Team:NYMU-Taipei/results/immunological-solution1
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→(ii) In our experiment, AMB-1 was introduced into primary mixed glial cells in vitro. Figures 1~4 show the photos captured under the microscope.) |
(→(i) Magnetotactic bacteria were introduced into guanulocytes and monocytes by phagocytosis.(Tadashi Matsunaga et all. 1986)) |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
===<font size=4><font color=green>'''<b>(i)</b> <font size=3>Magnetotactic bacteria were introduced into guanulocytes and monocytes by phagocytosis.(Tadashi Matsunaga et all. 1986)</font></font>=== | ===<font size=4><font color=green>'''<b>(i)</b> <font size=3>Magnetotactic bacteria were introduced into guanulocytes and monocytes by phagocytosis.(Tadashi Matsunaga et all. 1986)</font></font>=== | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | [[Image:monocyte.jpg]] | + | {| class="wikitable" border="0" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Image:monocyte.jpg]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
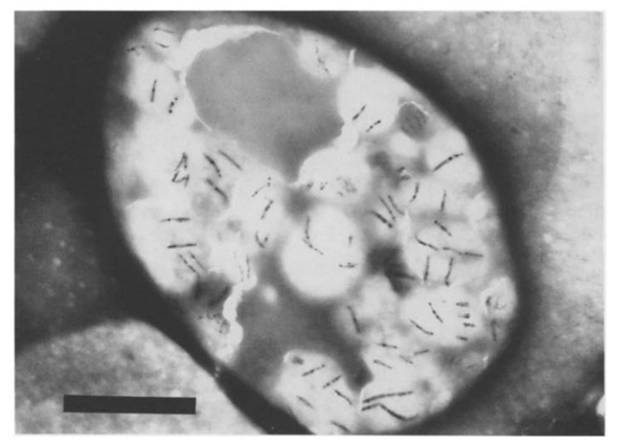
<font size=3>The figure represents the transmission electron micrograph(TEM) of a monocyte that had ingested magnetotactic bacteria. The bar represents 5 μm.</font> | <font size=3>The figure represents the transmission electron micrograph(TEM) of a monocyte that had ingested magnetotactic bacteria. The bar represents 5 μm.</font> | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 28 October 2011

Contents |
Constructs & Parts
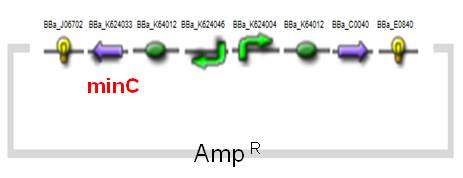
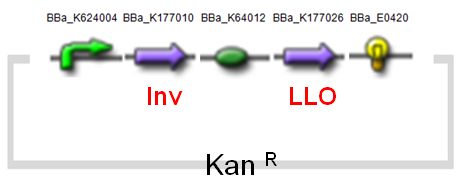
(i)MinC Construct and Inv & LLO Construct on AMB-1
| Fig. Design of minC construct on AMB-1 Backbone plasmid: pYMB | Fig. Design of Inv & LLO construct on AMB-1 Backbone plasmid: pRKm415 |
(ii)Related Parts
We have created several parts on the basis of Biobrick. The expression will be shown on the partregistry webpage.
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624033 BBa_K624033] | minC cell division inhibitor (revised) |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624034 BBa_K624034] | revised minC primer (forward) |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624035 BBa_K624035] | revised minC primer (reverse) |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624036 BBa_K624036] | minC+mcherry |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624037 BBa_K624037] | rbs+minC+mcherry |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624040 BBa_K624040] | pT7-tetO+rbs+minC |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624045 BBa_K624045] | Pmsp1(tetO) + rbs(Pmsp3) + minC + rbs(Pmsp3) + mcherry |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624056 BBa_K624056] | pYMB essentials + rbs(Pmsp3) + minC |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624057 BBa_K624057] | pYMB essentials + rbs(Pmsp3) + LLO |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624058 BBa_K624058] | pYMB essentials + rbs(Pmsp3) + Inv |
(iii)Nested-PCR Primers for Various Strains
nested-Inv
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624063 BBa_K624063] | nested_Inv F (inter-strain nested primer) |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624064 BBa_K624064] | nested_Inv R (inter-strain nested primer) |
nested-LLO
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624065 BBa_K624065] | nested_LLO F (inter-strain nested primer) |
| [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K624066 BBa_K624066] | nested_LLO R (inter-strain nested primer) |
(iiii)Results of PCR from genomic DNA

| 
| 
|
|---|---|---|
| Fig. invasin PCR cloned from Yersinia enterocolitica | Fig. LLO PCR cloned from Listeria monocytogenes | Fig. minC PCR cloned from E.coli K12 MG1655 |
(iiiii)Expression of TetR Protein Enabled Regulation

|
|---|
| Fig. From the left to right, there are separately marker labelled at 72kDa and 26kDa, supernatant control, supernatant experiment, pellet control, pellet experiment. |
Tetracyclin resistent protein and GFP were induced by IPTG to express in BL-21 E.coli strain for the confirmation of the construct.As SDS-PAGE shown above, there is no difference between supernatant control and experiment while tetracyclin resistent protein and GFP express in the pellet experiment.It is proved that the expression of tetracyclin resistent protein can enable the regulation.
 "
"