Team:EPF-Lausanne/Our Project/T7 promoter variants
From 2011.igem.org
(→The Making Of) |
(→The Making Of) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
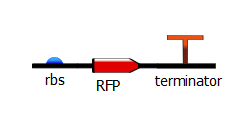
To produce these T7 promoter variants, we used a two-step PCR process. The first PCR, which we call "gene-specific" PCR, is a typical PCR that adds a ribosome-binding site (rbs) in front of either RFP or the Lysis operon and adds a terminator downstream. | To produce these T7 promoter variants, we used a two-step PCR process. The first PCR, which we call "gene-specific" PCR, is a typical PCR that adds a ribosome-binding site (rbs) in front of either RFP or the Lysis operon and adds a terminator downstream. | ||
| - | [[File:rbs_rfp_term.png | + | [[File:rbs_rfp_term.png]] |
| - | [[File:rbs_lys_term.png | + | [[File:rbs_lys_term.png]] |
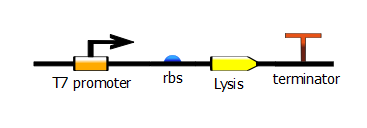
With this PCR product now serving as the DNA template, we start a second PCR which we call the "extension" PCR. It extends the product by adding the T7 promoter. | With this PCR product now serving as the DNA template, we start a second PCR which we call the "extension" PCR. It extends the product by adding the T7 promoter. | ||
| - | [[File:t7_rbs_lysis_term.png | + | [[File:t7_rbs_lysis_term.png]] |
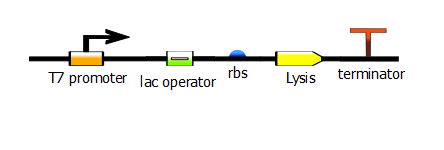
Of course, the primers can also be chosen in such a way that a lac operator (repressor site) is added downstream of the T7 operator. | Of course, the primers can also be chosen in such a way that a lac operator (repressor site) is added downstream of the T7 operator. | ||
| - | [[File:t7_lac_rbs_lysis_term.png | + | [[File:t7_lac_rbs_lysis_term.png]] |
== Characterization with RFP == | == Characterization with RFP == | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 17 September 2011
T7 promoter variants
We made two families of T7 promoter variants. One family has mutations on the T7 promoter consensus sequence while the other has the same set of mutations on the consensus sequence but also has a lac operator downstream of the T7 promoter (but upstream of the reporter RFP or Lysis). In each family, we made six designed variants with different predicted promoter strengths compared to the wildtype and also made three sets of randomer variants which we wanted to use to check the overall range of promoter strength.The Making Of
To produce these T7 promoter variants, we used a two-step PCR process. The first PCR, which we call "gene-specific" PCR, is a typical PCR that adds a ribosome-binding site (rbs) in front of either RFP or the Lysis operon and adds a terminator downstream.
With this PCR product now serving as the DNA template, we start a second PCR which we call the "extension" PCR. It extends the product by adding the T7 promoter.
Of course, the primers can also be chosen in such a way that a lac operator (repressor site) is added downstream of the T7 operator.
Characterization with RFP
For each family, we tested the randomers and the designed variants separately. To characterize the promoter strengths, we used RFP as the reporter gene and used a platereader to test for fluorescence during and after induction with IPTG.
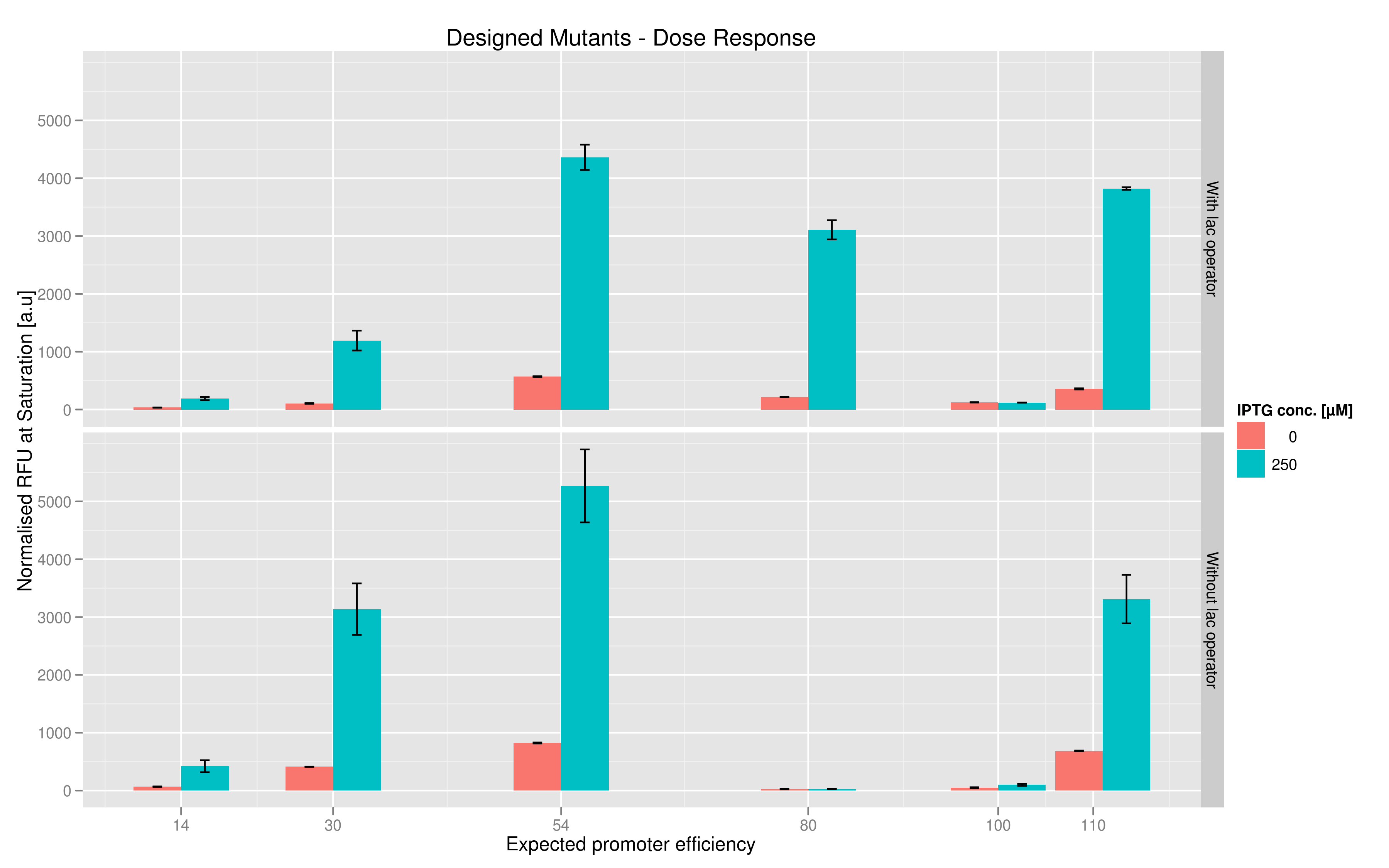
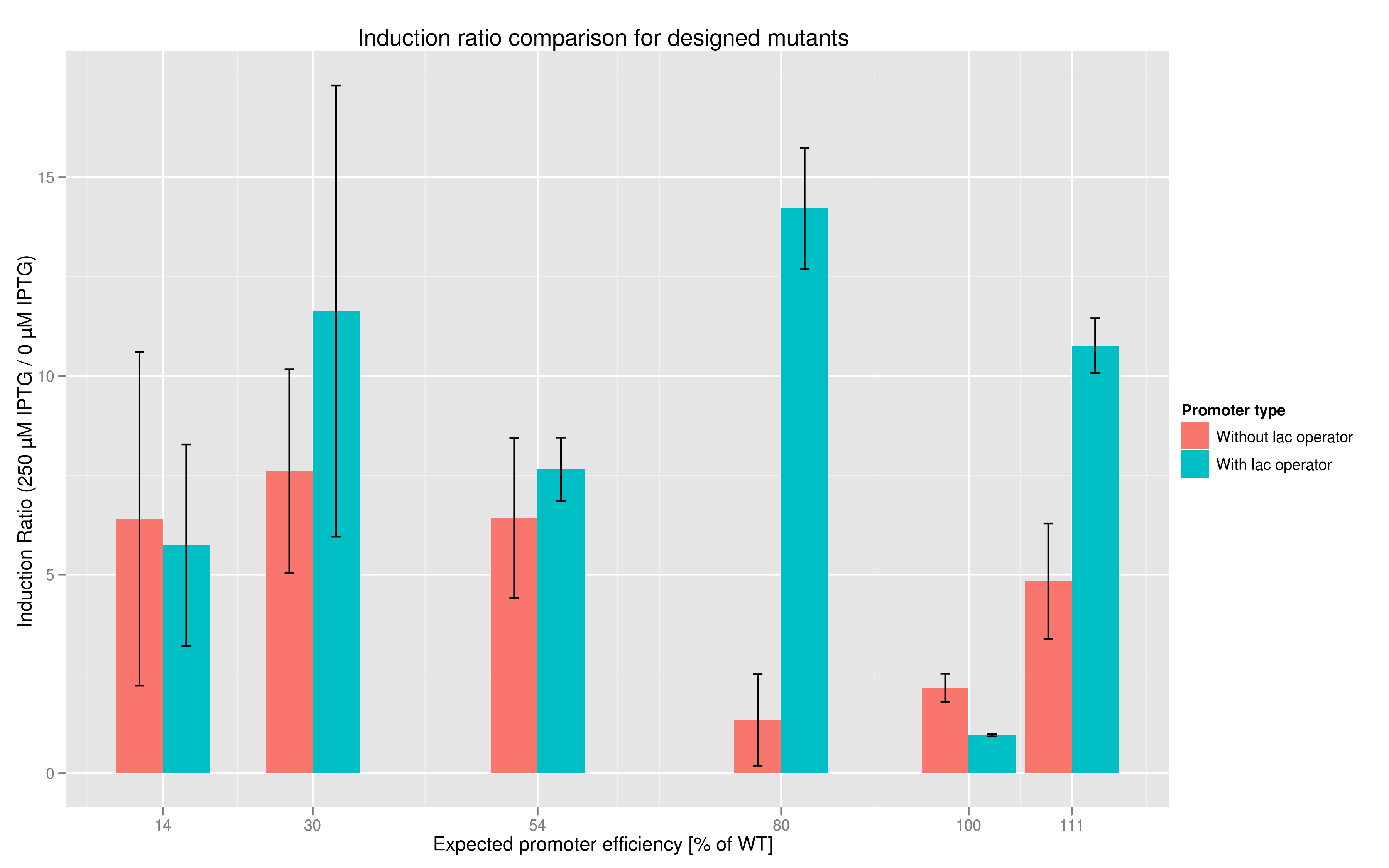
The six designed T7 promoter variants are named as a function of their predicted promoter efficiency, relative to the wildtype. For example, T7 14 has a predicted efficiency of 14% compared to the consensus T7 promoter, whereas T7 111 is predicted to be 111% more efficient than the wildtype. In the chart above, you find each of the designed promoter variants for both the T7 with and without the lac operator, arranged in increasing predicted efficiency. Contrary to our expectation, some variants that were designed to have a lesser efficiency than the wildtype (e.g. T7 54) seem to have a much higher strength (as measured by fluorescence at saturation, normalized by the optical density). Already in the designed variants, we see a substantial difference in the behavior of the promoters that have a lac operator as opposed to those that do not. The data for this graph was produced in triplicate, so the error bar represents the standard error across those three measurements.
In addition to fluorescence at saturation, another way to characterize promoter strength is to look at its induction ratio, which is the ratio, at saturation, of fluorescence produced by induction with IPTG versus fluorescence produced without induction. In layman's terms, it indicates how strongly the promoter reacts to induction. Here again, our results indicate that some promoter variants (T7 80 in particular) stand out with respect to this feature. Here too the importance of the lac operator in producing high induction ratios is not to be underestimated.
For the three sets of randomers for T7 with and without the lac operator, we tested seventy-two different variants and characterized their expression using the same IPTG induction protocol as with the designed variants. The goal of using these variants was to examine the range of expressions that can be produced by random mutations as opposed to directed mutations. The results, as presented in the graph, indicate that the designed variants (with and without lac operator put together) produce a much higher average normalized fluorescence than the randomers.
Characterization with Lysis
Since a major component of our scheme for selecting promoters and transcription factors with strong binding affinities required the ability to lyse cells, we also wanted to test a T7-driven lysis cassette.
Induction with various concentrations of IPTG reveals a stready increase in the amount of lysis that can be obtained. Here 500 uM yields the most substantial amount of lysis, and that concentration was used in all further experiments dealing with lysis. The negative controls were two-fold: one is an unsuccessful attempt at inserting the lysis cassette downstream of a T7 promoter in the psB3K1 plasmid, while the other is a T7 promoter upstream of an RFP gene. Neither should express lysis.
 "
"