Team:Colombia/Notebook/Plasmids
From 2011.igem.org
Template:Https://2011.igem.org/User:Tabima
Contents |
Plasmids
The Plasmids will be constructed as shown below

Plasmid 1
Plasmid 1 mission is to recognize the presence of chitin and to up regulate the promoter of the chitinolitic operon when chitin is abundant in the media. We´ve extracted and amplified chitoporin, chitin sensor and chitin binding protein (CBP) from Vibrio fischerii and aimed to create the bricks needed for the assembly of the plasmid that can recognize and break the chitin association.
Plasmid 2
Given that the chitin detection process is always active due to its basal expression, it is necessary to have a regulation so that the response signal to the plant could have two levels of expression. If the response signal to the plant is not regulated, it is possible to have fake or erroneous defense system activation signals when they are not needed, inducing resource losses that should be directed to plant normal growth and fruit production. It is therefore optimal to have the the signaling system activated only when there is a constant chitin presence.
The mechanism is planned to have two parts: a positive feedback that transforms the graduated input signal to an on/off signal with time delay, and an activation mechanism that requires both the delayed signal and the direct chitin signal, so that the system activates only when there is a constant time lapse with phytopatogen presence.
Positive Feedback
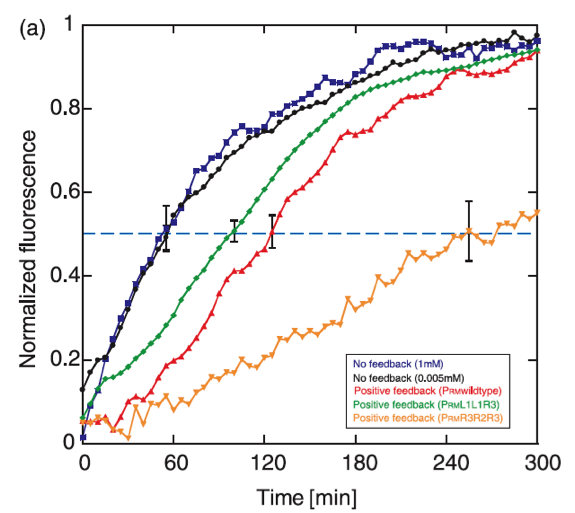
The positive feedback genetic system is well studied, and shows theoretically as well as experimentally a bistable response, moving between two discrete stable states without being able to stay in intermediate states. Another property that exhibits this type of feedback is the capability to delay the protein synthesis kinetics.
The operon chosen to control the response is based on the promoter PRM and the cI gene from the lambda bacteriophage. In this system, CI positively regulates its own synthesis, and the feedback activation guarantees the existance of two stable levels of expression. It has been found that the rise time of the positive feedback system expression is activated slower than a system without feedback, with delay times of approximately 70 minutes.
The dynamics of the graduated response of the positive feedback system shows also hysteretic propierties, which is useful in the signaling system to the plante, keeping the response active for an additional time after the phytopatogen is attacked with chitinase, so that the immunity is not lost when there is a chance of infection.
Mechanism of plant signaling activation
The defense system activation singaling gene is regulated by a two promotor system: one that is activated by the positive feedback system output (graduated and delayed signal) and another one that is activated directly by the presence of chitin (phytopatogen signal). The signal to the plant would be in its maximal expression only when the two input signals are active, which means in practical terms that only when there is a phytopatogen presence superior to 70 minutes the signal is sent, avoiding unnecesary resource expenses by the plant, for example, when an insect passes by the leaves. The hysteretic dynamics of the system has an additional advantage: the inmune response and the chitinase production (which attacks directly the phytopatogen) would be active for an additional time after the critical phytopatogen concentration is reached
Complete genetic circuit desing
In the figure the two planned mechanisms are shown. The first one is the positive feedback system, and its graduated, delayed output is the input for the second one, which is in charge of expressing the chitinase to attack the phytopatogen, and sending the input signal for the plant inmune system activation.
Plasmid 3
In a nutshell, P3’s mission is that of interpreting P2’s autoinduction signals (LuxI) in a way so that it responds with an appropriate production of the plant’s Systemic Aquired Resistance (SAR) stimulating factor (Salicylic Acid, SA). We have also included a negative feedback loop in order to control possible gene overexpressions by introducing a LuxI activated lactonase.
Test Plasmid
Building a whole working system is the challenge our group faces everyday. But, as important as the assemblage itself is to test our assumptions about how the designed parts work individually. Currently, this little group comprised by David Ayala-Usma and Óscar Ortega Sandoval with collaboration of Paola Reyes and Nathaly Montenegro, is working on the induction of the Systemic Acquired Resistance of Nicotiana benthamiana (model organism) by Salicylic Acid BioBrick (BBa_J45320) and the response of the designed chitin-induced promoter to (GlcNAc) polymers.
 "
"