Team:Calgary/Project/Chassis/Pseudomonas
From 2011.igem.org
Emily Hicks (Talk | contribs) |
Emily Hicks (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<p>In order to test that our constructs were working, we needed a selective marker. We performed a growth assay on our <i>Pseudomonas</i> strains, verifying if they can grow on different antibiotics. <i>Pseudomonas</i> was streaked on LB agar plates containing no antibiotics, tetracycline (25 ug/ml), chloramphenicol (35 ug/mL), kanamycin (50 ug/mL), ampicillin (100 ug/mL) and gentamyacin (50 ug/mL). Growth was observed on LB alone as well as on ampicillin, indicating that <i>Pseudomonas</i>, as expected, is naturally resistant to ampicillin. The lack of growth on the other antibiotics, however, indicated that resistance markers for these could possibly be used to test out the functionality of our constructs.</p> | <p>In order to test that our constructs were working, we needed a selective marker. We performed a growth assay on our <i>Pseudomonas</i> strains, verifying if they can grow on different antibiotics. <i>Pseudomonas</i> was streaked on LB agar plates containing no antibiotics, tetracycline (25 ug/ml), chloramphenicol (35 ug/mL), kanamycin (50 ug/mL), ampicillin (100 ug/mL) and gentamyacin (50 ug/mL). Growth was observed on LB alone as well as on ampicillin, indicating that <i>Pseudomonas</i>, as expected, is naturally resistant to ampicillin. The lack of growth on the other antibiotics, however, indicated that resistance markers for these could possibly be used to test out the functionality of our constructs.</p> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | </html>[[Image:UofC2011_Growth_assay_data.png|thumb|left|280px| Plates showing growth of ''E.coli'' (containing Amp resistance plasmid) and ''Pseudomonas spp.'' in LB, Amp, Chlor and Kan.]][[Image:UCalgary2011_GrowthAssay2.png|thumb|right|250px|]]<html> | + | </html>[[Image:UofC2011_Growth_assay_data.png|thumb|left|280px| Plates showing growth of ''E.coli'' (containing Amp resistance plasmid) and ''Pseudomonas spp.'' in LB, Amp, Chlor and Kan.]][[Image:UCalgary2011_GrowthAssay2.png|thumb|right|250px|Plates showing growth of ''E.coli'' (containing Amp resistance plasmid) and ''Pseudomonas spp.'' in LB, tet and gent.]]<html> |
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><Br><br><br><br><br><br> | + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><Br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> |
Based on this, we moved our constructs into tetracycline and kanamycin resistance vectors for testing. Colonies of <i>E.Coli</i> containing our plasmids were used to innocluate 5 mL LB cultures with kanamycin-50 and tetracycline-25. 100 μL of our two <i>Pseudomonas</i> strains were added and cultures were shaken in a 26°C incubator. OD readings of cultures were taken to standardize cell counts and cultures were then plated on MacConkey agar plates. MacConkey agar, which has a reddish-purple color, is able to distinguish between bacteria that can and cannot metabolize lactose via a color change. Bacteria that do not metabolize lactose, such as <i>Pseudomonas</i>, use peptone instead and reduce ammonia, which causes a yellow color change of the plates due to an increase in pH. <i>E. coli</i>, on the other hand, do metabolize lactose, and therefore no color change is seen.</p> | Based on this, we moved our constructs into tetracycline and kanamycin resistance vectors for testing. Colonies of <i>E.Coli</i> containing our plasmids were used to innocluate 5 mL LB cultures with kanamycin-50 and tetracycline-25. 100 μL of our two <i>Pseudomonas</i> strains were added and cultures were shaken in a 26°C incubator. OD readings of cultures were taken to standardize cell counts and cultures were then plated on MacConkey agar plates. MacConkey agar, which has a reddish-purple color, is able to distinguish between bacteria that can and cannot metabolize lactose via a color change. Bacteria that do not metabolize lactose, such as <i>Pseudomonas</i>, use peptone instead and reduce ammonia, which causes a yellow color change of the plates due to an increase in pH. <i>E. coli</i>, on the other hand, do metabolize lactose, and therefore no color change is seen.</p> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 03:23, 29 September 2011








A Chassis Using Native Tailings Pond Species

A Pseudomonas Conjugation System
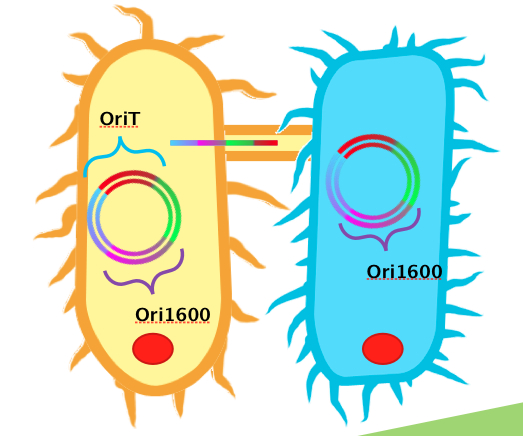
In order to use Pseudomonas spp. as an effective platform for sensing naphthenic acids, our team recognized that we would need it to take up our biosensor plasmid construct with high efficiency. To do this, we decided to design a conjugation system, capable of conjugating plasmids from E. coli to Pseudomonas spp. In order for conjugation to occur, the necessary plasmid DNA must already be inserted into E. coli. A unique sequence recognizable by relaxase and nickase called oriT (origin of transfer), must be coded into the plasmid. Additionally, the plasmid requires replication origins for both E. coli (such as ColE1) and Pseudomonas spp. (such as ori1600). Ori1600, which we used in our system, is a replication-stabilizing element for Pseudomonas spp., and requires ColE1 to function. All other enzymes required for conjugation are available in the receptor Pseudomonas species.
We obtained DNA for both oriT and ori1600, BioBricked them and have submitted them as BioBrick parts. Using BioBrick cloning, we put these two elements together on a single plasmid to make a testing construct. Already present in the registry is an oriT part J01003, which was characterized by Heidelberg in 2008. This part was used for conjugation between strains of E. coli. Theoretically, this part could also be used for conjugation between Pseudomonas and E. coli. Based on the sequences however, we hypothesized that our oriT, which is considerably longer, may have additional regions to improve efficiency in conjugating to Pseudomonas. To test this, we built additional constructs using J01003 and our ori1600 part to compare to our oriT- ori1600 construct.
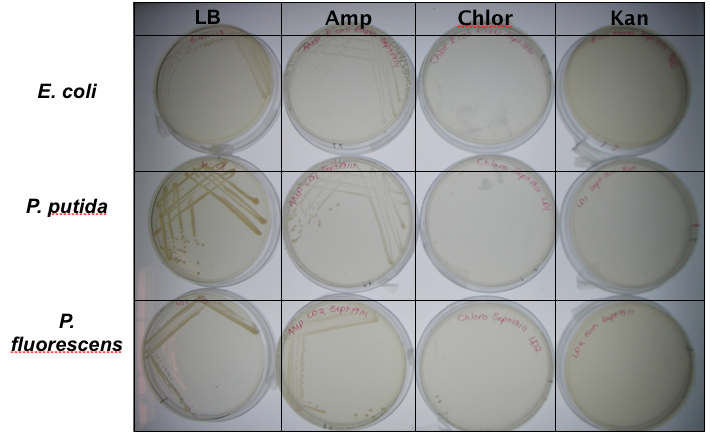
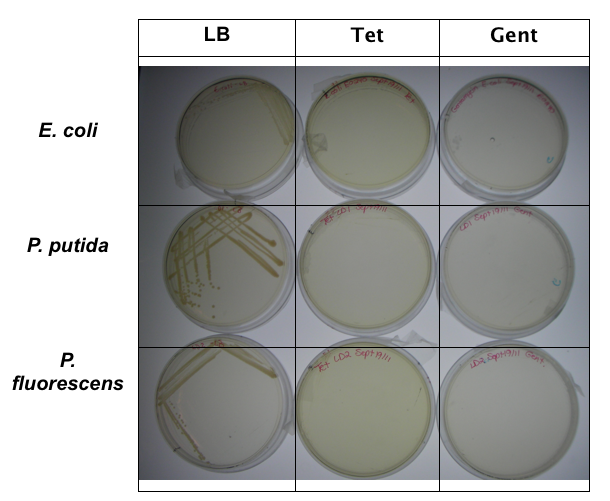
In order to test that our constructs were working, we needed a selective marker. We performed a growth assay on our Pseudomonas strains, verifying if they can grow on different antibiotics. Pseudomonas was streaked on LB agar plates containing no antibiotics, tetracycline (25 ug/ml), chloramphenicol (35 ug/mL), kanamycin (50 ug/mL), ampicillin (100 ug/mL) and gentamyacin (50 ug/mL). Growth was observed on LB alone as well as on ampicillin, indicating that Pseudomonas, as expected, is naturally resistant to ampicillin. The lack of growth on the other antibiotics, however, indicated that resistance markers for these could possibly be used to test out the functionality of our constructs.
Based on this, we moved our constructs into tetracycline and kanamycin resistance vectors for testing. Colonies of E.Coli containing our plasmids were used to innocluate 5 mL LB cultures with kanamycin-50 and tetracycline-25. 100 μL of our two Pseudomonas strains were added and cultures were shaken in a 26°C incubator. OD readings of cultures were taken to standardize cell counts and cultures were then plated on MacConkey agar plates. MacConkey agar, which has a reddish-purple color, is able to distinguish between bacteria that can and cannot metabolize lactose via a color change. Bacteria that do not metabolize lactose, such as Pseudomonas, use peptone instead and reduce ammonia, which causes a yellow color change of the plates due to an increase in pH. E. coli, on the other hand, do metabolize lactose, and therefore no color change is seen.
Characterization
Functionality Test
In our first assay, we wanted to see that our BBa_K640004 (oriT-ori1600) construct was working. We incubated the co-cutures for 12 hours at 37°c prior to plating. The plates were then left to grow overnight.Results
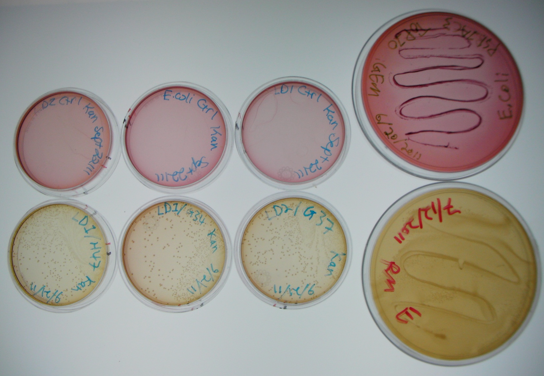
The large plates on the right show controls of Pseudomonas and E. coli on MacConkey plates indicating the normal expected colors for these organisms. The small plates on the bottom represent our construct, conjugated with two different strains of pseudomonas and plated on MacConkey agar with Kanamycin (50ug/mL). The yellow color indicates that the colonies are Pseudomonas. The small plates on the top show our two strains of Pseudomonas, as well as E. coli without kanamycin resistance plated on MacConkey agar plates with kanamycin (50 ug/mL). All of these plates are pink in color, and show no colonies. This was expected, as it shows that without a resistance marker, these organisms are not able to grow on the MacConkey kanamycin plates. This demonstrates that our part is working the way we expect it to!
Time Assay
Once we had demonstrated that our part was working, we went on to try to determine how long it would take for the conjugation to occur. We experimented with different incubation times of the co-cultures at 37° before plating. We tried incubating after 10 minutes, 2 hours, 6 hours and 12 hours.Results
The table below shows the colonie counts that we recorded after each interval. Counts are the average of two repeats.Incubation |
Average # |
10 min |
0 |
2 hrs |
2 |
6 hrs |
4.5 |
12 hrs |
150 |
Comparison between BBa_K640004 and BBa_K640005
As we mentioned before, there is an existing oriT in the registry (BBa_J01003), that the 2008 Heidelberg team had previously characterized in 2008 for the conjugation of plasmids in E. coli. This is the OriT that is present in our BBa_K640006 construct, which contains the oriT and our ori1600 (BBa_K640003). We had hypothesized that our OriT, given its longer sequence, may contain elements that improve the efficiency of conjugation to Pseudomonas spp. To test this, we did an assay using E. coli conatining our BBa_K640004 part (which contains our oriT: BBa_K640002 and BBa_K640003) as well as E. coli containing BBa_K640006. We used a simpler conjugation assay, adapted from Serna et al., 2010. Overnight cultures of the donor and the recipient were prepared in LB medium. Aliquots of 500 μl were mixed to obtain a donor/recipient ratio of 1:1. Each mixture was centrifuged to pellet the cells, and the supernatant was discarded. The cells were resuspended in 50 μl of LB broth. Mating mixtures were incubated at 37° for 4 h. Diluted and undiluted aliquots were then spread on selective plates.Results
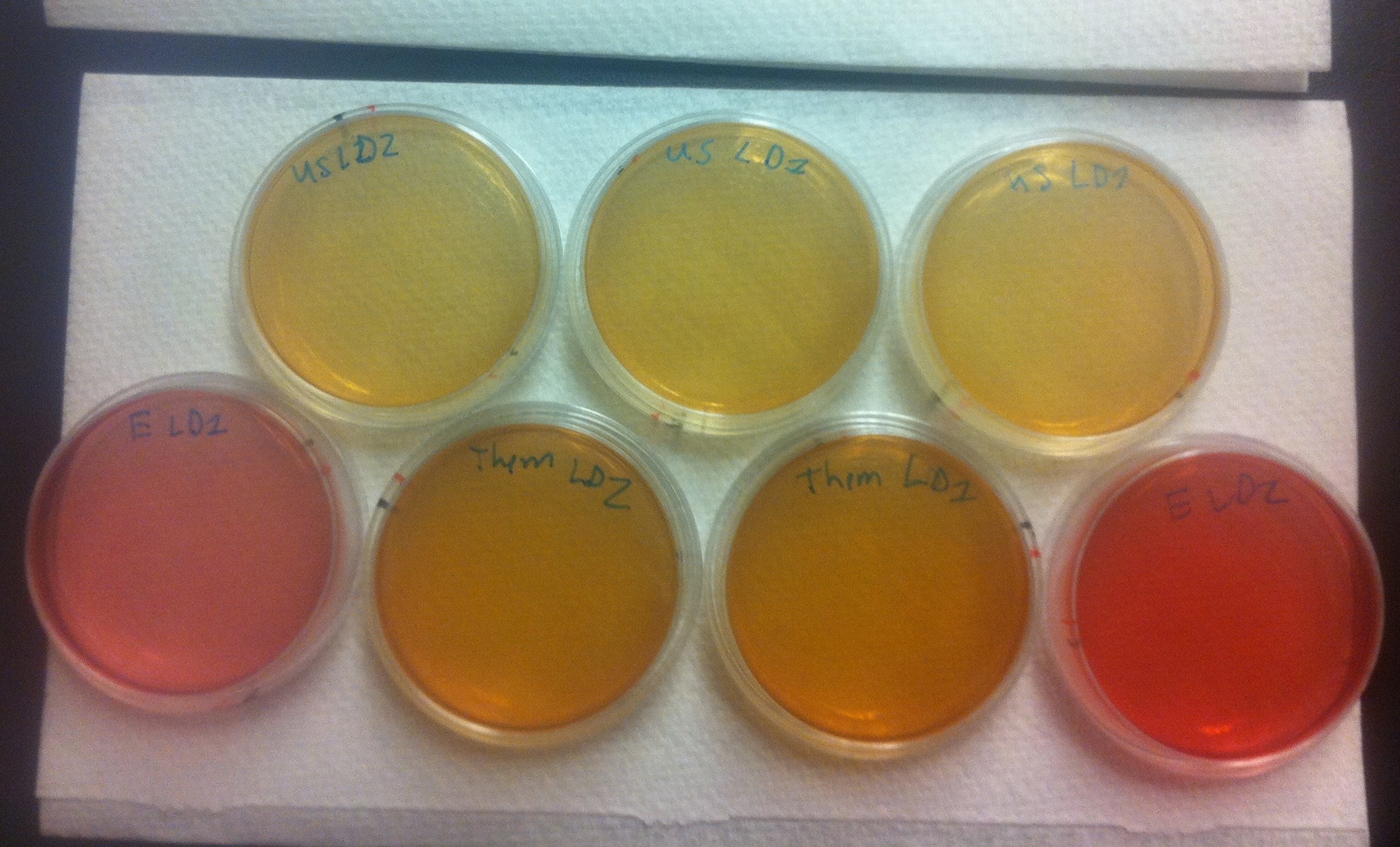
The image below shows our results. On the top, E. coli cells containing the BBa_K640004 construct (which contains our oriT) were used. On the bottom row, on either end, we see plates where E. coli cells containing a kanamycin resistant plasmid, but no OriT or ori1600 construct were used. These are pink in color, with no cells growing,indicating that Pseudomonas and E. coli are not able to naturally conjugate plasmids without our part. In the middle of the bottom row, we see plates where E. coli cells containing the BBa_K640005 construct was used (where we use the registry oriT with our ori1600). As we can see, the plates with the BBa_K640004 are much lighter in color, than the plates where the BBa_K640005 construct was used. This is indicative that there is increased pseudomonas growth, when we use our oriT, as compared to the registry oriT. This was exactly what we had expected, and we hope to have more quantitative data in the next few weeks!

 "
"