Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/T7 promoter variants/t7prom
From 2011.igem.org
(→Characterization of Designed Variants) |
(→Non-random T7 promoter variants) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
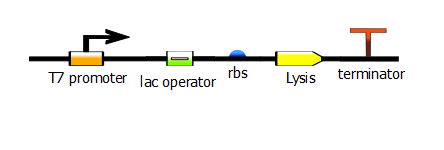
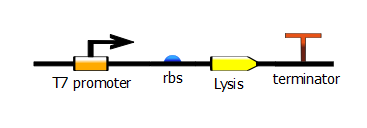
| - | We made two families of T7 promoter variants. Each family has six designed mutants and three randomer mutants. The only difference between the two families is the addition of a lac operator sequence downstream of the T7 promoter | + | We made two families of T7 promoter variants. Each family has six designed mutants and three randomer mutants. The only difference between the two families is the addition of a lac operator sequence downstream of the T7 promoter. |
| - | + | [[File:t7_lac_rbs_lysis_term.png|470px|center]] | |
| - | + | [[File:t7_rbs_lysis_term.png|400px|center]] | |
| + | These promoter variants were characterized using fluorescence, revealing a wide range of promoter efficiencies. To find out more about how these T7 promoter variants were made, please click [[Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/T7 promoter variants/t7prom/making|here]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here is a version of the T7 promoter consensus sequence: | ||
| + | |||
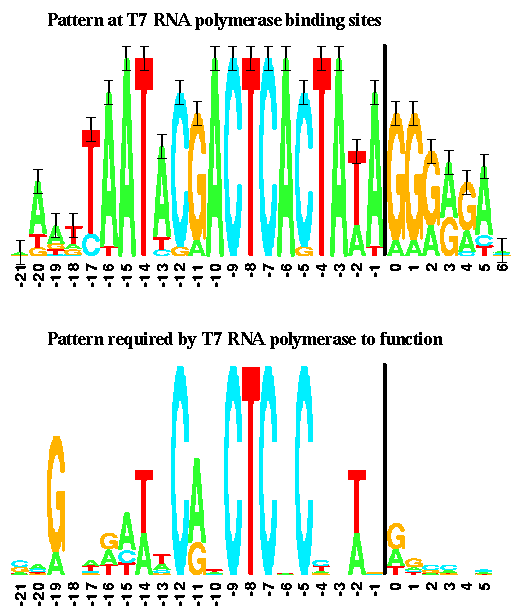
| + | [[File:t7_logo.png|400px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is taken from Schneider and Stephens, ''Sequence Logos: A New Way to Display Consensus Sequences'' Nucleic Acids Research, 18 6097-6100, 1990 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Non-random T7 promoter variants=== | ||
| + | The T7 promoter variants in this section were designed based on considerations from the relevant literature. These sequences, and their corresponding predicted strengths, also come from literature. The exact source is Imburgio, D., Rong, M., Ma, K. & McAllister, W.T. Studies of promoter recognition and start site selection by T7 RNA polymerase using a comprehensive collection of promoter variants. Biochemistry 39, 10419–10430 (2000). | ||
Variants without additional lac operator (constitutive): | Variants without additional lac operator (constitutive): | ||
| Line 115: | Line 125: | ||
[[File:non_random_response.png|700px]] | [[File:non_random_response.png|700px]] | ||
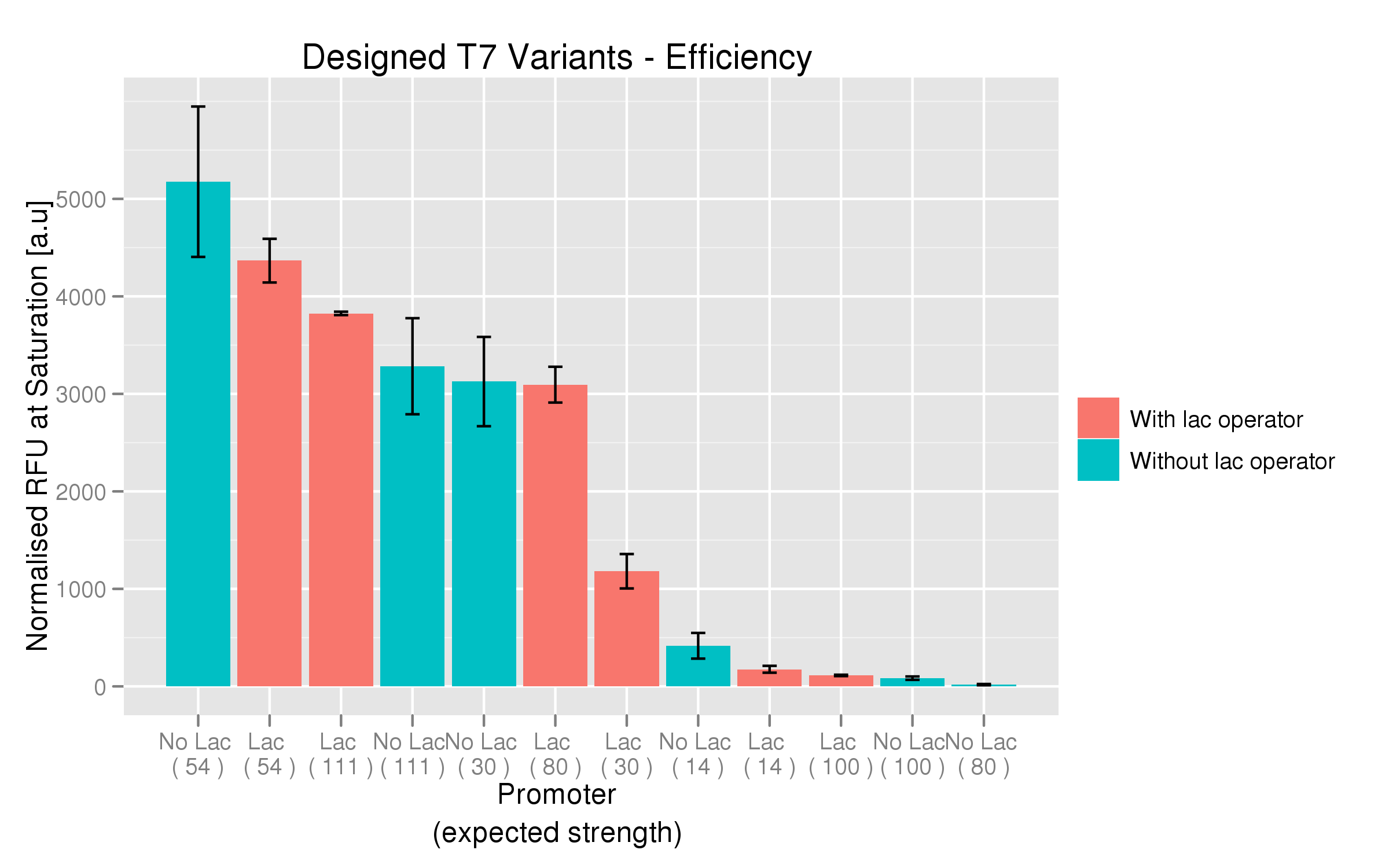
| - | The six designed T7 promoter variants are named as a function of their predicted promoter efficiency, relative to the wildtype. For example, T7 14 has a predicted efficiency of 14% compared to the consensus T7 promoter, whereas T7 111 is predicted to be 111% more efficient than the wildtype. In the chart above, each of the designed promoter variants for both the T7 with and without the lac operator are arranged in increasing predicted efficiency. Contrary to our expectation, some variants that were designed to have a lesser efficiency than the wildtype (e.g. T7 54) seem to have a much higher strength (as measured by fluorescence at saturation, normalized by the optical density) | + | The six designed T7 promoter variants are named as a function of their predicted promoter efficiency, relative to the wildtype. For example, T7 14 has a predicted efficiency of 14% compared to the consensus T7 promoter, whereas T7 111 is predicted to be 111% more efficient than the wildtype. In the chart above, each of the designed promoter variants for both the T7 with and without the lac operator are arranged in increasing predicted efficiency. Contrary to our expectation, some variants that were designed to have a lesser efficiency than the wildtype (e.g. T7 54) seem to have a much higher strength (as measured by fluorescence at saturation, normalized by the optical density). The data for this graph was produced in triplicate, so the error bar represents the standard error across those three measurements. |
=== Characterization of Randomer Variants === | === Characterization of Randomer Variants === | ||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 22 September 2011
Lysis Selection System
Lysis selection system Main | Lysis Characterization | DNA Recovery | DNA Selection | T7 Promoter VariantsContents |
T7 Promoter Variants
Introduction
The success of any piece of biological circuitry, like the kind we are presenting in our system, hinges substantially on the time-scales required for the activation of its components. If one component reacts more quickly than another, the whole system will desynchronize and all pertinent biological information will be lost.
In our case, one of the key steps is the activation of the lysis cassette which is controlled by the T7 promoter. The rest of the system -- including any reporter systems that would lead to T7 RNA polymerase binding to a T7 promoter -- may depend on other parameters that affect the timescales in very delicate ways. It becomes crucial to have a variety of T7 promoter variants on hand, each of which has different strengths and efficiencies in order to accomodate the various system time-scales.
We made two families of T7 promoter variants. Each family has six designed mutants and three randomer mutants. The only difference between the two families is the addition of a lac operator sequence downstream of the T7 promoter.
These promoter variants were characterized using fluorescence, revealing a wide range of promoter efficiencies. To find out more about how these T7 promoter variants were made, please click here.
Here is a version of the T7 promoter consensus sequence:
It is taken from Schneider and Stephens, Sequence Logos: A New Way to Display Consensus Sequences Nucleic Acids Research, 18 6097-6100, 1990
Non-random T7 promoter variants
The T7 promoter variants in this section were designed based on considerations from the relevant literature. These sequences, and their corresponding predicted strengths, also come from literature. The exact source is Imburgio, D., Rong, M., Ma, K. & McAllister, W.T. Studies of promoter recognition and start site selection by T7 RNA polymerase using a comprehensive collection of promoter variants. Biochemistry 39, 10419–10430 (2000).
Variants without additional lac operator (constitutive):
| Parts Registry Number | Strength | Mutation Position | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613001 K613001] | Wildtype | None | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613002 K613002] | .14 | -16 | TGATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613003 K613003] | .3 | -2 | TAATACGACTCACTACAGGGAGA |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613004 K613004] | .54 | -17 | CAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613005 K613005] | .8 | 3 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGA |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613006 K613006] | 1.11 | 3 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGA |
Variants with additional lac operator (LacI repressed):
| Parts Registry Number | Strength | Mutation Position | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613007 K613007] | Wildtype | None | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613008 K613008] | .14 | -16 | TGATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613009 K613009] | .3 | -2 | TAATACGACTCACTACAGGGAGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613010 K613010] | .54 | -17 | CAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613011 K613011] | .8 | 3 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
| [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K613012 K613012] | 1.11 | 3 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGAGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATT |
Randomer T7 Promoter Variants
The randomer variants were made by ordering random mutants at the following positions with respect to the consensus logo for the T7 promoter:
- -7-12
- +1+3, -1-3
- -10
These were produced both for the T7 and the T7-lac promoter.
Characterization of Designed Variants
For each family, we tested the randomers and the designed variants separately. To characterize the promoter strengths, we used RFP as the reporter gene and used a platereader to test for fluorescence during and after induction with IPTG.
The six designed T7 promoter variants are named as a function of their predicted promoter efficiency, relative to the wildtype. For example, T7 14 has a predicted efficiency of 14% compared to the consensus T7 promoter, whereas T7 111 is predicted to be 111% more efficient than the wildtype. In the chart above, each of the designed promoter variants for both the T7 with and without the lac operator are arranged in increasing predicted efficiency. Contrary to our expectation, some variants that were designed to have a lesser efficiency than the wildtype (e.g. T7 54) seem to have a much higher strength (as measured by fluorescence at saturation, normalized by the optical density). The data for this graph was produced in triplicate, so the error bar represents the standard error across those three measurements.
Characterization of Randomer Variants
We used the same platereader protocol to test the efficiency and induction ratios of the randomers using RFP fluorescence. Twelve colonies per variant were tested. The results indicate that the T7 -10 randomers, both the non-lac and lac varieties, have the highest fluorescence saturation levels (normalized by OD). The other randomer types seem to have negligible strength. 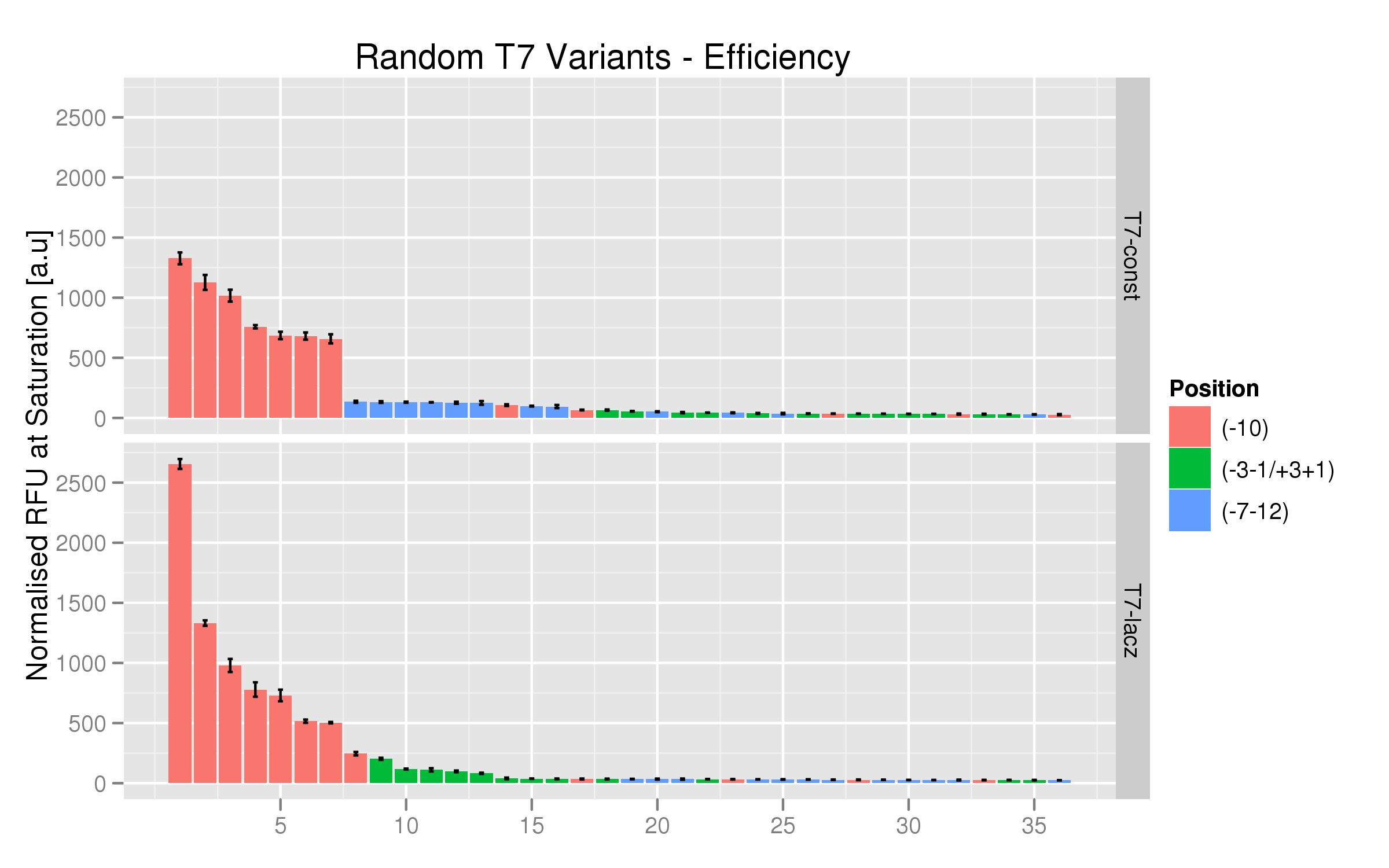
On the whole, the T7-lac promoters with random mutations at position -10 have higher fluorescence expressions than their T7 non-lac counterparts.
 "
"