Team:EPF-Lausanne/Protocols/Agar Plates
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(Created page with "{{:Team:EPF-Lausanne/Templates/ProtocolHeader|title=Agar plate preparation}} Agar plates are used for cell cultures. Their preparation is relatively simple: first an agar broth ...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
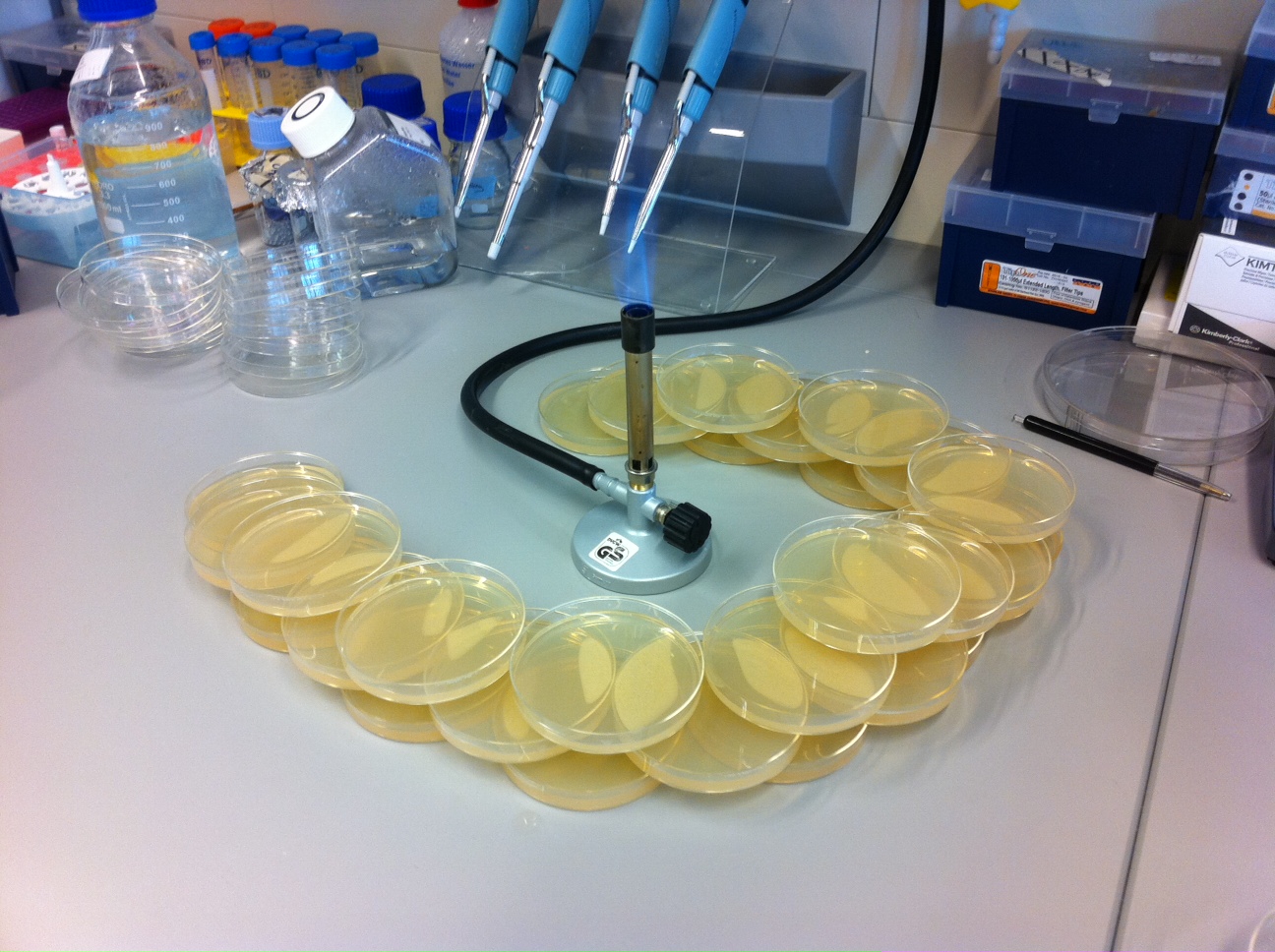
Agar plates are used for cell cultures. Their preparation is relatively simple: first an agar broth is mixed and autoclaved. Then an antibacterial agent such as Ampicillin is mixed in. Finally, the solution is poured into disposable petri plates and let gelify for 20 minutes around a bunzen burner flame, as illustrated below. | Agar plates are used for cell cultures. Their preparation is relatively simple: first an agar broth is mixed and autoclaved. Then an antibacterial agent such as Ampicillin is mixed in. Finally, the solution is poured into disposable petri plates and let gelify for 20 minutes around a bunzen burner flame, as illustrated below. | ||
| - | [[File:EPFL-Growth_plate_gelification.JPG|600px]] | + | [[File:EPFL-Growth_plate_gelification.JPG|600px|center]] |
== Agar broth == | == Agar broth == | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 20 July 2011
Agar plate preparation
Back to protocols.Agar plates are used for cell cultures. Their preparation is relatively simple: first an agar broth is mixed and autoclaved. Then an antibacterial agent such as Ampicillin is mixed in. Finally, the solution is poured into disposable petri plates and let gelify for 20 minutes around a bunzen burner flame, as illustrated below.
Agar broth
Pouring the plates
Arrange empty petri dishes in a crescent around a Bunzen burner. Half-fill them with agar broth. Stack another layer of empty dishes above, and repeat until all the broth has been poured. One liter of broth fills approximately 30 plates.
Leave the plates around the flame for approximately twenty minutes, until the gel is solidified.
 "
"