Team:USTC-China/Project/module
From 2011.igem.org

Contents |
Modules
Riboswitch
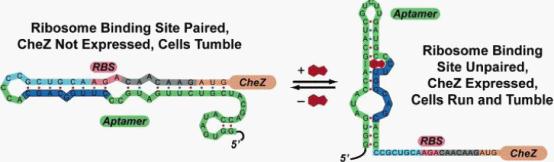
Figure 1: Model for how the theophylline-sensitive synthetic riboswitch controls the translation of the CheZ protein. In the absence of theophylline (left),the mRNA adopts a conformation in which the ribosome binding site is paired and translation of CheZ is inhibited. In the absence of CheZ, the protein CheY-P remains phosphorylated and the cells tumble in place. In the presence of theophylline (shown in red), the mRNA can adopt a conformation in which the ribosome binding site is exposed and CheZ is expressed, thus allowing the cells to run and tumble. (Images from: Shana Topp, Justin P. Gallivan (2006) Guiding Bacteria with Small Molecules and RNA. J.Am.Chem.Soc, 129,6870-6811)
Toggle-switch
Figure 2: Toggle switches incorporate three mechanisms: positive feedback, double-negative feedback, and the repressor binding cooperatively and two different kinds of bacteria differentiate out of homogeneous conditions. (Images from: Chunbo Lou, Xili Liu, Ming Ni.etc (2010) Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch. Molecular Systems Biology, 6:350)
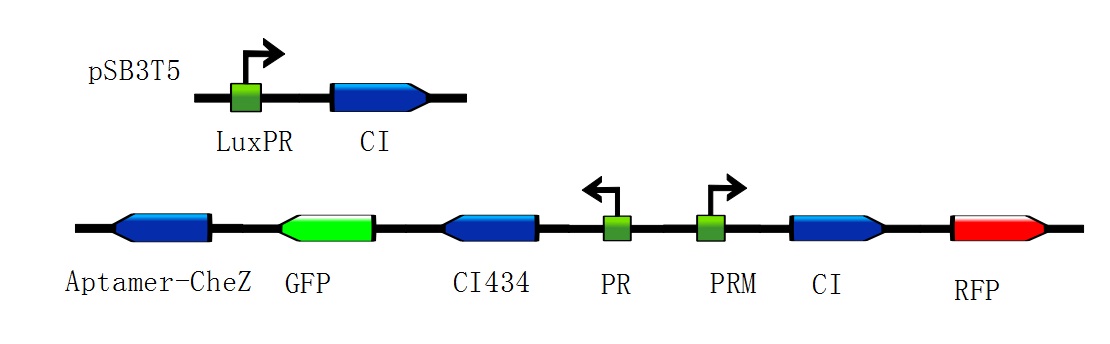
Figure 3: Constructions to modulate the ratio of toggle switches. The above bar represents pSB3T5, a low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector, where LuxpR (BBa_R0062) controls the expression of cI repressor which would influence the ratio of toggle switch. (Images by USTC-IGEM with TinkerCell)
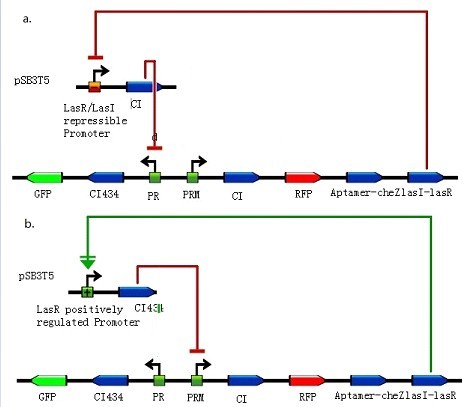
Quorum Sensing
Andrée M. Lazdunski, Isabelle Ventre and James N. Sturgis(2004) Regulatory circuits and communication in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology, Volume 2, July 2004, 581-592
 "
"