Team:XMU-China/Project/Background
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
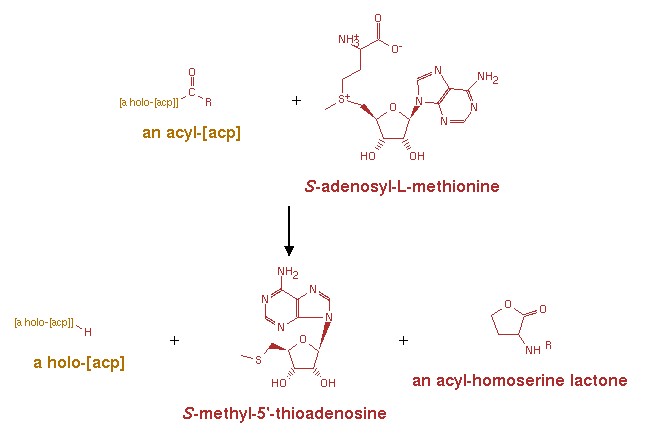
[[Image:XMU_China_135.jpg|left|frame|Figure 1:The reaction mechanism of the synthesis of AHL.]] | [[Image:XMU_China_135.jpg|left|frame|Figure 1:The reaction mechanism of the synthesis of AHL.]] | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/4/41/XMU_China_block.jpg"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
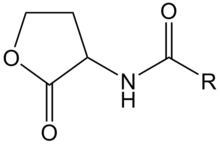
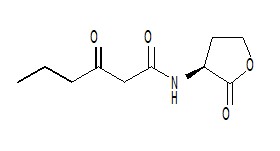
[[Image:XMU_China_137.jpg|left|frame|Figure 3: N-Hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone.]] | [[Image:XMU_China_137.jpg|left|frame|Figure 3: N-Hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone.]] | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/4/41/XMU_China_block.jpg"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 41: | Line 49: | ||
[[Image:XMU_China_138.jpg|left|frame|Figure 4 General chemical structure of IPTG.]] | [[Image:XMU_China_138.jpg|left|frame|Figure 4 General chemical structure of IPTG.]] | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/4/41/XMU_China_block.jpg"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 64: | Line 76: | ||
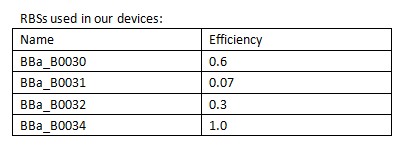
[[Image:XMU_China_139.jpg|left|frame|Table 1 RBSs of different strength.]] | [[Image:XMU_China_139.jpg|left|frame|Table 1 RBSs of different strength.]] | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/4/41/XMU_China_block.jpg"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 72: | Line 88: | ||
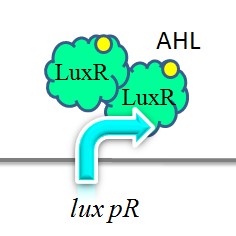
[[Image:XMU_China_140.jpg|left|frame|Figure 5: Two molecules of LuxR protein form a complex with two molecules of the signalling compound homoserine lactone (HSL). This complex binds to a palindromic site on the promoter, increasing the rate of transcriptionTwo molecules of LuxR protein form a complex with two molecules of the signalling compound homoserine lactone (HSL). This complex binds to a palindromic site on the promoter, increasing the rate of transcription.]] | [[Image:XMU_China_140.jpg|left|frame|Figure 5: Two molecules of LuxR protein form a complex with two molecules of the signalling compound homoserine lactone (HSL). This complex binds to a palindromic site on the promoter, increasing the rate of transcriptionTwo molecules of LuxR protein form a complex with two molecules of the signalling compound homoserine lactone (HSL). This complex binds to a palindromic site on the promoter, increasing the rate of transcription.]] | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/4/41/XMU_China_block.jpg"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 78: | Line 98: | ||
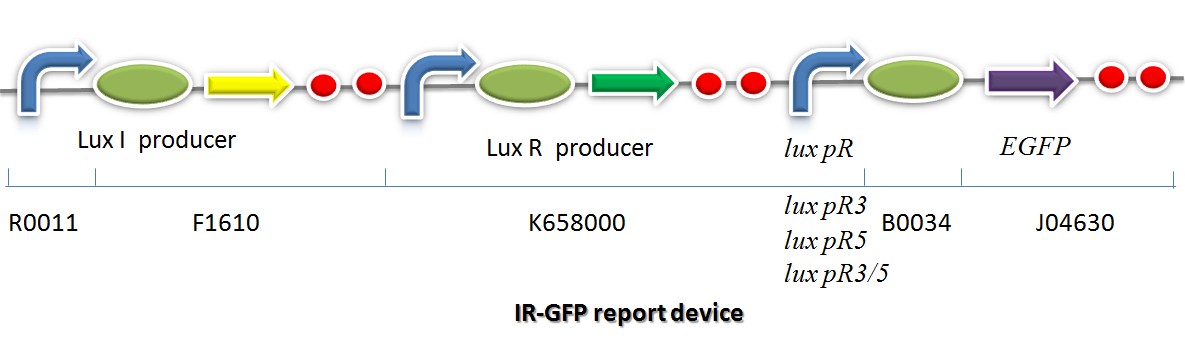
IR-GFP is a series of report devices designed for testing the performance of lux R promoters before and after mutagenesis. These four IR-GFP report devices have been transformed into E.coli string BL21 separately. These devices produced greenish tint visible by naked eyes when induced by IPTG. We measured and compared their florescent intensities at steady state. As the only difference between the four devices is Lux R promoter, the efficiency of the four Lux R promoters could be defined. | IR-GFP is a series of report devices designed for testing the performance of lux R promoters before and after mutagenesis. These four IR-GFP report devices have been transformed into E.coli string BL21 separately. These devices produced greenish tint visible by naked eyes when induced by IPTG. We measured and compared their florescent intensities at steady state. As the only difference between the four devices is Lux R promoter, the efficiency of the four Lux R promoters could be defined. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:XMU_China_141.jpg|left|frame|Figure 6: Promoter lux pR strength testing circuit.]] |
Revision as of 01:29, 6 October 2011
 "
"