Team:USTC-China/Project/application/Discussion
From 2011.igem.org
|
Project |
Parts |
Team |
Wetlab |
HumanPractice |
Conclusion and Discussion
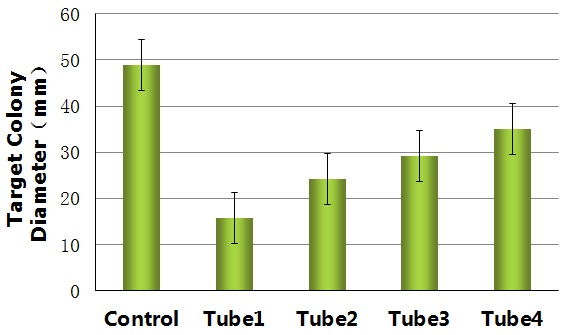
Comparing with the control, the reprogrammed bacteria actually can destroy the target bacteria as the design requires and basically decrease the range of motion of the target bacteria.
By measuring the range of motion of the control and the target bacteria dealed with the reprogrammed bacteria from different tubes(tube1, tube2, tube3, tube4), we get histogram below.
Figure13.
Figure13 shows that the capability of eliminating the target bacteria grows with the number of bacteria with red fluorescen decreases. This result reveal a fact that the properties of the reprogrammed bacteria mainly depend on the random fluctuation of the expression of the Toggle Switch Device.This fact also explain the differences between the form of the colony1 from tube2(Figure10 left) and the colony1 from tube3(Figure12 left)
References
Timothy S. Gardner, Charles R. Cantor, James J. Collins (2000) Construction of a Genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature, 403,339-342
Shana Topp, Justin P. Gallivan (2006) Guiding Bacteria with Small Molecules and RNA. J.Am.Chem.Soc, 129,6870-6811
Chunbo Lou, Xili Liu, Ming Ni.etc (2010) Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch. Molecular Systems Biology, 6:350
Joy Sinha, Samuel J Reyes, Justin P Gallivan (2010) Reprogramming bacteria to seek and destroy an herbicide. Nature Chemical Biology, 6,464-470
Steven L. Porter, George H. Wadhams, Judith P. Armitage (2011) Signal processing in complex chemotaxis pathways. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 9,153-165
Warren C. Ruder, Ting Lu, James J. Collins (2011) Synthetic Biology Moving into the Clinic. Science,333,1248-1252
Nazanin Saeidi, Choon Kit Wong, Tat-Ming Lo .etc (2011) Engineering microbes to sense and eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a human pathogen. Molecular Systems Biology,7:251
 "
"