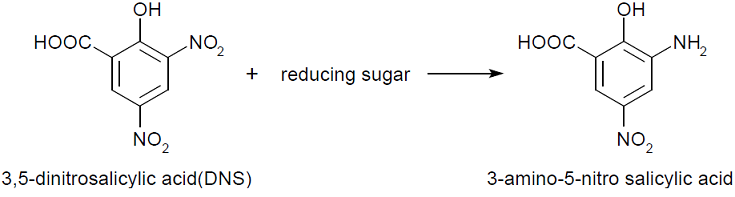Team:Kyoto/Digestion
From 2011.igem.org
Contents |
Project Digestion
Introduction
Streptomyces is a kind of prokaryotic bacteria which decompose bodies in nature. We extract protease and chitinase genes from this bacterium and introduce into Escherichia coli. Secretion-signal sequences are included in these genes so that the proteins coded by them will go out without occurring cell lysis. After assembling all genes, we examined the activity of these two enzymes in both of qualitative and quantitative ways.
Method
Construction
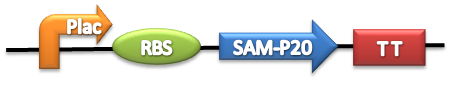
We created following constructions to allow secretion of Serine protease, SAM-P20 and chitinase, chiA1. These genes are regulated by lactose promoter, BBa_R0011. We used Streptmyces’s RBS into these constructions, because reference article [1] used them to allow E.coli to secrete these proteins.
Assay
We performed following qualitative and quantitative assays. These method take a little time and cost a little money.
Serine Protease
- Experiment 1 : Skim milk-hydroryzing assay
- In order to identify the expression of SAM-P20 gene, a skim milk-hydroryzing assay was performed. A plate containing 2% skim milk, IPTG(final concentration, 0.5mM), and 0.1% yeast extract was used for this assay.
- Experiment 2 : Measurement of enzyme activity
- In order to measure the activity of serine protease, the fluorescent assay was done, using fluorescein-labeled casein as a substrate.
Chitinase A
In order to identify the expression of ChiA genes, Chitin plate assay was conducted. We used a LB plate whose surface chitin flour is on
- Experiment 2 : 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid assay (DNS method)
- This assay is based on this fact: 3,5-dinitorosalicylic acid (DNS) is changed into 3-amino- 5-nitorosalicylic acid by reducing saccharide in reaction solution and the absorbance of this liquid increase in direct proportion to the amount of reducing sugar.
Result
Chitinase A1
1. Standard Measurement for ChiA1.
- From the result, a strong correlation between glucose concentration and its A550 was observed.
2. Consideration of medium and growth of E.coli.
Discussion
Reference
[1] Molecular Characterization of a Gene Encoding Extracellular Serine Protease Isolated from a Subtilisin Inhibitor-Deficient Mutant of Streptmyces albogriseolus S-3253
[2]Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis
[3]Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites
[4]還元糖の定量法 (生物化学実験法)福井 作蔵
[5]Quantitative Analysis of Cellulose-Reducing Ends
 "
"