Team:Harvard/Results/Tools
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{:Team:Harvard/Template:ResultsGrayBar}} | {{:Team:Harvard/Template:ResultsGrayBar}} | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| + | <head> | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
jQuery Coda-Slider v2.0 - http://www.ndoherty.biz/coda-slider | jQuery Coda-Slider v2.0 - http://www.ndoherty.biz/coda-slider | ||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
#coda-slider-1 h2.title { display: none } | #coda-slider-1 h2.title { display: none } | ||
#coda-slider-2 h2.title { display: none } | #coda-slider-2 h2.title { display: none } | ||
| + | </head> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
<div class="whitebox"> | <div class="whitebox"> | ||
Revision as of 05:03, 28 October 2011
Overview | Biobricks | Source Code | Acknowledgments | Accomplishments
body { padding: 0px } .panel h2.title { margin-bottom: 10px } noscript div { background: #a00; border: 1px solid #900; margin: 20px 0; padding: 15px } .coda-slider-wrapper { padding: 20px 0 } .coda-slider { background: #dedede } .coda-slider-no-js .coda-slider { height: 200px; overflow: auto !important; padding-right: 20px } .coda-slider, .coda-slider .panel { width: 550px } .coda-slider-wrapper.arrows .coda-slider, .coda-slider-wrapper.arrows .coda-slider .panel { width: 865px } .coda-slider-wrapper.arrows .coda-slider { margin: 0 10px } .coda-nav-left a { background: #000; color: #fff; padding: 5px; width: 10px } .coda-nav-right a { background: #000; color: #fff; padding: 5px; width: 10px } .coda-nav ul li a.current { background: #900} .coda-slider .panel-wrapper { padding: 20px } .coda-slider p.loading { padding: 20px; text-align: center } .coda-nav ul { clear: both; display: block; margin: auto; overflow: hidden } .coda-nav ul li { display: inline } .coda-nav ul li a { background: #000; color: #fff; display: block; float: left; margin-right: 1px; padding: 3px 6px; text-decoration: none } .coda-slider-wrapper { clear: both; overflow: auto } .coda-slider { float: left; overflow: hidden; position: relative } .coda-slider .panel { display: block; float: left } .coda-slider .panel-container { position: relative } .coda-nav-left, .coda-nav-right { float: left } .coda-nav-left a, .coda-nav-right a { } #coda-slider-1 h2.title { display: none } #coda-slider-2 h2.title { display: none }
Zinc Finger Sequence Generator
Make your own zinc finger sequences using our [http://sourceforge.net/projects/harvardigem/ generator].
Written in Python 2.7, this program is what team members created to generate 55,000 zinc finger sequences, as described on our Design page.
Zinc Finger Binding Site Finder
Check out our Zinc Finger Binding Site Finder Tool.
Background
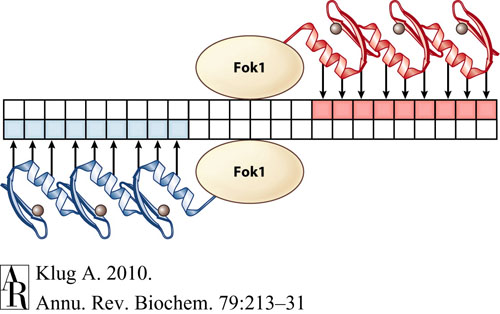
This tool is designed specifically to find binding sites for zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) in order to create double stranded breaks in DNA. Ultimately, through these double stranded breaks, ZFNs allow genome editing with the insertion or deletion of genes at very specific target DNA sites. Each ZFN recognizes and binds to a specific 9-bp DNA sequence that is unique to each ZFN, and the binding sites are arranged such that two ZFNs flank the cut site on opposite strands of DNA:
Given two 9-bp DNA sequences, this program will search a string of DNA to find a configuration such that these two 9-bp sequences are located on opposite strands with a short gap in between them (5-7 bp long), where the double stranded break will occur. This is useful due to the fact that we currently do not have a library of ZFNs that spans the space of all 9-bp recognition sites. Therefore, if the 9-bp binding sites for two zinc fingers are known and well-characterized, this program will search for a site in which these two known zinc fingers can be used to make a cut for gene insertion or deletion.
 "
"