Team:Harvard/Results
From 2011.igem.org
Overview | Biobricks | Source Code | Acknowledgments | Accomplishments
Novel Zinc Fingers
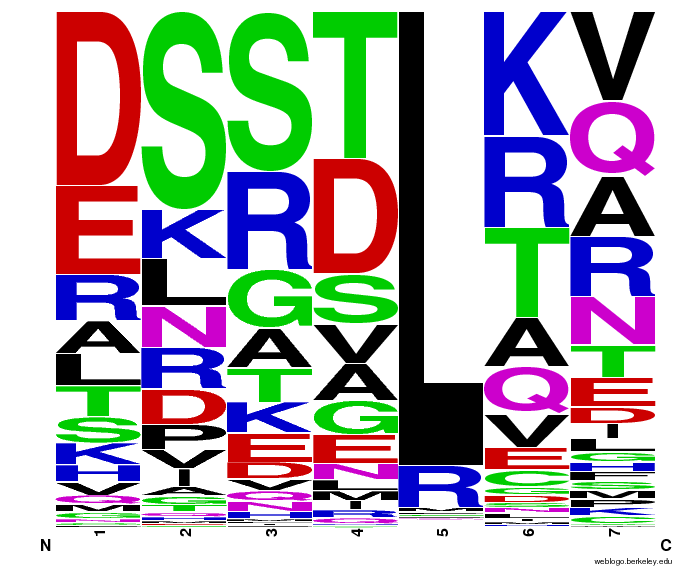
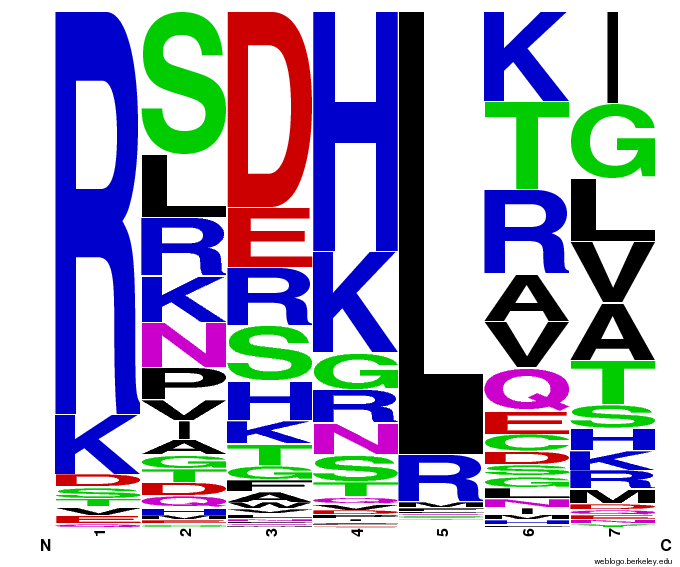
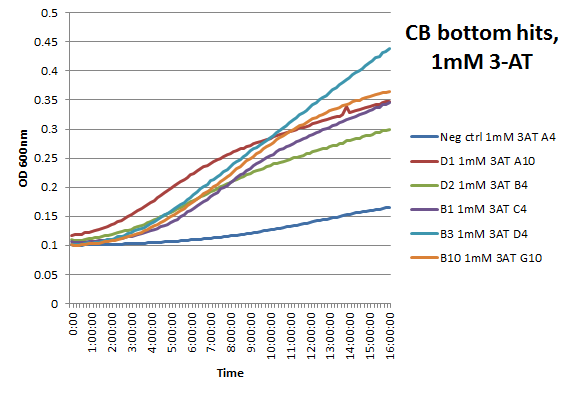
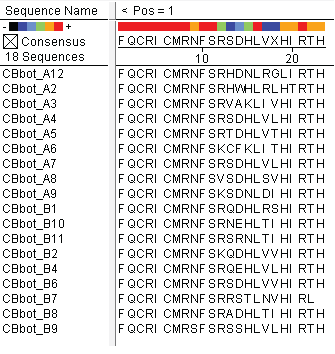
We did not have time to test all 6 targets as planned: we chose to focus on zinc finger binders to DNA tripplet TGG, which is found in the color blindness gene bottom target. The TGG library was assembled and transformed into the selection strain with the proper binding site. So far we have screened 26 colonies and found 15 possible novel zinc finger binders to the sequence 5'-GTGGGATGG-3'. See here for more details.
 | | 
|
One-Hybrid Selection Strain
Genome-Based Selection System
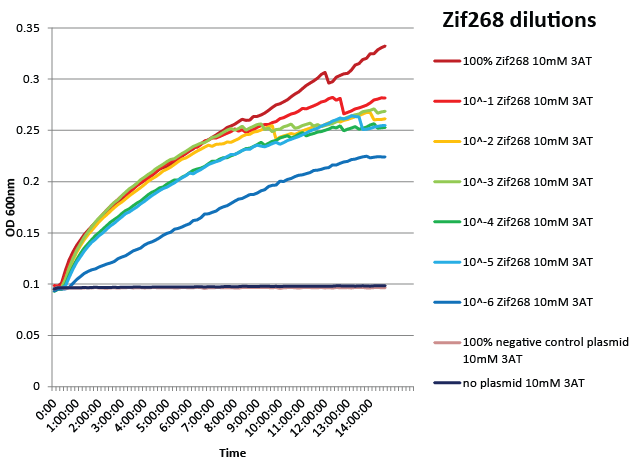
We designed a one-hybrid metabolic system that was entirely genome-based. Using multiplex automated genome engineering (MAGE) and lambda red, we knocked out HisB, PyrF, and rpoZ; inserted a kanamycin cassette-zinc finger binding site-His3-URA3 construct into the 1529620 locus; and changed the zinc finger binding site directly on the genome. The strain was fully characterized and was sensitive enough to recognize a valid zinc finger when diluted as much as one into one million of negative controls. See here for more details.
Bioinformatics
55,000 Potential Zinc Fingers
We made 55,000 sequences, distributed evenly among 6 DNA target triplets. That's 9150 per target.
Because our program's output changes dramatically based on the input triplet, no two sets of sequences are the same:
Sequencing results of Library transformation
Error rates
- Perfect sequence matches a designed ZF: 57.1% (44/77)
- Single SNP: 2.6% (2/77)
- Two or more SNPs: 18.2% (14/77)
- Frame shift: 22.1% (17/77)
We determined the overall per base pair error rate for this set sequenced to be around 1/200, which includes errors generated by the chip, or generated during PCR and assembly. These are a bit higher than those found by Kosuri, et al., but within a reasonable margin.
 "
"