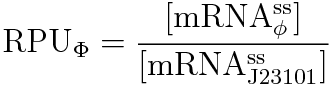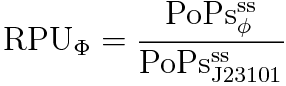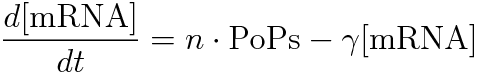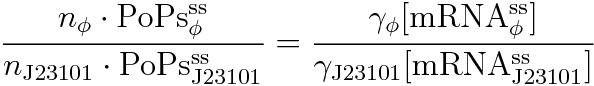Team:Kyoto/Hunger/Modeling
From 2011.igem.org
Hunger Modeling
We get this new equation for measuring RPU.
derivation
RPU is defined as follows.
PoPS (Polymerase Per Second) is the unit of absolute “promoter activity”. It is defined as the number of RNA polymerase molecules that pass by the final base pair of the promoter and continue along DNA as an elongation complex.
Where:
- [mRNA] is the concentration of mRNA,
- γ is the mRNA degradation rate,
- n is the copy number of the plasmid containing the promoter
In the steady state, d[mRNA]/dt = 0.
Following equations related to promoterφ and J23101 are derived because d[mRNA]/dt = 0.
If the test promoter φ and the reference standard promoter are measured under the same culture conditions and both promoters are carried on the same backbone plasmid, following equations are approved.
Equation(3) divided by (4) is (7) .
We can reduce (7) because of (5) and (6) and use (1). Then we get this equation.
So, we can calculate RPU with this equation.
Reference
[1] J. R. Kelly et al., “Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard.,” Journal of biological engineering, vol. 3, p. 4, Jan. 2009.
 "
"