Team:Paris Bettencourt/Experiments/Methodologies/Integration
From 2011.igem.org
LauradaSilva (Talk | contribs) |
LauradaSilva (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
<p>Right now, we can clone each of our parts into this plasmid in order to get our final construct into B.subtilis.</p> | <p>Right now, we can clone each of our parts into this plasmid in order to get our final construct into B.subtilis.</p> | ||
| - | <p>To integrate our integrative plasmid into B.subtilis, we chose to use two different methods. The first one is the starvation methos which one is based on the natural competence in B.subtilis.</p> | + | <p>To integrate our integrative plasmid into B.subtilis, we chose to use two different methods. The first one is the starvation methos which one is based on the natural competence in B.subtilis.</p><p>The second method used to integrate our integrative plasmid in B.subtilis is based on the electroporation.</p> |
<h1>Starvation</h1> | <h1>Starvation</h1> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
</li></ul> | </li></ul> | ||
| - | + | ||
<h1>Electroporation</h1> | <h1>Electroporation</h1> | ||
Revision as of 21:43, 28 October 2011

Integration plasmid
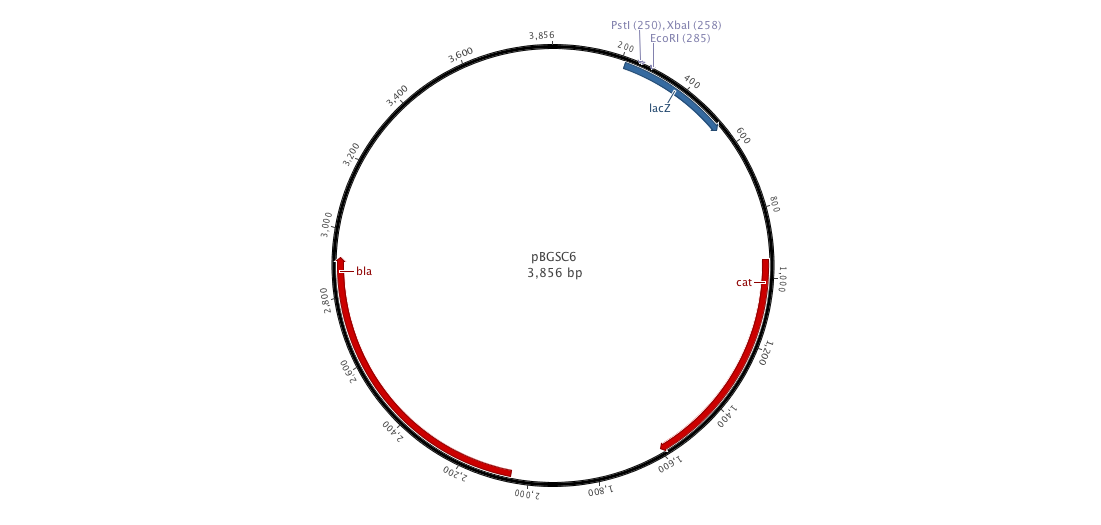
Since we have a lot of problems with the clonning of our parts into replivative plasmid we created, we decided to ;anaged a integrative plasmid which could give us certainly better results since contrary to the replicative plasm we cannot observe a varialibity in its expression. To do that, we created the biobriked plasmid pDCPKO from the Bacillus Genetic Stock Center under the name pBGCS6.
Into this plasmidm we cloned the both AmyE sequences created by the 2008 Imperial College of London team 5 (<partinfo>K143001</partinfo> and <partinfo>K090403</partinfo>)). What we want to do is to clone the whole plasmid into B.subtilis. Thus, we get our next new plasmid pDCPKO which one encodes chloramphenicol acetyl transferase selectable in either E.coli or B.subtilis (chloramphenicol 5μg/ml), β-lactamase selectable in E.coli only (ampicillin 100μg/ml).).
Right now, we can clone each of our parts into this plasmid in order to get our final construct into B.subtilis.
To integrate our integrative plasmid into B.subtilis, we chose to use two different methods. The first one is the starvation methos which one is based on the natural competence in B.subtilis.
The second method used to integrate our integrative plasmid in B.subtilis is based on the electroporation.
Starvation
</p>MDCH medium
- Phosphate-citrate buffer (10 x PC) 10 x concentrated stock solution contains per liter : K2H PO4 (anhydrous) 107 g; KH2 PO4 (anhydrous) 60 g; Trisodium citrate (5 H2O) 10 g.
- Dilute stock solution, check pH of 1 x PC buffer and adjust (if necessary) to pH=7. (1 x PC corresponds to Spizizen's salts without ammonium sulfate)
- 10 ml MD medium : 1 x PC buffer 9.2 ml; Glucose (50 %, w/v) 0.4 ml; L-tryptophan (5 mg/ml) 0.1 ml; Ferric ammonium citrate (2.2 mg/ml) 0.05 ml; Potassium aspartate or potassium glutamate (100 mg/ml) 0.25 ml; 1 M MgSO4 0.03 ml.
- Add 0,2mL of casein hydrolysate in the MD medium
- A 10 ml preculture is grown overnight at room temperature in LM broth (liquid LB medium supplemented with auxotrophic requirements and 3 mM MgSO4). MDCH medium is prepared by adding 0.2 ml 5 % casein hydrolysate to 10 ml MD. Use the preculture to inoculate MDCH medium at an OD600 of about 0.05. Grow this culture at 37° C with shaking to To (transition from exponential to stationary phase). Sometimes, To do not appears and we can see a decrease of the OD: do not use the culture. Advice: launch 2 or 3 culture for each strain.
- Add 1 volume of fresh MD medium without casein hydrolysate to 1 volume of culture. Continue shaking at 37° C for 1 hour.
- Make aliquots of 500μL
- Add DNA (up to 1μg) and continue shaking in the presence of DNA for 20 minutes. Eventually, allow for expression of antibiotic resistance for 20mn (as described inJ. Bacteriol. (1988), 170 : 5093-5101) and plate.
- Cm: 5μg/mL; Spec: 50 to 100μg/mL; Kan: 5μg/mL, Erm: 1μg/mL with 25μg/mL of Lincomycin; Tet: ?μg/mL
Electroporation
 "
"