Team:Paris Bettencourt/Lambda switch
From 2011.igem.org
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<p>We also want to study E.Coli-B.Subtilis communication using existing bistable switch in E.Coli.</p> | <p>We also want to study E.Coli-B.Subtilis communication using existing bistable switch in E.Coli.</p> | ||
| - | <p>Many synthetic biology tools came from IGEM. In <a href=" | + | <p>Many synthetic biology tools came from IGEM. In <a href="https://2007.igem.org/Peking_Push-on-push-off">2007 Beiijing team</a>, winner of the competition, constructed a push on push off switch derivated from lambda phage.</p> |
<p>The toggle switch consists of two mutually repressed repressors, CI and CI434. The corresponding cI and cI434 genes come from the lambda and 434 phages, respectively. The promoters PR and PRM control the transcription of cI434 and cI genes and they are in turn repressed by CI and CI434.</p> | <p>The toggle switch consists of two mutually repressed repressors, CI and CI434. The corresponding cI and cI434 genes come from the lambda and 434 phages, respectively. The promoters PR and PRM control the transcription of cI434 and cI genes and they are in turn repressed by CI and CI434.</p> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[File:c1_principle3.jpg|center|The Lambda switch principle]] | [[File:c1_principle3.jpg|center|The Lambda switch principle]] | ||
[[File:c1_principle4.jpg|center|The Lambda switch principle]] | [[File:c1_principle4.jpg|center|The Lambda switch principle]] | ||
| - | |||
<html> | <html> | ||
| + | <h2>Experiments</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>To know more about what we have done with this system, we invite you to visit the corresponding <em>modeling</em> and <em>experiment</em> pages:</p> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li><em><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Paris_Bettencourt/Experiments/Lambda_switch">Experiments</a></em></li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
<div id="citation_box"> | <div id="citation_box"> | ||
<p id="references">References</p> | <p id="references">References</p> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 83: | ||
</div> <!-- close footer-wrapper --> | </div> <!-- close footer-wrapper --> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="scroll_right"><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Paris_Bettencourt/Experiments/Lambda_switch"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/e/e0/Arrow-right-big.png" style="width:100%;"></a><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Paris_Bettencourt/Experiments/Lambda_switch">Lambda switch experiments</a></div> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:19, 29 October 2011

Lambda switch
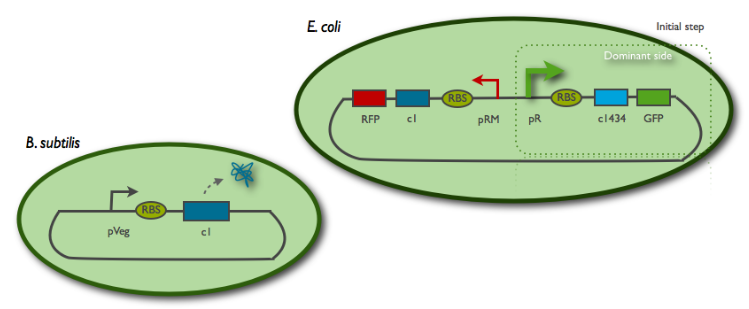
We also want to study E.Coli-B.Subtilis communication using existing bistable switch in E.Coli.
Many synthetic biology tools came from IGEM. In 2007 Beiijing team, winner of the competition, constructed a push on push off switch derivated from lambda phage.
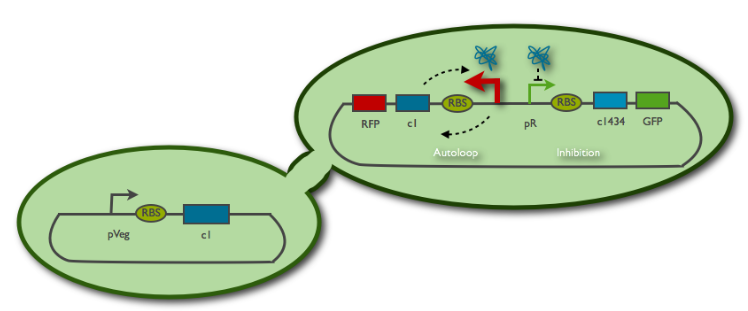
The toggle switch consists of two mutually repressed repressors, CI and CI434. The corresponding cI and cI434 genes come from the lambda and 434 phages, respectively. The promoters PR and PRM control the transcription of cI434 and cI genes and they are in turn repressed by CI and CI434.

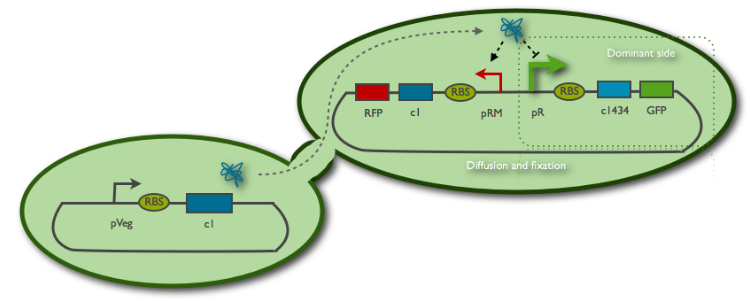
The emmiter is a B.subtillis cell producing cI, protein from lambda phage.
The receiver is an E.Coli cell harboring the toggle switch made by PKU. By making diffusing cI protein, we expect to switch the cell in red. The number of cI sufficient to switch in red is estimated at 150 per cell, according to the model and experiments of the PKU 2007 team.
Experiments
To know more about what we have done with this system, we invite you to visit the corresponding modeling and experiment pages:
References
- Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch; Molecular systems biology 2010; 2007 PKU iGEM team
Thanks to Minh for all his help with this design.
 "
"