptides from degradation by gastrointenstinal endoproteases, but also presents a target for drug design. Any peptidase capable of cleaving at or near the P-Q bond while remaining active at the temperature and harsh pH of the stomach would have pharmacological potential as a therapy for celiac sprue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ='''There is currently a protein therapeutic in clinical trials, but a second generation is needed'''= | ||
| + | |||
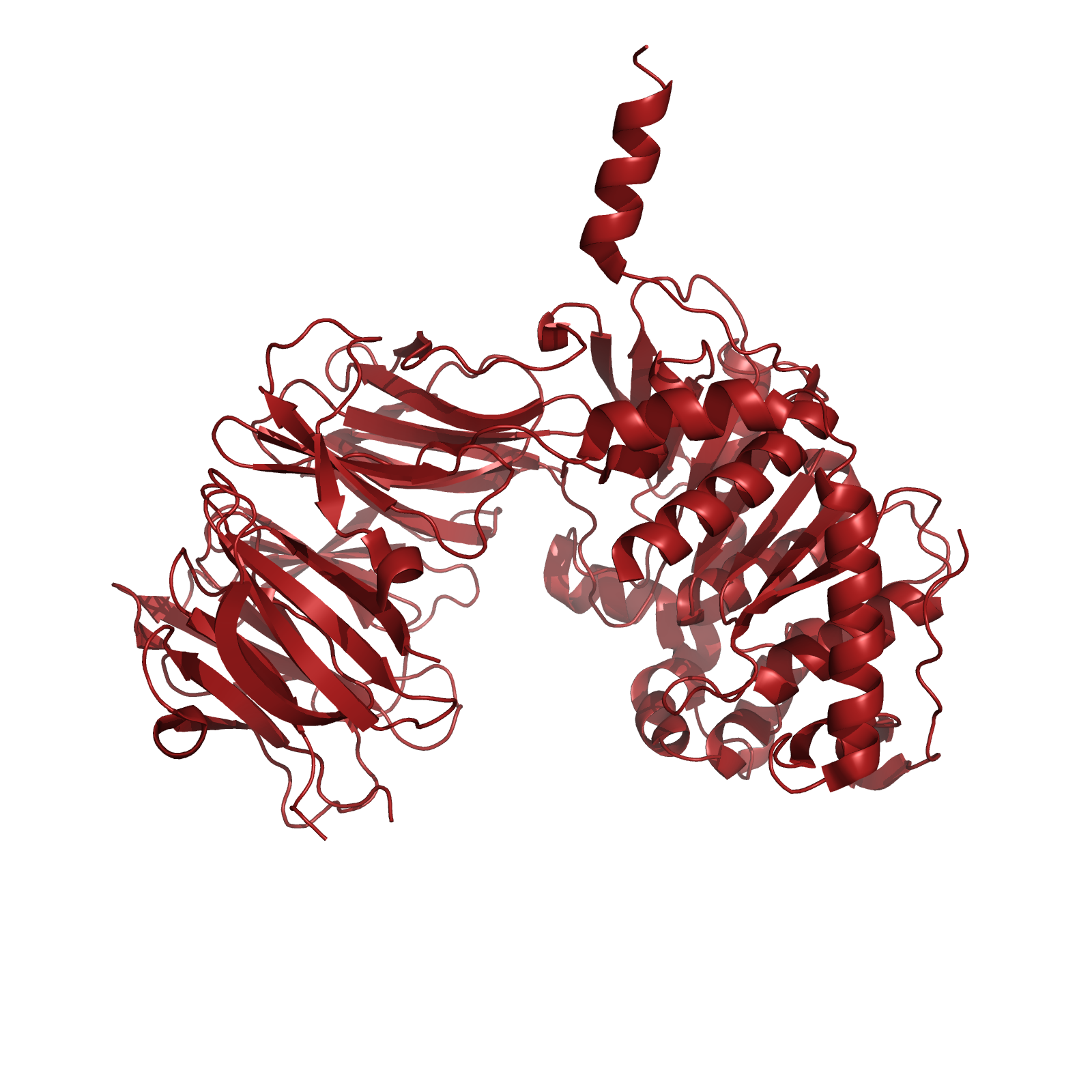
| + | [[File:Washington_SC-PEP.png|left|250px|thumb|SC-PEP, a prolyl endopeptidase from ''Sphingomonas capsulata'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | One candidate enzyme, currently in clinical trials, utilizes a prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) from ''Sphingomonas capsulata'' (SC) to hydrolyze gliadins. This enzyme was a logical drug candidate as it has a native specificity for the proline rich gliadin peptides. Unfortunately, the enzyme’s optimal activity is at pH 7, and engineering attempts to enhance its activity at relevant gastric pH levels has not yet been met with significant success. It is therefore pertinent to identify new candidate enzymes that have both activity on the gliadin PQ structural motif, as well as optimal activity at gastric pH levels during digestion around pH 4. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Here, we describe an alternative approach to identifying and engineering an enzyme therapeutic for celiac sprue | + | Here, we describe an alternative approach to identifying and engineering an enzyme therapeutic for celiac sprue. Rather than focusing primarily on substrate specificity when choosing our candidate enzyme, we identified an enzyme already capable of catalyzing peptide hydrolysis at gastric pH levels, regardless of peptide substrate specificity. Upon identification of such an enzyme we used computational tools to reengineer its substrate specificity for enhanced activity on immunogenic gliadin peptides with the common PQ structural motif. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
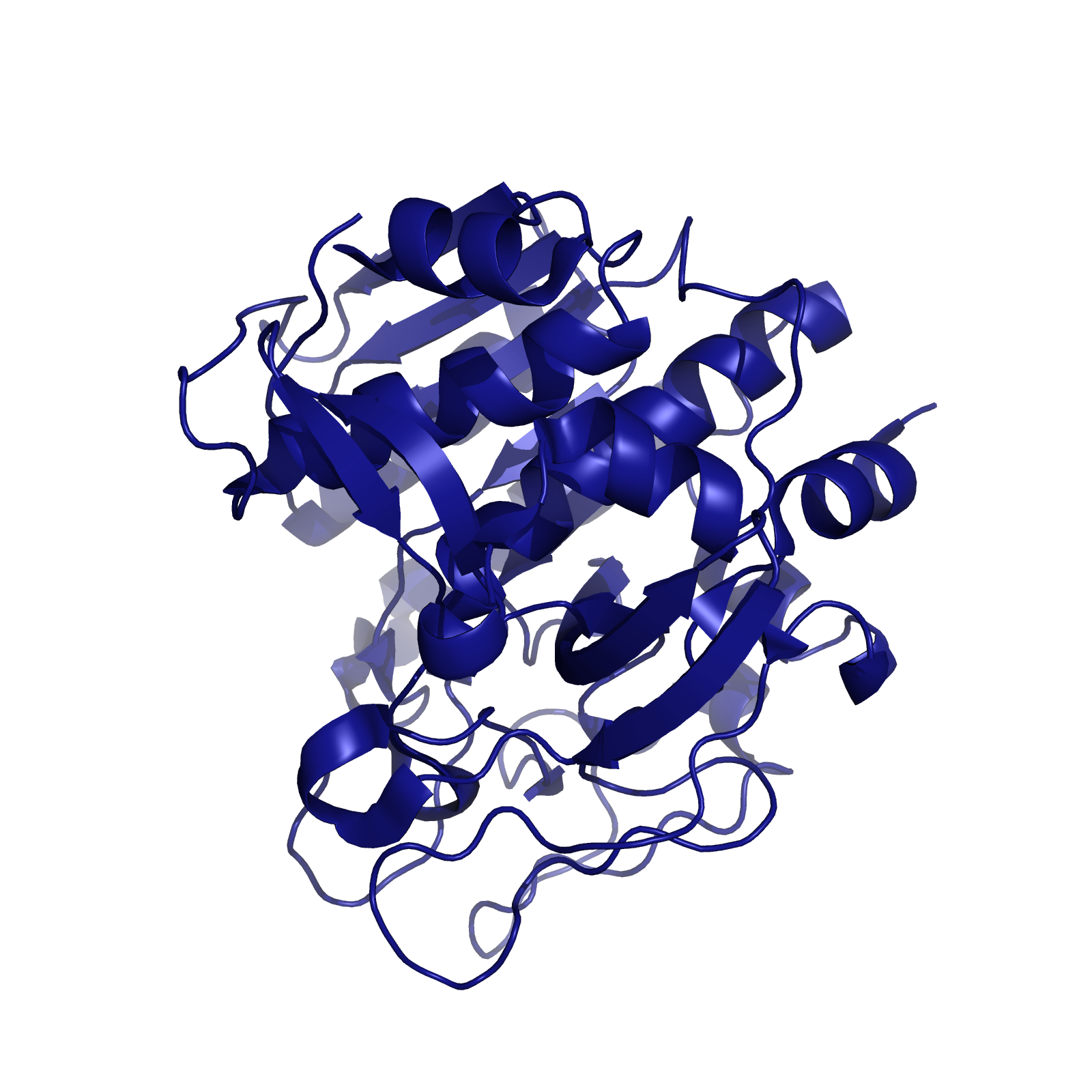
| + | [[File:Washington_Kumamolisin-As.png|right|250px|thumb|Kumamolisin-As, a protease from the thermoacidophilic bacterium ''Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ='''We have identified an enzyme that could potentially act as a therapeutic for gluten intolerance'''= | ||
| + | |||
| + | When searching for a protease with optimal activity at gastric pH levels that could be produced in a recombinant host, we identified an enzyme known as Kumamolisin-As. Kumamolisin-As, isolated from the thermoacidophilic bacterium ''Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis'' strain NTAP-1, has been shown to be produced in a recombinant host, and exhibits significant enzymatic activity at pH 2.5 and above. Its maximal activity is at about pH 4.0. It is this robust activity under acidic, gastric conditions that makes Kumamolisin-As so promising for the development of a pill for gluten intolerance. | ||
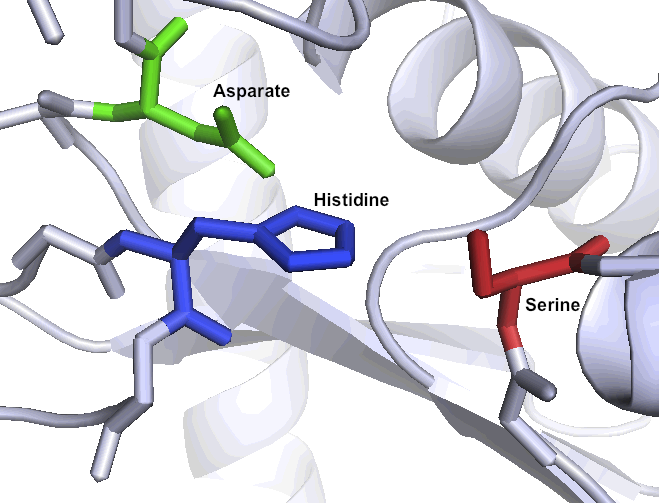
| - | = | + | ='''A special set of catalytic residues enables high activity at gastric pH levels'''= |
| - | + | One of the primary reasons that Kumamolisin-As is more active than SC-PEP at low pH is due its catalytic triad, the three amino acid residues most heavily involved in conducting the chemistry of cleaving peptides. SC-PEP is part of a large class of enzymes known as serine proteases, which make use of the catalytic triad Serine-Histidine-Aspartate. Acidic conditions can impede the histidine's ability to play its role in this triad, rendering most serine proteases inactive at low pH. Kumamolisin-As, on the other hand, is a member of the sedolisin family of serine-carboxyl peptidases, which utilize the key catalytic triad Serine-Glutamate-Aspartate to hydrolyze their substrates. It is the acidic Glutamate, as opposed to Histidine, in the triad that makes Kumamolisin-As optimal for catalyzing peptide cleavage at low pH. The native substrate for this enzyme in ''Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis'' is unknown. In addition, this enzyme has been shown to be thermostable, with an ideal temperature at 60ºC, but still showing significant activity at 37ºC. | |
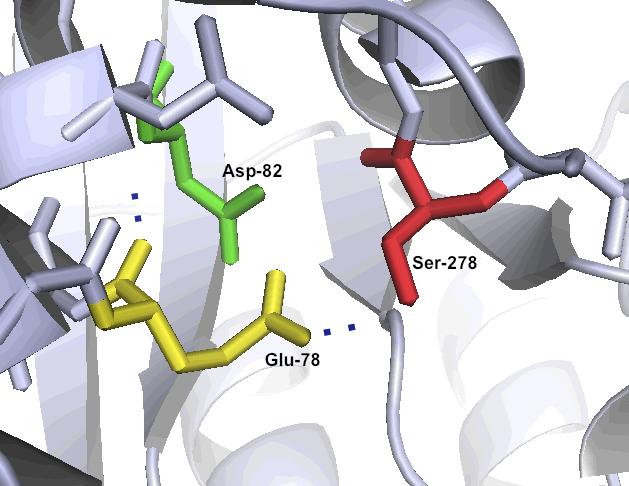
| - | + | [[File:Washington_Kuma Bonded triad.png|left|250px|thumb|Kumamolisin-As' unusual catalytic triad Ser278-Glu78-Asp82 makes the enzyme well suited to a low pH environment.]] | |
| + | [[File:Washington_serine protease triad2.png|left|250px|thumb|The traditional Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad found in serine proteases like SC-PEP does not function optimally at low pH.]] | ||
| - | + | ='''Kumamolisin-As is already active for the dipeptide motif PR, we just need to change it to PQ'''= | |
| - | + | :::::::::::::::::::::<p>Specificity studies have been conducted on the native enzyme, which is most efficient at hydrolyzing peptides at the carboxyl side after the PR dipeptide motif (where the P1 and P2 subsites are arginine and proline, respectively, in standard proteolysis nomenclature). The enzyme shows little preference for what is on the amino S1 and S2 subsites. The combination of Kumamolisin-As having the desired enzymatic activity under gastric pH levels, and the P2 subsite already having the specificity for the proline from the desired PQ motif makes it a highly attractive candidate for further engineering. In addition, several crystal structures of this enzyme have been solved, allowing for the use of computational design techniques.</p> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ---- | |
| - | + | ==References== | |
1.Shan, Lu, et al. "Structural Basis for Gluten Intolerance in Celiac Sprue." Science 297.5590 (2002): 2275-2279. | 1.Shan, Lu, et al. "Structural Basis for Gluten Intolerance in Celiac Sprue." Science 297.5590 (2002): 2275-2279. | ||
Latest revision as of 04:04, 17 October 2011
What is Gluten Intolerance?
People who suffer from gluten intolerance have an adverse reaction to gluten proteins found in wheat, barley, and rye products. The glutens invoke an immune response in the digestive tract of genetically predisposed individuals resulting in inflammation of the gut, impeding the absorption of nutrients. Symptoms can appear in early childhood or later in life, and range widely in severity, from diarrhea, fatigue and weight loss to abdominal distension, anemia, and neurological symptoms. There are currently no effective therapies for this lifelong disease except the total elimination of glutens from the diet. Although celiac sprue remains largely underdiagnosed, its prevalence in the US and Europe is estimated at 0.5-1.0% of the population. With this in mind, we set out to design an enzyme therapeutic for gluten intolerance that could be taken in pill form.
Proline (P)- and glutamine (Q)-rich components of gluten known as ‘gliadins’ appear to be responsible for the bulk of the immune response in most patients. Their high PQ content protects gliadin oligopeptides from degradation by gastrointenstinal endoproteases, but also presents a target for drug design. Any peptidase capable of cleaving at or near the P-Q bond while remaining active at the temperature and harsh pH of the stomach would have pharmacological potential as a therapy for celiac sprue.
There is currently a protein therapeutic in clinical trials, but a second generation is needed
One candidate enzyme, currently in clinical trials, utilizes a prolyl endopeptidase (PEP) from Sphingomonas capsulata (SC) to hydrolyze gliadins. This enzyme was a logical drug candidate as it has a native specificity for the proline rich gliadin peptides. Unfortunately, the enzyme’s optimal activity is at pH 7, and engineering attempts to enhance its activity at relevant gastric pH levels has not yet been met with significant success. It is therefore pertinent to identify new candidate enzymes that have both activity on the gliadin PQ structural motif, as well as optimal activity at gastric pH levels during digestion around pH 4.
Here, we describe an alternative approach to identifying and engineering an enzyme therapeutic for celiac sprue. Rather than focusing primarily on substrate specificity when choosing our candidate enzyme, we identified an enzyme already capable of catalyzing peptide hydrolysis at gastric pH levels, regardless of peptide substrate specificity. Upon identification of such an enzyme we used computational tools to reengineer its substrate specificity for enhanced activity on immunogenic gliadin peptides with the common PQ structural motif.
We have identified an enzyme that could potentially act as a therapeutic for gluten intolerance
When searching for a protease with optimal activity at gastric pH levels that could be produced in a recombinant host, we identified an enzyme known as Kumamolisin-As. Kumamolisin-As, isolated from the thermoacidophilic bacterium Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis strain NTAP-1, has been shown to be produced in a recombinant host, and exhibits significant enzymatic activity at pH 2.5 and above. Its maximal activity is at about pH 4.0. It is this robust activity under acidic, gastric conditions that makes Kumamolisin-As so promising for the development of a pill for gluten intolerance.
A special set of catalytic residues enables high activity at gastric pH levels
One of the primary reasons that Kumamolisin-As is more active than SC-PEP at low pH is due its catalytic triad, the three amino acid residues most heavily involved in conducting the chemistry of cleaving peptides. SC-PEP is part of a large class of enzymes known as serine proteases, which make use of the catalytic triad Serine-Histidine-Aspartate. Acidic conditions can impede the histidine's ability to play its role in this triad, rendering most serine proteases inactive at low pH. Kumamolisin-As, on the other hand, is a member of the sedolisin family of serine-carboxyl peptidases, which utilize the key catalytic triad Serine-Glutamate-Aspartate to hydrolyze their substrates. It is the acidic Glutamate, as opposed to Histidine, in the triad that makes Kumamolisin-As optimal for catalyzing peptide cleavage at low pH. The native substrate for this enzyme in Alicyclobacillus sendaiensis is unknown. In addition, this enzyme has been shown to be thermostable, with an ideal temperature at 60ºC, but still showing significant activity at 37ºC.
Kumamolisin-As is already active for the dipeptide motif PR, we just need to change it to PQ
Specificity studies have been conducted on the native enzyme, which is most efficient at hydrolyzing peptides at the carboxyl side after the PR dipeptide motif (where the P1 and P2 subsites are arginine and proline, respectively, in standard proteolysis nomenclature). The enzyme shows little preference for what is on the amino S1 and S2 subsites. The combination of Kumamolisin-As having the desired enzymatic activity under gastric pH levels, and the P2 subsite already having the specificity for the proline from the desired PQ motif makes it a highly attractive candidate for further engineering. In addition, several crystal structures of this enzyme have been solved, allowing for the use of computational design techniques.
References
1.Shan, Lu, et al. "Structural Basis for Gluten Intolerance in Celiac Sprue." Science 297.5590 (2002): 2275-2279.
2.Mustalahti, Kirsi, et al. "The prevalence of celiac disease in Europe: Results of a centralized, international mass screening project." Annals of Medicine 42.8 (2010): 587-595.
3.Ehren, Jennifer, et al. "Protein engineering of improved prolyl endopeptidases for celiac sprue therapy." Protein Engineering, Design & Selection 21.12 (2008): 699-707.
4.Wlodawer, Alexander, et al. "Crystallographic and Biochemical Investigations of Kumamolisin-As, a Serine-Carboxyl Peptidase with Collagenase Activity." The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279.20 (2004): 21500-21510.
 "
"