Team:HKU-Hong Kong/Description
From 2011.igem.org
| Super Silencer | |
| Promoter
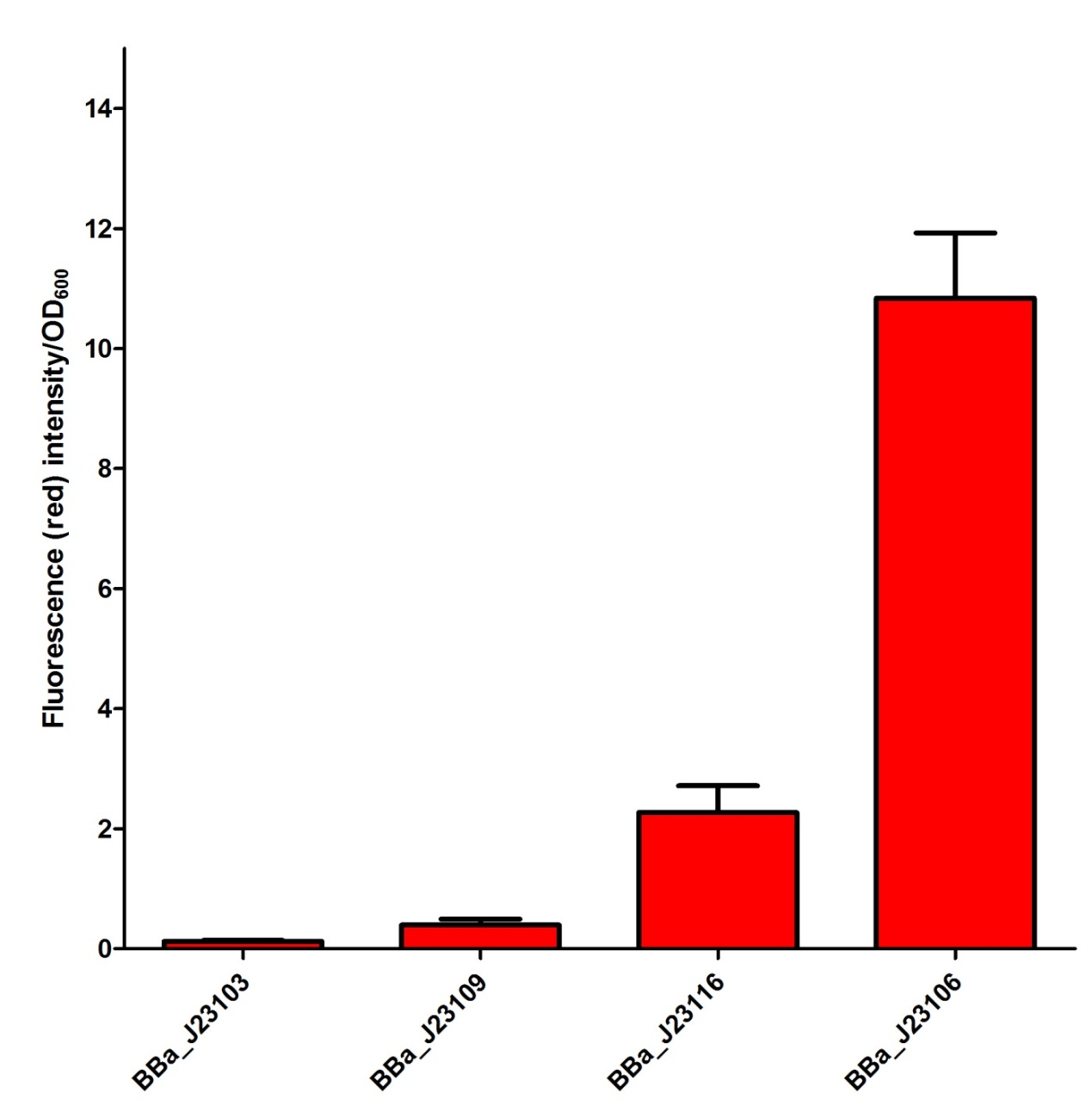
Our Team has planned to utilize four different constitutive promoters first. We have selected BBa_J23103, BBa_J23106, BBa_J23109 and BBa_J23116 in the constitutive promoter family. In our project, we would like to select some of the suitable promoters to fine-tune our fusion protein expression so that a better repression activity can be achieved. We have tried to characterize the selected promoters by measuring the mRFP intensity in the plasmid J61002 as a confirmation of promoter activity. The confirmation data of the promoter activity have been shown as follow and input into the Experience page of these promoters. From the experimental data for promoter in this project, we believed that BBa_J23109 and BBa_J23116 are some of the suitable promoters to be used and further investigate. | Super Silencer |
| Ribosome binding sites
There have been various characterizations of various ribosome binding sites by a number of iGEM teams. The characterization of the ribosome binding sites is as important as the characterization of the promoters to fine tune our fusion protein expression. Unfortunately, due to time constraints and a number of experiment reasons, our team has failed to characterize the ribosome binding sites. As a result, our team finally decided to use BBa_B0034 in our project as its strength is one of the highest in the Registry collection. | Super Silencer |
| DNA-binding domain
DNA-binding domain (DBD) is a protein domain that contains at least one motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. DBD can recognize and bind on a specific DNA sequence, which is called recognition site, with different affinity. The Tet repressor (tetR) we used in the experiment is a transcription factor for regulating gene expression. It binds to the operator site (tetO) by using a multi-helical DBD of the N-terminal of the proteins, while the C-terminal is for regulation of DNA binding which depends on the co-factors. Advantage:
The binding of tetR on the tetO is regulated by the antibiotic tetracycline. When tetracycline is absent, the DBD of tetR binds to the tetO and transcription halt. If tetracycline enters the cell, it binds magnesium cations (Mg++) to form the [MgTc]+ complex. This complex acts as an inducer to bind the TetR, causing conformational changes of the DBD, causing tetR dissociates from the tetO site. In structural basis, tetR is a homodimer, which composed of 2 polypeptide chains. Each chain consists of 10 alpha helices.α1 - α3 are the DBD, in which α2 and 3 constitude a classical helix-turn-helix motif. α4 contributes to the hydrophobic center of the DBD and links the DBD to the regulatory domain. α5- α10 are the core for regulation of the binding between tetR of [MgTc]+. |
 "
"