Team:UNAM-Genomics Mexico/Notebook/pBBR1MCS-5
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
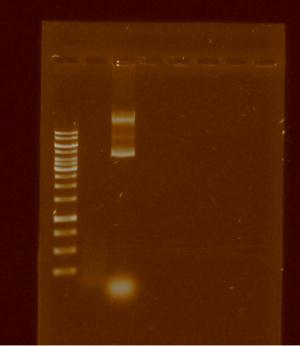
Once decided the way to add the prefix and suffix to pBBR1MCS-5, we spent the rest of the week isolating the plasmid and trying to digest the plasmid by apaI, knowing that only works with strains dcm-. Knowing that E. coli DH5α is dsc+ we tried unsuccessfully to cut with ApaI, the following gel shows it: | Once decided the way to add the prefix and suffix to pBBR1MCS-5, we spent the rest of the week isolating the plasmid and trying to digest the plasmid by apaI, knowing that only works with strains dcm-. Knowing that E. coli DH5α is dsc+ we tried unsuccessfully to cut with ApaI, the following gel shows it: | ||
| - | [[File:Unamgenomicsfig1pbbr.jpg|center|frame|Lanes:1.Ladder 10 kb 2.pBBR1MCS-5 digested by apaI 3.pBBRMCS-5 | + | [[File:Unamgenomicsfig1pbbr.jpg|150px|center|frame|Lanes:1.Ladder 10 kb 2.pBBR1MCS-5 digested by apaI 3.pBBRMCS-5]] |
==Week: june 20 to 25== | ==Week: june 20 to 25== | ||
Revision as of 08:53, 28 September 2011
Contents |
Lab Logbook -pBBR1MCS.
Week: june 13 to 18
At beginning of the week was decided the best way to insert a prefix-RFP-suffix fragment to thepBBR1MCS-5 plasmid, which is a plasmid with broad host-range and is capable to conjugate to R. etli through E. coli S17, being the most efficient way to introduce genes into R. eltli. The pBBR1MCS-5 has a multiple cloning site (MCS) with the following restriction sites:
KpnI
ApaI
XhoI
Sal I
Bsp106 I
ClaI
HindIII
EcoR1
PstI
SmaI
Bam H1
SpeI
XbaI
BstXI
SacI
So we want to eliminate the most of the restriction sites and obviously we need to eliminate the prefix and suffix sites (italic). To do it we are going to cut in the ApaI and SacI site, on the other hand we're going to amplify a region which contains the suffix, an RFP and the prefix of the plasmid pSB1T3, this PCR amplification will be done with primers containing ApaI and SacI respectively, thereafter we'll can insert this amplification in our pBBRMCS-5.
Once decided the way to add the prefix and suffix to pBBR1MCS-5, we spent the rest of the week isolating the plasmid and trying to digest the plasmid by apaI, knowing that only works with strains dcm-. Knowing that E. coli DH5α is dsc+ we tried unsuccessfully to cut with ApaI, the following gel shows it:
Week: june 20 to 25
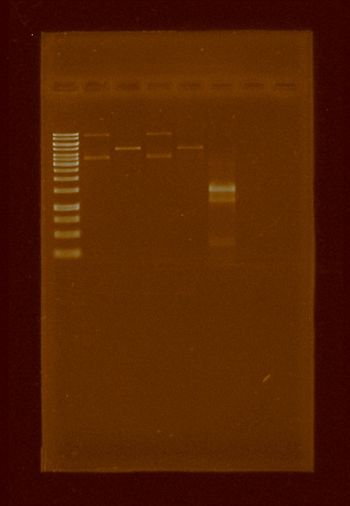
It was made competent BL21 E. coli cells, because that strain is dmc-. After done, the transformation of the pBBR1MCS-5 using the previous competent cell was done and further plasmid isolations were also done. We tested if apaI works well in this strain, the results were successful and are shown in the following electrophoresis gel, however our plasmid isolation were too dirty to obtain a single band
Week: june 27 to july 1
In this week we did plasmid isolations again, but rather using mini-preps we used a Roche kit, this in order to obtain plasmid clean enough to further digestion. Once the plasmid isolations were done it was proceeded to do a double digestion using apaI and sacI(see week: june 13 to 18). A PCR amplifying a prefix-RFP-suffix fragment also was done; to that fragment were added ApaI and SacI at the ends through the primers:
We spent the rest of the week doing the ligation between the pBBR1MCS-5 and the prefix-RFP-suffix fragment and doing the further transformation. But we failed to obtain any colony with our insert probably because of the dirty PCR, so we did the PCR(prefix-RFP-suffix) again.
Week July 4 to 9
In this week the ligation and transformation of the digested clean PCR(prefix-RFP-suffix) and pBBR1MCS-5 was repeated. Of 18 colonies that grew only one became red, indicating that the assembly was done:
In order to see if the new plasmid properly contains the prefix and suffix a digestion with EcoR1 was made, this was successful. Digestions with other enzymes were done in the following week.
Week July 11 to 16
Following testing restriction enzymes on our new plasmid, a transformation in sp. BL21 was done in order to digest with ApaI both, the transformation and the digestion were successful. A digestion with sacI was also and successful made:
Digestions with XbaI and SpeI were also successful. We did not do a digestion with PsteI because we didn’t have it. Once we checked the plasmid integrity we proceeded to try to conjugate the plasmid into R. etli in order to see if it conserves that capability. But the most efficient conjugation protocol require a S17 E. coli strain which didn’t have, so we tried to conjugate with an alternative protocol. The results are in the next week.
Week July 18 to 23
On this week negative results about the conjugation were obtain, attempts to fix and improve the alternative conjugation protocol were made, but they were unsuccessful. We ask to other lab for E. coli s17 in order to do the original protocol, and they were placed to give it to us.
Week July 25 to 30
Competent S17 cells were made and transformation of the new plasmid (pBBR1MCS-5) into them was done. After, the conjugation with the original protocol was made and we waited for the results until next week. Simultaneously the plasmid stability characterization was started. It consists to watch the percentage of bacteria without any selection that loose the plasmid. To do it we started with a 100 ml culture at O.D of 0.01 without selection, and every 12 hours we re-plated an aliquot in both antibiotic medium and antibiotic-free medium and observed the percentage of bacteria that loose the plasmid. This experiment was long, because we made observations for 72 hrs. The results are shown the next week.
| Hour | Colonies without antibiotic | Colonies with antibiotic | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 100 | 1 |
| 12 | 100 | 100 | 1 |
| 24 | 97 | 96 | 0.989691 |
| 36 | 68 | 65 | 0.955882 |
| 48 | 100 | 98 | 0.98 |
| 60 | 100 | 99 | 0.99 |
| 72 | 100 | 99 | 0.99 |
 "
"