Team:HokkaidoU Japan/Project
From 2011.igem.org
(→Plasmid Backbone for protein injection) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/header}} | {{Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/header}} | ||
| - | + | {{Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/LeftContent}} | |
| + | <div id="hokkaidou-right-content"> | ||
=Abstract= | =Abstract= | ||
| - | Bacteria living around us evolved ways to effect their surrounding environment. | + | Bacteria living around us evolved ways to effect their surrounding environment. Some bacteria can change its surroundings by injecting whole protein molecules into targeted eukaryotic cells through Type 3 secretion system (T3SS). During iGEM 2010 we showed that ''E. coli'' containing a part of ''Salmonella'' genome expresses T3SS. We thought this system can be applied to direct reprogramming of somatic cells from eukaryote. |
| - | This year we tried to make it more convenient. For this purpose we designed a plasmid backbone which can instantly produce ready-to-inject fusion proteins from | + | This year we tried to make it more convenient. For this purpose we designed a plasmid backbone which can instantly produce ready-to-inject fusion proteins from biobrick parts. Using it, we tried further characterization of this system by injecting various proteins to see if they can be secreted. |
| - | = | + | =What`s T3SS?= |
| - | T3SS is a system of pathogenic gram-negative bacterium such as Salmonella, Yersinia and EPEC (entero pathogenic E. coli). Using this system bacteria can inject whole protein molecules through a syringe like organelle named T3S Apparatus. The target of this system is a eukaryotic cell. Naturally it is used to inject | + | T3SS is a system of pathogenic gram-negative bacterium such as ''Salmonella'', ''Yersinia'' and EPEC (entero pathogenic ''E. coli''). Using this system bacteria can inject whole protein molecules through a syringe like organelle named T3S Apparatus. The target of this system is a eukaryotic cell. Naturally it is used to inject virulence effector proteins. Last year, we showed that T3SS works in ''E. coli'' by injecting GFP into RK13 cells. |
| - | See [[Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/T3SS|here]] for details about T3SS and our achievements on iGEM 2010. | + | See [[Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/T3SS|here]] for the details about T3SS and our achievements on iGEM 2010. |
| - | = | + | =Injection assay using onion cells= |
| - | + | We developed a new method of injection assay using onion cells to evaluate the functions, which is a easier than using mammalian cultured cells. However it requires some treatments specific to plant cells. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | See [[Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/Onion|here]] for the details about Injection assay using onion cells. | |
| - | + | =Plasmid Backbone for protein injection= | |
| - | + | ==Bsa I cloning site== | |
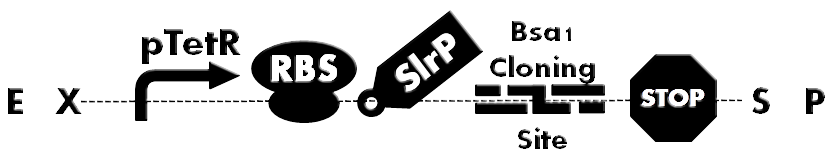
| - | + | [[File:HokkaidoU_BsaI_Backbone.png|thumb|500px|Fig. 1 Ready-to-inject backbone. SlrP is an T3SS injection signal. Bsa I Cloning Site is used for inserting various BioBricks directly. A protein fused to T3S signal can be expressed under control of constitutive promoter(pTetR).]] | |
| - | + | Last year we made injectable GFP as a reporter of injection assay. This year, our project started with an aim to conduct direct reprogramming as an application of T3SS. But first we wanted to try injecting various proteins. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Fusion of signal peptide, required for secretion , to each protein would have been a laborious task. So development of ready-to-inject backbone was anticipated. To accomplish this, we designed Bsa I Cloning Site and developed plasmid backbone which can facilitate quick assembly of to be injected proteins (Fig. 1). | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | See [[Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/Backbone|here]] for the details about plasmid backbone and Bsa I cloning site. | |
| - | |||
| + | ==GSK Tag system== | ||
| + | [[File:HokkaidoU_Japan_2011_GSK_Backbone_lv.png|thumb|500px|Fig. 2 GSK is a tag for detecting phosphorylation of it in eukaryotic cells.]] | ||
| + | Another problem is how to check if a protein was successfully injected. GFP is easy, but what about the ones that cannot be visualised? To solve this problem, we used a distinct property of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β (GSK-3β). It is phosphorylated only in eucaryotic cells. By fusing a small part of GSK-3β as a tag and by detecting its state of phosphorylation, we can know if and what amount of protein has been injected into the eukaryotic cells (Fig. 2). | ||
| + | See [[Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/Project/GSK|here]] for the details about GSK tag. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
{{Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/footer}} | {{Team:HokkaidoU_Japan/footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:48, 15 December 2011
HokkaidoU Japan
iGEM 2011 Team of Hokkaido University
Contents |
- Abstract
- What`s T3SSDetailed information about T3SS and summary of our achievements on iGEM 2010
- Injection assay using onion cellsExperiments using plant cells are easier to perform than with mammalian ones
- Ready-to-inject backbone and Bsa I cloning siteReady-to-inject backbone and Bsa I cloning site enables easy fusion of T3S signal and protein
- GSK tag systemA neat injection assay using GSK tag, which can specifically detect successfully injected proteins
- Bsa I cloning site, RFC submissionDetailed documentation of costructing a BioBrick cloning site a BioBrick!
Abstract
Bacteria living around us evolved ways to effect their surrounding environment. Some bacteria can change its surroundings by injecting whole protein molecules into targeted eukaryotic cells through Type 3 secretion system (T3SS). During iGEM 2010 we showed that E. coli containing a part of Salmonella genome expresses T3SS. We thought this system can be applied to direct reprogramming of somatic cells from eukaryote. This year we tried to make it more convenient. For this purpose we designed a plasmid backbone which can instantly produce ready-to-inject fusion proteins from biobrick parts. Using it, we tried further characterization of this system by injecting various proteins to see if they can be secreted.
What`s T3SS?
T3SS is a system of pathogenic gram-negative bacterium such as Salmonella, Yersinia and EPEC (entero pathogenic E. coli). Using this system bacteria can inject whole protein molecules through a syringe like organelle named T3S Apparatus. The target of this system is a eukaryotic cell. Naturally it is used to inject virulence effector proteins. Last year, we showed that T3SS works in E. coli by injecting GFP into RK13 cells.
See here for the details about T3SS and our achievements on iGEM 2010.
Injection assay using onion cells
We developed a new method of injection assay using onion cells to evaluate the functions, which is a easier than using mammalian cultured cells. However it requires some treatments specific to plant cells.
See here for the details about Injection assay using onion cells.
Plasmid Backbone for protein injection
Bsa I cloning site
Last year we made injectable GFP as a reporter of injection assay. This year, our project started with an aim to conduct direct reprogramming as an application of T3SS. But first we wanted to try injecting various proteins.
Fusion of signal peptide, required for secretion , to each protein would have been a laborious task. So development of ready-to-inject backbone was anticipated. To accomplish this, we designed Bsa I Cloning Site and developed plasmid backbone which can facilitate quick assembly of to be injected proteins (Fig. 1).
See here for the details about plasmid backbone and Bsa I cloning site.
GSK Tag system
Another problem is how to check if a protein was successfully injected. GFP is easy, but what about the ones that cannot be visualised? To solve this problem, we used a distinct property of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β (GSK-3β). It is phosphorylated only in eucaryotic cells. By fusing a small part of GSK-3β as a tag and by detecting its state of phosphorylation, we can know if and what amount of protein has been injected into the eukaryotic cells (Fig. 2).
See here for the details about GSK tag.
 "
"