Team:NYMU-Taipei
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
=='''<font size=4><font color=green>Goal</font>'''== | =='''<font size=4><font color=green>Goal</font>'''== | ||
| - | <font size=3>Create <b>wireless neuro-stimulator</b>, focusing on achieving remote neuro-stimulation to minimize | + | <font size=3>Create <b>wireless neuro-stimulator</b>, focusing on achieving remote neuro-stimulation to minimize invasion and damage to the neuron.</font> |
=='''<font size=4><font color=green>Why do we want to do that?</font>== | =='''<font size=4><font color=green>Why do we want to do that?</font>== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
<font size=3> | <font size=3> | ||
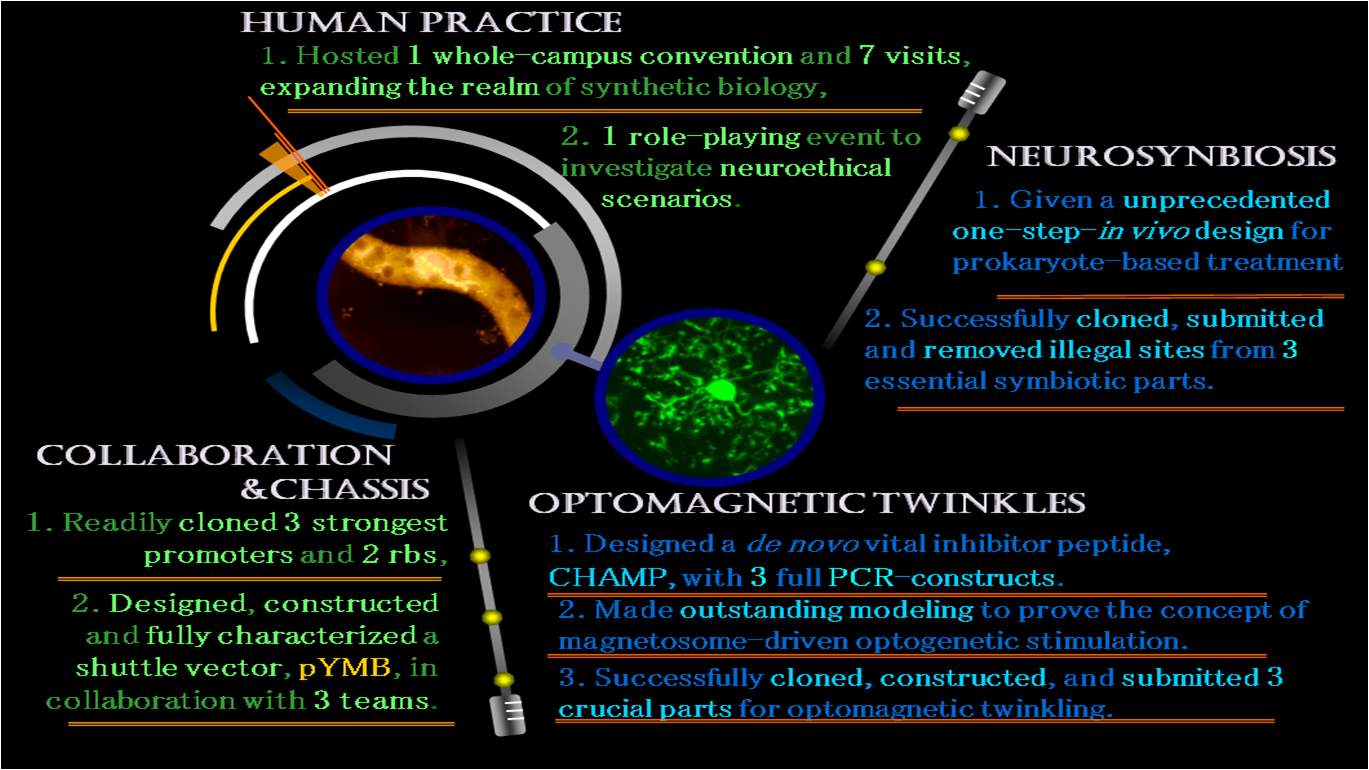
| - | To achieve this goal, we use a species of magnetic | + | To achieve this goal, we use a species of magnetic bacterium,'' Magnetospirillum magneticum'' AMB-1. We have chosen <b>mms13</b>, a transmembrane protein as our target for protein design in this bacterium, as it serves as a linker between reception of wireless magnetic field and optogenetic neuro-stimulation output. Regarding the neuroimmune response, we utilized three genes to achieve <b>neurosymbiosis</b> within glial cells: <b>''MinC''</b>, a division inhibitor, <b>''INV''</b>, a gene for invasion and <b>''LLO''</b>, a gene for facilitated escaping from phagosomes.</font> |
'''<font size=3>Our design is made up of the following two devices:</font>''' | '''<font size=3>Our design is made up of the following two devices:</font>''' | ||
Revision as of 20:29, 28 October 2011

Contents |
Tailoring Your Avatar
Goal
Create wireless neuro-stimulator, focusing on achieving remote neuro-stimulation to minimize invasion and damage to the neuron.
Why do we want to do that?
Optogenetics, the latest neuroscientific method, has improved specificity for stimulating certain cell types of neurons, reversible bi-directional stimulation, and elevated spatiotemporal precision. However, to achieve neuronal network stimulation, light cables are still needed, leaving long-standing annoying issues regarding immune responses unresolved.
Specific aims
(1) Wireless stimulation for neurons
(2) Minimization of neuro-immuno response
Our design
To achieve this goal, we use a species of magnetic bacterium, Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. We have chosen mms13, a transmembrane protein as our target for protein design in this bacterium, as it serves as a linker between reception of wireless magnetic field and optogenetic neuro-stimulation output. Regarding the neuroimmune response, we utilized three genes to achieve neurosymbiosis within glial cells: MinC, a division inhibitor, INV, a gene for invasion and LLO, a gene for facilitated escaping from phagosomes.
Our design is made up of the following two devices:
Bridge magnetics and optogenetics.
Enable magnetotactic bacteria to be neurosymbiosis with glia cells.
Achievements
Our institute
- The official web pages of our school - National Yang Ming University (NYMU):
- [http://web.ym.edu.tw/front/bin/home.phtml in Chinese]
- [http://nymu-e.web.ym.edu.tw/front/bin/home.phtml in English]
- Follow the two links below to see The Beauty of NYMU
- [http://issue.ym.edu.tw/cia/new/ Take a panoramic scenery view of our university]
- [http://issue.ym.edu.tw/cia/new/tw/ym720.html Take a tour of our university]

 "
"









