Team:Valencia/Pruebahardware
From 2011.igem.org
Detailed description
I. Bacteriocin production systemIn this section there are two streams, one flows in a permanent loop and contains the E. Coli resistant bacteriocin producer with own synthesized bacteriocins. The second one passes through the UF membrane, so it is rich in bacteriocins and other small particles.
Constituent elements:
- Peristaltic pump (PP):
- Module of Bacteriocins Separation (MoBS):
This kind of pump is perfect to work with biological cultures since there is no direct contact between the cells and the mechanical parts of the PP, so no cell membrane damage and no temperature increase is expected. The fluid is contained within a flexible silicone tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. This tube is compressed by two rollers attached to the rotor, pulling the fluid in one direction.
Our PP comes from a used hemodialysis machine which motor didn’t work, so we decided to substitute it with a flamboyant Volkswagen Golf windscreen wiper motor. In order to assemble the wiper motor with the pump we used following additional material:
The motor is coupled with threaded rods to a reinforced steel plate, which at the same time supports the PP. Thanks to the threaded rods we can regulate the distance from the motor to the pump and the angle of the shaft. In order to use the original shaft of the pump, we welded it to a nut with the same metric threat to the one of the motor shaft, achieving a cheap functional peristaltic pump.
The aim of this device is to separate the bacteriocins from the E. Coli harvest. In the market you can find ultrafiltration modules, which cost around 1000 €. So we tried to obtain a low-cost solution. We had several designs and built different models until we hit the nail on the head and found a fully functional one.
Our final MoBS device consists of different brass piping fittings. The main element is a 1’’ pipe tee with two reduced elbows where the central exit of the tee has an amplifier fitting connected to a hexagonal screw top. On the inside top surface the 2 ’’ Ø UF membrane is supported and its outline part its glued to the metal applying a thin layer of neutral silicone, sealing and fixing the membrane at the same time. The two elbows have another fitting to end in a threaded nipple with ¼ ‘’ hose barb whereby the flow which doesn’t pass the membrane comes and returns to the E. Coli bacteriocin production flask through polyurethane tubes.
The UF membrane is a flat NADIR® polysulfone membrane which is chemical and thermal stable and efficiently working for a wide pH range. Its MWCO value is 20 kDa, so bacteoricin peptides are able to pass the membrane in contrast to other big molecules and cells that are blocked by it. The incoming and outcoming flow of the tee are perpendicular to the permeate so that depositions on the membrane surface are prevented.
The pump is switched off when the proper concentration of bacteriocins is reached in the contaminated water.
This is the section of the whole system that controls the activity of the bacteriocins. It connects the flask containing pH regulating cyanobacteria with the water vessel. CopH consists of a ½ ‘’ M-F pipe union with and ending fitting for polyurethane tubes. Inside the pipe union a dialysis membrane has been included to permit small molecules and ion exchanges but avoiding the pass of big molecules, peptides and bacteria, allowing proton transient transfer along the tubes that link the two flasks. In this way, the pH value of the system is directly controlled by the photosynthetic bacteria to permit or inhibit the peptides actuation.
The dialysis membrane is a SnakeSkin™ Pleated Dialysis Tubing with a 3,500 MWCO value. We cut the tubing dialysis to form a ½ ‘’ round and flat membrane and put it inside the pipe union, held by two equal size toric joints. Contrary to the UF membrane, this type is active at both sides of its surface.
All tubes with the exception of the one that is compressed by the peristaltic pump are made of polyurethane, while the one inside the PP is softer, made of silicone, so that the rotor is able to squeeze properly this tube. All tubes have a ¼ ’’ Ø. In addition, we have included throttle valves to all tubes that link the different functional parts of the machine (that means after the UF membrane and before the dyalisis one) as safety elements to be able to regulate the flows. Finally, it is critically required to include a throttle valve in the tube returning to the bacteriocin flask after the MoBS to be able to achieve enough P for the UF membrane separation process.
3.Hardware workSo far the main equipment of the apparatus has been described. Nevertheless, there are several instruments required to allow cultures to grow and to develop.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a diverse group of gene-encoded natural antibiotics found in all living organisms. In multicellular organisms, such as mammalians, defensins and cathelicidins are a principal component of innate immunity. In unicellular organisms, bacteriocins function to suppress competitor species. AMPs kill bacteria by disruption of membrane integrity and are less likely to induce resistance than common antibiotics, so they have attracted attention in different fields such as medicine and food safety.
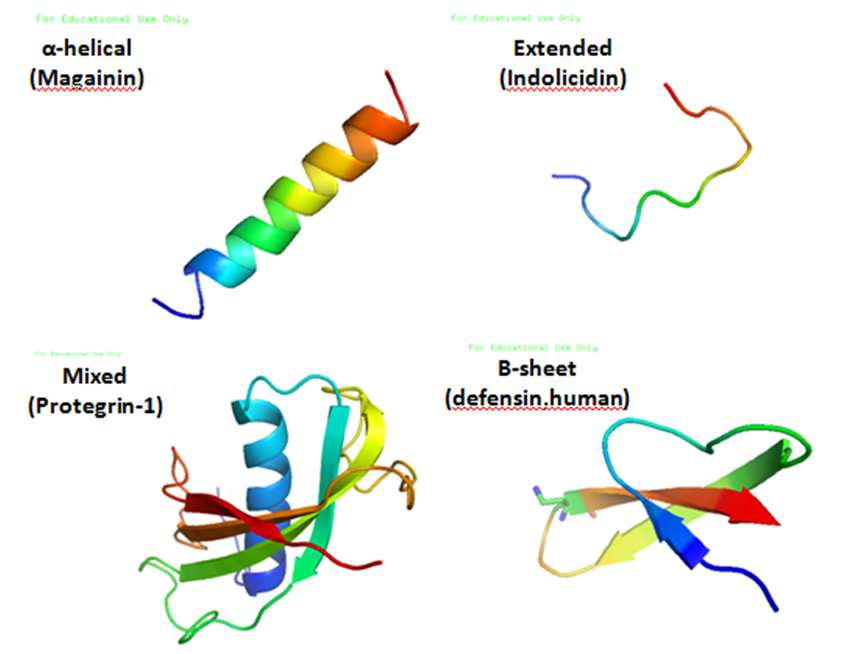
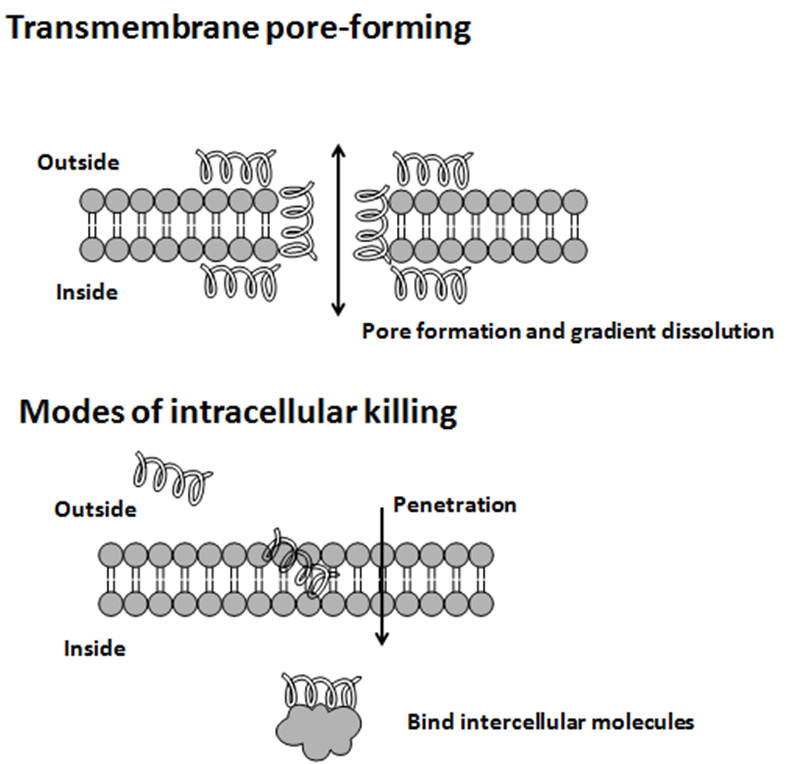
Bacteriocins
Bacteriocins are lethal to bacteria other than the producing strain. As a group, bacteriocins are heterogeneous and are classified according to their molecular weight. The activity spectrum of bacteriocins can be narrow and confined to inhibition of closely related species, or it can be relatively broad and include many different bacterial species. Bacteriocins are often considered more natural than common antibiotics because they are thought to have been present in many of the foods eaten since ancient times. This is one of the reasons why we have chosen bacteriocins over other antimicrobial peptides.
Microcins
Microcins are a peculiar class of gene-encoded low-molecular-mass antibacterial peptides secreted by enterobacteria. They contribute to the regulation of microbial competition within the intestinal microbiota. The genetic systems involved in microcin biosynthesis share a conserved organization. Similar to bacteriocins, microcins exert potent antibacterial activity directed against phylogenetically-related bacterial strains, with minimal inhibitory concentrations in the nanomolar range.
Usually, microcins exhibit "Trojan horse" mechanisms of antibacterial activity: some microcin structures are a mime of essential elements, permitting recognition by outer membrane receptors used for vital functions in bacteria and further translocation into the periplasmic space, other microcins are secreted as harmless molecules and further processed in susceptible bacteria to form the toxic entity. When inside target bacteria, microcins bind essential enzymes or interact with the inner membrane to form a bacterial killing structure.
Microcin C51
Microcin C51 is a nucleopeptide of 1.18 kDa molecular mass and the first described nucleopeptide antibiotic. It contains a heptapeptide with the N-terminal formylmethionine and C-terminal asparagine bound to AMP via an aliphatic chain. Microcine C51 is characterized by a broad spectrum of action. Expression in Escherichia coli is activated upon decelerated growth of cells during their transition to the stationary growth phase. This synthesis is controlled by four genes organized in an operon.
Our microcin strain has come from Severinov Laboratory at Rutgers State University (Severinov et al. Mol Microbiol. 2007)
Colicin G and Colicin H
Colicins are proteins produced by some strains of Escherichia coli that are lethal for related strains of E. coli. Colicins of strain CA46 (colicin G producer) and of strain CA58 (colicin H producer) should be the same, and indeed, the sensitivity patterns were nearly identical.
Only the triple mutant receptors fepA cir fiu was completely resistant to the colicins from these strains. (i) the production of colicin by colicinogenic E. coli cells is induced by SOS agents, as is seen with lysogenic phages, and is lethal for producing cells. (ii) the produced colicin is released into the medium late after synthesis (later shown not to be the case for all colicins). (iii) colicin kills sensitive cells according to single-hit kinetics. (iv) colicin is not active against the producing bacteria if there is presence of a specific antagonist protein called the immunity protein.
All colicins are organized into three domains, each corresponding to one step of colicin action:
- The N-terminal domain is involved in translocation through the membrane.
- The central domain is involved in binding to the receptor.
- The C-terminal domain contains the active part.
The sequence of the colicin G and colicin H determinants have been deposited under the accession numbers AJ515251 and AJ515252, respectively, in the EMBL/GenBank database.
- Escherichia coli microcin operon, strain CA46 (CA46 ColG)
- Escherichia coli microcin operon, strain CA58 (CA58 ColH)

Bibliography
Cascales E et al. Colicin Biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 March; 71(1): 158–229.
Joerger RD. Alternatives to Antibiotics: Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacteriophages. 2003 Poultry Science 82:640–647
Patzer SI et al. The colicin G, H and X determinants encode microcins M and H47, which might utilize the catecholate siderophore receptors FepA, Cir, Fiu and IroN. Microbiology (2003), 149, 2557–2570
Severinov K, Semenova E, Kazakov A, Kazakov T, Gelfand MS. Low-molecular-weight post-translationally modified microcins. Mol Microbiol. 2007 Sep;65(6):1380-94
 "
"
